Abstract
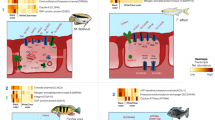
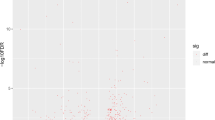
Cryptocaryon irritans (Brown 1951) frequently infect the Pomacentridae fishes causing severe economic losses. However, the anti-C. irritans’ molecular mechanism in these fishes remains largely unknown. To address this issue, we conducted RNA-Seq for C. irrtians-infected gills of the clownfish Amphiprion percula (Lacepède 1802) at the early (day 1) and late (day 3) stages of infection. A total of 1655 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified. Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analyses of DEGs showed a vast genetic variation related to the following aspects: ECM-receptor interaction, P13K-Akt signalling, cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, and endocytosis. During the early phase of infection, key genes involved in ATP production, energy homeostasis, and stress control were abruptly increased. In the late phase, however, acute response molecules of the peripheral nervous system (synaptic transmission and local immunity), metabolic system triggering glycogen synthesis, energy maintenance, and osmoregulation were found to be critical. The highest number of upregulated genes (URGs) recovered during the early phase was included under the ‘biological process’ category, which primarily functions as response to stimuli, signalling, and biological regulation. In the late phase, most of the URGs were related to gene regulation and immune system processes under ‘molecular function’ category. The immune-related URGs of early infection include major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class-II molecules apparently triggering CD4+ T-cell–activated Th responses, and that of late infection include MHC class-1 molecules for the possible culmination of CD8+ T-cell triggered cytotoxicity. The high level of genic single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) identified during the late phase of infection is likely to influence their susceptibility to secondary infection. In summary, the identified DEGs and their related metabolic and immune-related pathways and the SNPs may provide new insights into coordinating the immunological events and improving resistance in Pomacentridae fishes against C. irritans.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available in the NCBI repository, [gene ID: PRJNA832516].
References
Abram QH, Dixon B, Katzenback BA (2017) Impacts of low temperature on the teleost immune system. Biology 6:39
Al-Rasheed A, Handool KO, Alhelli AM, Garba B, Muhialdin BJ, Masomian M, Daud HHM (2020) Assessment of some immune components from the bioactive crude extract derived from the epidermal mucus of climbing perch Anabas testudines. Turk J Fish Aquat Sci 20:755–766
Bai JS, Li YW, Deng Y, Huang YQ, He SH, Dai J, Luo XC (2017) Molecular identification and expression analysis of TLR5M and TLR5S from orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides). Fish Shellfish Immunol 63:97–102
Bayne CJ, Gerwick L (2001) The acute phase response and innate immunity of fish. Dev Comp Immunol 25:725–743
Boutet A, Schierwater B (Eds) (2021) Handbook of marine model organisms in experimental biology: established and emerging. CRC press
Brown EM (1951) A new parasitic protozoan, the causal organism of a white spot disease in marine fish Cryptocaryon irritans gen. and sp. n. (Agenda and abstr. Sci. Meet., Zool. Soc. London, 1950). In Proc Zool Soc London 11:1–2
Buonocore F, Randelli E, Trisolino P, Facchiano A, Pascale D, Scapigliati G (2014) Molecular characterization, gene structure and antibacterial activity of a g-type lysozyme from the European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.). Mol Immunol 62:10–18
Burgess PJ, Matthews RA (1995) Cryptocaryon irritans (Ciliophora): acquired protective immunity in the thick-lipped mullet. Fish Shellfish Immunol 5:459–468
Cervera L, González-Fernández C, Arizcun M, Cuesta A, Chaves-Pozo E (2022) Severe natural outbreak of Cryptocaryon irritans in gilthead seabream produces leukocyte mobilization and innate immunity at the gill tissue. Int J Mol Sci 23:937
Chen W, Sun HY, Xie MQ, Bai JS, Zhu XQ, Li AX (2008) Development of specific PCR assays for the detection of Cryptocaryon irritans. Parasitol Res 103:423–427
Cheng JX, Xia YQ, Liu YF, Liu PF, Liu Y (2021) Transcriptome analysis in Takifugu rubripes and Dicentrarchus labrax gills during Cryptocaryon irritans infection. J Fish Dis 44:249–262
Chi H, Goldstein M, Pichardo A, Wei ZH, Chang WJ, Gong H (2020) Infectivity and genes differentially expressed between young and aging theront cells of the marine fish parasite Cryptocaryon irritans. PLoS ONE 15:e0238167
Colorni A (1985) Aspects of the biology of Cryptocaryon irritans and hyposalinity as gilt-head sea bream Sparus aurata. Dis Aquat Org 22:19–22
Colorni A, Burgess P (1997) Cryptocaryon irritans Brown 1951, the cause of ‘white spot disease’in marine fish: an update. Aquarium Sci Conserv 1(4):217–238
Deng JJ, Xu S, Li YW, Xu DD, Mo ZQ, Li JZ, Luo XC (2020) Role of major histocompatibility complex II antigen-presentation pathway genes in orange-spotted grouper infected with Cryptocaryon irritans. J Fish Dis 43:1541–1552
Dickerson HW, Dawe DL (2006) Ichthyophthirius multifiliis and Cryptocaryon irritans (phylum Ciliophora). Fish Diseases and Disorders 1:116–153
Ercan MD, Karataş S, Turgay E, Kolukirik M, Ince O, Ince B (2013) Changes in transferrin gene expression in sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) challenged with Vibrio anguillarum. Turkish J Vet Anim Sci 37:141–146
Firdaus-Nawi M, Zamri-Saad M (2016) Major components of fish immunity: a review. Pertanika J Trop Agric Sci 39:393–420
Freitas-Mesquita AL, Dos-Santos ALA, Meyer-Fernandes JR (2021) Involvement of Leishmania phosphatases in parasite biology and pathogeny. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 11:327
Gaji RY, Sharp AK, Brown AM (2021) Protein kinases in Toxoplasma gondii. Int J Parasitol 51:415–429
Ganeshamurthy R, Raj MM, Kumar VS, Veerappan N (2014) Effect of copepod parasites Caligus longipedis (Bassett-Smith in 1898) infection in marine ornamental fish Amphiprion percula and Amphiprion clarkia. Int J Fish Aquat Stud 1:173–175
Guo HY, Li WF, Zhu KC, Liu BS, Zhang N, Liu B, Yang JW, Zhang DC (2023) Pathology, enzyme activity and immune responses after Cryptocaryon irritans infection of golden pompano Trachinotus ovatus (Linnaeus 1758). J Mar Sci Eng 11:262
Hall C, Flores MV, Storm T, Crosier K, Crosier P (2007) The zebrafish lysozyme C promoter drives myeloid-specific expression in transgenic fish. BMC Dev Biol 7:42
Huang K, Jiang L, Huang W, Li X, Yuan L, Jiang J, Zhou S, Wang Y, Xie J (2023) Investigating the interplay between Cryptocaryon irritans ectoparasite infection and the immune responses of the head kidney in silver pomfret (Pampus argenteus). Aquaculture, 739780
Jiang B, Du JJ, Li YW, Ma P, Hu YZ, Li AX (2019) Transcriptome analysis provides insights into molecular immune mechanisms of rabbitfish Siganus oramin against Cryptocaryon irritans infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol 88:111–116
Jiménez-Cantizano RM, Infante C, Martin-Antonio B, Ponce M, Hachero I, Navas JI, Manchado M (2008) Molecular characterization, phylogeny, and expression of c-type and g-type lysozymes in brill (Scophthalmus hombus). Fish Shellfish Immunol 25:57–65
Jose Priya TA, Sudha K (2020) Molecular remedies against Cryptocaryon irritans Brown 1951—Practical difficulties. Aquac Res 51:3935–3946
Josepriya TA, Chien KH, Lin HY, Huang HN, Wu CJ, Song YL (2015) Immobilisation antigen vaccine adjuvanted by parasitic heat shock protein 70C confers high protection in fish against cryptocaryonosis. Fish Shellfish Immunol 45:517–527
Kumar S, Gupta S, Mohmad A, Fular A, Parthasarathi BC, Chaubey AK (2021) Molecular tools-advances opportunities and prospects for the control of parasites of veterinary importance. Int J Trop Insect Sci 41:33–42
Lacepède BGE (1802) Histoire naturelle des poissons: IV. chez Plassan: Paris, France. v. 4: i-xliv + 1-728, Pl. 1-16
Lai X, Wu H, Guo W, Li X, Wang J, Duan Y, Zhang P, Huang Z, Li Y, Dong G, Dan X, Mo Z (2023) Vibrio harveyi co-infected with Cryptocaryon irritans to orange-spotted groupers Epinephelus coioides. Fish Shellfish Immunol 108879
Li L, Cardoso JCR, Félix RC, Mateus AP, Canário AVM, Power DM (2021) Fish lysozyme gene family evolution and divergent function in early development. Dev Comp Immunol 114:103772
Li Y, Jiang B, Mo Z, Li A, Dan X (2022) Cryptocaryon irritans (Brown 1951) is a serious threat to aquaculture of marine fish. Rev Aquac 14:218–236
Li YW, Luo XC, Dan XM, Huang XZ, Qiao W, Zhong ZP, Li AX (2011) Orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) TLR2, MyD88 and IL-1β involved in anti-Cryptocaryon irritans response. Fish Shellfish Immunol 30:1230–1240
Lin B, Qing X, Liao J, Zhuo K (2020) Role of protein glycosylation in host-pathogen interaction. Cells 9:1022
Lipton AP (1993) Cryptocaryon irritans (Protozoa: Ciliata) infection among aquarium-held marine ornamental fish and its control. Current Science (bangalore) 65:571–572
Lokanathan Y, Mohd-Adnan A, Wan KL, Nathan S (2010) Transcriptome analysis of the Cryptocaryon irritans tomont stage identifies potential genes for the detection and control of cryptocaryonosis. BMC Genom 11:1–15
Manjili A (2015) Amyloodinium ocellatum (Brown 1931) (Dinoflagellata) infestations in ornamental fish (Amphiprion xanthurus) imported into Iran. Veterinary Researches & Biological Products 28:75–78
Mo ZQ, Li YW, Wang HQ, Wang JL, Ni LY, Yang M, Dan XM (2016) Comparative transcriptional profile of the fish parasite Cryptocaryon irritans. Parasit Vectors 9:1–12
Mo ZQ, Wang JL, Yang M, Ni LY, Wang HQ, Lao GF, Dan XM (2017) Characterisation and expression analysis of grouper (Epinephelus coioides) co-stimulatory molecules CD83 and CD80/86 post Cryptocaryon irritans infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol 67:467–474
Mo ZQ, Wu HC, Hu YT, Lu ZJ, Lai XL, Chen HP, He ZC, Luo XC, Li YW, Dan XM (2021) Transcriptomic analysis reveals innate immune mechanisms of an underlying parasite-resistant grouper hybrid (Epinephelus fuscogutatus× Epinephelus lanceolatus). Fish Shellfish Immunol 119:67–75
Mohapatra A, Parida S, Mohanty J, Sahoo PK (2019) Identification and functional characterization of a g-type lysozyme gene of Labeo rohita, an Indian major carp species. Dev Comp Immunol 92:87–98
Mohd-Shaharuddin N, Mohd-Adnan A, Kua BC, Nathan S (2013) Expression profile of immune-related genes in Lates calcarifer infected by Cryptocaryon irritans. Fish Shellfish Immunol 34:762–769
Nakamoto M, Takeuchi Y, Akita K, Kumagai R, Suzuki J, Koyama T, Sakamoto T (2017) A novel C-type lectin gene is a strong candidate gene for Benedenia disease resistance in Japanese yellowtail Seriola quinqueradiata. Dev Comp Immunol 76:361–369
Natnan ME, Low CF, Chong CM, Bunawan H, Baharum SN (2021) Integration of omics tools for understanding the fish immune response due to microbial challenge. Front Mar Sci 8:751
Neves JV, Wilson JM, Rodrigues PNS (2009) Transferrin and ferritin response to bacterial infection: the role of liver and brain in fish. Dev Comp Immunol 33:848–857
Olivotto I, Planas M, Simões N, Holt GJ, Avella MA, Calado R (2011) Advances in breeding and rearing marine ornamentals. J World Aquaculture Soc 42:135–166
Park JI, Semyonov J, Chang CL, Hsu SYT (2005) Conservation of the heterodimeric glycoprotein hormone subunit family proteins and the LGR signalling system from nematodes to humans. Endocrine 26:267–276
Parveen S, Bandhyopadhyay S, Das S, Majumdar SB, Jawed JJ, Chowdhury BP, Majumdar S (2016) Mycobacterium indicus pranii (Mw)-mediated protection against visceral leishmaniasis by reciprocal regulation of host dual-specificity phosphatases. Int Immunol 28:585–595
Peatman E, Baoprasertkul P, Terhune J, Xu P, Nandi S, Kucuktas H, Li P, Wang S, Somridhivej B, Dunham R, Liu Z (2007) Expression analysis of the acute phase response in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) after infection with a Gram-negative bacterium. Dev Comp Immunol 31:1183–1196
Priya TJ, Lin YH, Wang YC, Yang CS, Chang PS, Song YL (2012) Codon changed immobilisation antigen (iAg) a potent DNA vaccine in fish against Cryptocaryon irritans infection. Vaccine 30:893–903
Ramudu KR, Sanil NK, Vijayagopal P, Shivam S, Suresh Babu PP, Anuraj A, Loka J (2017) Report on Amyloodinium spp cysts infection in clownfish. Mar Fish Inf Serv, Tech Ext Ser (234):25–26
Rodrigues RM, Silva NM, Gonçalves ALR, Cardoso CR, Alves R, Gonçalves FA, Costa‐Cruz JM (2009) Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II but not MHC class I molecules are required for efficient control of Strongyloides venezuelensis infection in mice. Immunology 128(1pt2):e432–e441
Rombout JH, Huttenhuis HB, Picchietti S, Scapigliati G (2005) Phylogeny and ontogeny of fish leucocytes. Fish Shellfish Immunol 19:441–455
Romo RM, Pérez-Martínez D, Ferrer CC (2016) Innate immunity in vertebrates: an overview. Immunology 148:125–139
Ropert C, Gazzinelli RT (2000) Signalling of immune system cells by glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor and related structures derived from parasitic protozoa. Curr Opin Microbiol 3:395–403
Roy S, Kumar V, Kumar V, Behera BK (2017) Acute phase proteins and their potential role as an indicator for fish health and in diagnosis of fish diseases. Protein Pept Lett 24:78–89
Rudd PM, Elliott T, Cresswell P, Wilson IA, Dwek RA (2001) Glycosylation and the immune system. Science 291:2370–2376
Saurabh S, Sahoo PK (2008) Lysozyme: an important defence molecule of fish innate immune system. Aquac Res 39:223–239
Singh SB, Davis AS, Taylor GA, Deretic V (2006) Human IRGM induces autophagy to eliminate intracellular mycobacteria. Science 313:1438–1441
Subramanian S, MacKinnon SL, Ross NW (2007) A comparative study on innate immune parameters in the epidermal mucus of various fish species. Comp Biochem Physiol B: Biochem Mol Biol 148:256–263
Sudhagar A, Kumar G, El-Matbouli M (2018) Transcriptome analysis based on RNA-Seq in understanding pathogenic mechanisms of diseases and the immune system of fish: a comprehensive review. Int J Mol Sci 19:245
Sufardin S, Sriwulan S, Anshary H (2022) Gyrodactylus (Monogenea: Gyrodactylidae) on marine ornamental fish Amphiprion percula from a marine aquaculture facility in Indonesia. Biodiversitas 23(2)
Szczypka M (2020) Role of phosphodiesterase 7 (PDE7) in T cell activity effects of selective PDE7 inhibitors and dual PDE4/7 inhibitors on T cell functions. Int J Mol Sci 21:6118
Taylor GA, Collazo CM, Yap GS, Nguyen K, Gregorio TA, Taylor LS, Eagleson B, Secrest L, Southon EA, Reid SW, Tessarollo L (2000) Pathogen-specific loss of host resistance in mice lacking the IFN-γ-inducible gene IGTP. Proc Natl Acad Sci 97:751–755
Tripathi A, Singha UK, Cooley A, Gillyard T, Krystofiak E, Pratap S, Chaudhuri M (2021) Trypanosoma brucei Tim50 possesses PAP activity and plays a critical role in cell cycle regulation and parasite infectivity. Mbio 12:e01592-e1621
Wahab W, Zakariah MI, Mazelan S, Shaharom F (2009) Parasites of marine ornamental fish. Jabatan Perikanan Malaysia
Wang P, Wang J, Su YQ, Mao Y, Zhang JS, Wu CW, Zheng WQ (2016) Transcriptome analysis of the Larimichthys crocea liver in response to Cryptocaryon irritans. Fish Shellfish Immunol 48:1–11
Wright ADG, Colorni A (2002) Taxonomic re-assignment of Cryptocaryon irritans a marine fish parasite. Eur J Protistol 37:375–378
Xie X, Jiang Y, Miao R, Huang J, Zhou L, Kong J, Yin F (2021) The gill transcriptome reveals unique antimicrobial features that protect Nibea albiflora from Cryptocaryon irritans infection. J Fish Dis 44:1215–1227
Yambot AV, Song YL (2006) Immunization of grouper, Epinephelus coioides, confers protection against a protozoan parasite. Aquac 260:1–9
Yin F, Gao Q, Tang B, Sun P, Han K, Huang W (2016) Transcriptome and analysis on the complement and coagulation cascades pathway of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) to ciliate ectoparasite Cryptocaryon irritans infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol 50:127–141
Yin F, Liu W, Bao P, Jin S, Qian D, Wang J, Tang B (2018) Comparison of the susceptibility and resistance of four marine perciform fishes to Cryptocaryon irritans infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol 77:298–303
Yin F, Qian D (2017) Transcriptomic analysis reveals the key immune-related signalling pathways of Sebastiscus marmoratus in response to infection with the parasitic ciliate Cryptocaryon irritans. Parasit Vectors 10:1–16
Zhao J, Bai H, Ke Q, Li B, Zhou Z, Wang H, Xu P (2021) Genomic selection for parasitic ciliate Cryptocaryon irritans resistance in large yellow croaker. Aquaculture 531:735–786
Zheng L, Qiu J, Chen J, Zheng WQ, Pan Y (2020) Histopathological changes and piscidin 5-like location in infected Larimichthys crocea with parasite Cryptocaryon irritans. Fish Shellfish Immunol 99:52–58
Zheng LB, Mao Y, Wang J, Chen RN, Su YQ, Hong YQ, Hong YC (2018) Excavating differentially expressed antimicrobial peptides from transcriptome of Larimichthys crocea liver in response to Cryptocaryon irritans. Fish Shellfish Immunol 75:109–114
Zhokhov AE, Thi HV, Kieu OLT, Pugacheva MN, Hai TNT (2019) Parasites of Anemonefish (Pomacentridae amphiprioninae) in the Gulf of Nha Trang South China Sea. Vietnam Biol Bull 46:791–803
Zou J, Secombes CJ (2011) Teleost fish interferons and their role in immunity. Dev Comp Immunol 35:1376–1387
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank M/s Eurofins Genomics India Pvt. Ltd., Bengaluru, for sequencing and bioinformatics support. We are very grateful to the Central University of Kerala for providing us the laboratory space and literature resources.
Funding
This study was supported by Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, DST WOS-A research project (No. SR/WOS-A/LS-78/2018 (G), 28.06.2019), DST-RFBR collaborative research project (No. INT/RUS/RFBR/P-330, 10.01.2019), and DST-SERB Research project (No. EMR/2016/001163/AS, 28.08. 2017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jose Priya TA conceived and designed the project, carried out the experiment, analysed data, and wrote the manuscript; Charutha Karunakaran contributed to sample collection and assisted with data processing; Aishwarya Nath discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript; Sudha Kappalli did critical reading and editing. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
All experiments in this study were conducted according to the guidelines of Institutional Animal Ethics Committee (IAEC), Central University of Kerala.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Infection with Cryptocaryon irritans resulted in a large number of DEGs in the gill tissue of Amphiprion percula.
• At the initial phase of infection, C. irritans induced significant responses on key genes involved in ATP production, energy homeostasis, stress control, and MHC-II-mediated immunity.
• At the late phase, acute responses of local immunity, glycogen metabolism, osmoregulation, and MHC-I-mediated immunity were induced.
• Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were estimated to be 1.4-fold higher during the late phase of infection, revealing a higher probability of secondary infection.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
T. A., J., Karunakaran, C., Nath, A. et al. Transcriptomic Variation of Amphiprion Percula (Lacepède, 1802) in Response to Infection with Cryptocaryon Irritans Brown, 1951. Mar Biotechnol 25, 858–890 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-023-10246-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-023-10246-z