Abstract
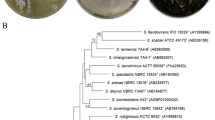
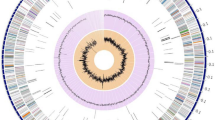
The marine bacterium Pseudoalteromonas xiamenensis STKMTI.2 was isolated from a mangrove soil sediment on Setokok Island, Batam, Indonesia. The genome of this bacterium consisted of 4,563,326 bp (GC content: 43.2%) with 1 chromosome, 2 circular plasmids, 2 linear plasmids, 4,824 protein-coding sequences, 25 rRNAs, 104 tRNAs, 4 ncRNAs, and 1 clustered, regularly interspaced, short palindromic repeated (CRISPR). This strain possessed cluster genes which are responsible for the production of brominated marine pyrroles/phenols (bmp), namely, bmp8 and bmp9. Other gene clusters responsible for the synthesis of secondary metabolites were identified using antiSMASH and BAGEL4, which yielded five results, namely, non-ribosomal peptides, polyketide-like butyrolactone, Lant class I, and RiPP-like, detected in chromosome 1, while prodigiosin was detected in the unnamed plasmid 5. This suggests that these whole genome data will be of remarkable importance for the improved understanding of the biosynthesis of industrially important bioactive and antibacterial compounds produced by P. xiamenensis STKMTI.2.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The following is information regarding the deposition of whole-genome sequences:
The complete genome sequence has been deposited at GenBank under the following accession number Chromosome 1 (CP072133.1); Plasmid Unnamed1 (CP072131.1); Plasmid Unnamed2 (CP072132.1); Plasmid Unnamed4 (CP072134.1); and Plasmid Unnamed5 (CP072135.1), BioProject PRJNA716124, and Biosample SAMN18395665. The raw sequencing reads have been deposited in the SRA under accession number SRR14179988.
References
Agarwal V, El Gamal AA, Yamanaka K, Poth D, Kersten RD, Schorn M, Allen EE, Moore BS (2014) Biosynthesis of polybrominated aromatic organic compounds by marine bacteria. Nat Chem Biol 10:640–647
Alkhalili RN, Canbäck B (2018) Identification of putative novel Class-I lanthipeptides in firmicutes: a combinatorial in silico analysis approach performed on genome sequenced bacteria and a close inspection of ZGeobacillin lanthipeptide biosynthesis gene cluster of the thermophilic geobacillus sp. Strain ZGt-1. Int J Mol Sci 19:2650. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092650
Andreyeva IN, Ogorodnikova TI (2015) Pigmentation of Serratia marcescens and spectral properties of prodigiosin. Microbiology 84:28–33
Annamalai R, Jin B, Cao Z, Newton SM, Klebba PE (2004) Recognition of ferric catecholates by FepA. J Bacteriol 186:3578–3589
Arnison PG, Bibb MJ, Bierbaum G, Bowers AA, Bugni TS, Bulaj G, Camarero JA et al (2013) Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide natural products: overview and recommendations for a universal nomenclature. Nat Prod Rep 30:108–160
Atencio LA, Boya P CA, Martin H C, Mejía LC, Dorrestein PC, Gutiérrez M (2020) Genome Mining, Microbial interactions, and molecular networking reveals new dibromoalterochromides from strains of Pseudoalteromonas of Coiba National Park-Panama. Mar Drugs 19:456–474
Balibar CJ, Walsh CT (2006) In vitro biosynthesis of violacein from L-tryptophan by the enzymes VioA-E from Chromobacterium violaceum. Biochemistry 45:15444–15457
Batiha GE, Alqahtani A, Ilesanmi OB, Saati AA, El-Mleeh A, Hetta HF, Magdy Beshbishy A (2020) Avermectin derivatives, pharmacokinetics, therapeutic and toxic dosages, mechanism of action, and their biological effects. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 13:198
Blin K, Simon S, Katharina S, Rasmus V, Nadine Z, Sang YL, Marnix HM, Tilmann W (2019) antiSMASH 5.0: updates to the secondary metabolite genome mining pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res 47:81–87
Bosi E, Fondi M, Orlandini V, Perrin E, Maida I, de Pascale D, Tutino ML, Parrilli E, Lo Giudice A, Filloux A, Fani R (2017) The pangenome of (Antarctic) Pseudoalteromonas bacteria: evolutionary and functional insights. BMC Genom 18:93
Bowman JP (2007) Bioactive compound synthetic capacity and ecological significance of marine bacterial genus Pseudoalteromonas. Mar Drugs 5:220–241
Bucchini F, Andrea D C, Łukasz K, Alexander B, Michiel V, Klaas V (2020) TRAPID 2.0: a web application for taxonomic and functional analysis of de novo transcriptomes. Biorxyv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.10.19.345835
Busch J (2018) The diversity, distribution, and biological activity of brominated natural products in the genus Pseudoalteromonas. Dissertation. University of California San Diego
Davis JJ, Alice RW, Ramy KA, Thomas B, Ralph B, Rory MB, Philippe C, Neal C, Allan D, Emily MD, Joseph LG, Svetlana G, Andrew G, Ronald WK, Dustin M, Chunhong M, Dan M-O, Marcus N, Eric KN, Gary JO, Robert DO, Jamie CO, Ross O, Bruce P, Gordon DP, Maulik S, Chris T, Margo V, Veronika V, Andrew SW, Fangfang X, Dawen X, Hyunseung Y, Rick S (2020) The PATRIC Bioinformatics Resource Center: expanding data and analysis capabilities. Nucleic Acids Res 48:606–612
de Coster W, D’Hert S, Schultz DT, Cruts M, van Broeckhoven C (2018) NanoPack: visualizing and processing long-read sequencing data. Bioinformatics 34:2666–2669
Demain AL (1999) Pharmaceutically active secondary metabolites of microorganisms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 52:455–463
Fehér D, Barlow RS, Lorenzo PS, Hemscheidt TK (2008) A 2-substituted prodiginine, 2-(p-hydroxybenzyl) prodigiosin, from Pseudoalteromonas rubra. J Nat Prod 71:1970–1972
Fischbach MA, Walsh CT (2006) Assembly-line enzymology for polyketide and nonribosomal peptide antibiotics: logic, machinery, and mechanisms. Chem Rev 106:3468–3496
Gharpure SJ, Nanda LN (2017) Application of oxygen/nitrogen substituted donor-acceptor cyclopropanes in the total synthesis of natural products. Tetrahedron Lett 58:711–720
Harms H, Kurita K, Pan L, Wahome P, He H, Kinghorn A, Carter G, Linington R (2016) Discovery of anabaenopeptin from freshwater algal bloom material: insights into the structure-activity relationship of anabaenopeptin protease inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 26:4960–4965
Ichinose K, Bedford DJ, Tornus D, Bectthold A, Bibb MJ, Revill WP, Floss HG, Hopwood DA (1998) The granaticin biosynthetic gene cluster of Streptomyces violaceoruber Tü22: sequence analysis and expression in a heterologous host. Chem Biol 5:647–659
Isnansetyo A, Kamei Y (2003) MC21-A, a bactericidal antibiotic produced by a new marine bacterium, Pseudoalteromonas phenolica sp. nov. O-BC30T, against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 47:480–488
Isnansetyo A, Istiqomah I, Muhtadi Sinansari S, Hernawan RK, Triyanto WJ (2009) A potential bacterial biocontrol agent, strain S2V2 against pathogenic marine Vibrio in aquaculture. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:1103–1113
Ivanova EP, Gorshkova NM, Zhukova NV, Lysenko AM, Zelepuga EA, Prokof’eva NG, Mikhailov VV, Nicolau DV, Christen R (2004) Characterization of Pseudoalteromonas distincta-like sea-water isolates and description of Pseudoalteromonas aliena sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:1431–1437
Jenul C, Sieber S, Daeppen C, Mathew A, Lardi M, Pessi G, Hoepfner D, Neuburger M, Linden A, Gademann K (2018) Biosynthesis of fragin is controlled by a novel quorum sensing signal. Nat Commun 9:1–13
Kallies R, Kiesel B, Schmidt M, Ghanem N, Zopfi J, Hackermüller J, Harms H, Wick L Y, Chatzinotas A (2019) Complete genome sequence of Pseudoalteromonas virus vB_PspP-H6/1 that infects Pseudoalteromonas sp. strain H6. Mar Genomic 47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margen.2019.03.002.100667
Kelecom A (2002) Secondary metabolites from marine microorganisms. An Acad Bras Ciênc 74:151–170
Knerr PJ, van der Donk WA (2012) Discovery, biosynthesis, and engineering of lantipeptides. Annu Rev Biochem 81:479–505
Kolmogorov M, Yuan J, Lin Y, Pevzner PA (2019) Assembly of long error-prone reads using repeat graphs. Nat Biotechnol 37:540–546
Laursen JB, Nielsen J (2004) Phenazine natural products: biosynthesis, synthetic analogues, and biological activity. Chem Rev 104:1663–1686
Liu F, Wang Y, Qu C, Zheng Z, Miao J, Xu H, Xiao T (2017) The complete genome of hydrocarbon-degrading Pseudoalteromonas sp. NJ289 and its phylogenetic relationship. Acta Oceanol Sin 36:88–93.
Liu Q, Han Y, Wang D, Wang Q, Liu X, Li Y, Song X, Wang M, Jiang Y, Meng Z, Shao H, McMinn A (2018) Complete genomic sequence of bacteriophage J2–1: a novel Pseudoalteromonas phenolica phage isolated from the coastal water of Qingdao. China Mar Genomics 39:15–18
Morisaka H, Yoshimi K, Okuzaki Y, Gee P, Kunihiro Y, Sonpho E, Xu H, Sasakawa N, Naito Y, Nakada S, Yamamoto T, Sano S, Hotta A, Takeda J, Mashimo T (2019) CRISPR-Cas3 induces broad and unidirectional genome editing in human cells. Nature Communication 10:5302
Murakami M, Suzuki S, Itou Y, Kodani S, Ishida K (2000) New anabaenopeptins, potent carboxypeptidase-A inhibitors from cyanobacterium Aphanizomenon flos-aquae. J Nat Prod 63:1280–1282
Offret C, Desriac F, Le Chevalier P, Mounier J, Jégou C, Fleury Y (2016) Spotlight on antimicrobial metabolites from the marine bacteria Pseudoalteromonas: chemodiversity and ecological significance. Mar Drugs 14:129–155
Ortega MA, Wilfred VD (2016) New insights into the biosynthetic logic of ribosomally synthesized and posttranslationally modified peptide natural products. Cell Chem Biol 23:31–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2015.11.012
Parks DH, Imelfort M, Skennerton CT, Hugenholtz P, Tyson GW (2015) CheckM: Assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Genome Res 25:1043–1055. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.186072.114
Paulsen SS, Strube ML, Bech PK, Gram L, Sonnenschein EC (2019) Marine chitinolytic Pseudoalteromonas represents an untapped reservoir of bioactive potential. mSystems 4:e00060–19
Qin QL, Li Y, Zhang YJ, Zhou ZM, Zhang WX, Chen XL, Zhang XY, Zhou BC, Wang L, Zhang YZ (2011) Comparative genomics reveals a deep-sea sediment-adapted life style of Pseudoalteromonas sp. SM9913. ISME J 5:274–284
Richards GP, Michael WA, David SN, Joseph U, Boyd EF, Johnna PF (2017) Mechanisms for Pseudoalteromonas piscicida killing of vibrios and other bacterial pathogens. Appl Environ Microbiol 83:1–17
Sakai-Kawada FE, Ip CG, Hagiwara KA, Awaya JD (2019) Biosynthesis and bioactivity of prodiginine analogs in marine bacteria, Pseudoalteromonas: a mini review. Front Microbiol 10:1715–1715
Saraswathy N, Ramalingam P (2011) Concepts and techniques in genomics and proteomics. Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1533/9781908818058
Sekurova ON, Schneider O, Zotchev SB (2019) Novel bioactive natural products from bacteria via bioprospecting, genome mining and metabolic engineering. Microb Biotechnol 12:828–844
Setiyono E, Adhiwibawa MAS, Indrawati R, Prihastyanti MNU, Shioi Y, Brotosudarmo THP (2020) An Indonesian marine Bacterium, Pseudoalteromonas rubra, produces antimicrobial prodiginine pigments. ACS Omega 5:4626–4635
Shan K, Wang C, Liu W, Liu K, Jia B, Hao L (2018) Genome sequence and transcriptomic profiles of a marine bacterium. Pseudoalteromonas agarivorans Hao Sci Data 6:10
Sieber S, Daeppen C, Jenul C, Mannancherril V, Eberl L, Gademann K (2020) Biosynthesis and structure-activity relationship investigations of the diazeniumdiolate antifungal agent fragin. Chembiochem 21:1587–1592
Simão FA, Waterhouse RM, Ioannidis P, Kriventseva EV, Zdobnov EM (2015) BUSCO: assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinformatics 31:3210–3212
Sobolevskaya MP, Smetanina OF, Speitling M, Shevchenko LS, Dmitrenok PS, Laatsch H, Kuznetsova TA, Ivanova EP, Elyakov GB (2005) Controlling production of brominated cyclic depsipeptides by Pseudoalteromonas maricaloris KMM 636T. Lett Lett Appl Microbiol 40:243–248
Speitling M, Smetanina OF, Kuznetsova TA, Laatsch H (2007) Bromoalterochromides A and A′, unprecedented chromopeptides from a marine Pseudoalteromonas maricaloris strain KMM 636T. J Antibiot 60:36–42
Strieker M, Tanović A, Marahiel MA (2010) Nonribosomal peptide synthetases: structures and dynamics. Curr Opin Struct Biol 20:234–240
Sulieman F, Ahmad A, Usup G, Kuang LC (2018) Diketopiperazine from marine bacterium Pseudoalteromonas ruthenica KLPp3. J Biol Res 91:7197
Supardy NA, Ibrahim D, Mat Nor SR, Noordin WNM (2019) Bioactive compounds of Pseudoalteromonas sp. IBRL PD4.8 inhibit growth of fouling bacteria and attenuate biofilms of Vibrio alginolyticus FB3. Pol J Microbiol 68:21–33
Tanizawa Y, Fujisawa T, Kaminuma E, Nakamura Y, Arita M (2016) DFAST and DAGA: web-based integrated genome annotation tools and resources. Biosci Microbiota Food Health 35:173–184
Thomas T, Evans FF, Schleheck D, Mai-Prochnow A, Burke C, Penesyan A, Dalisay DS et al (2008) Analysis of the Pseudoalteromonas tunicata genome reveals properties of a surface-associated life style in the marine environment. PLOS One 3:e3252
Thøgersen MS, Marina WD, Jette M, Mogens K, Maria M, Boyke B, Cathrin S, Jörg O, Kristian FN, Lone G (2016) Production of the bioactive compounds violacein and indolmycin is conditional in a maeA mutant of Pseudoalteromonas luteoviolacea S4054 lacking the malic enzyme. Front Microbiol 16:1461
van Dijk EL, Auger H, Jaszczyszyn Y, Thermes C (2014) Ten years of next-generation sequencing technology. Trends Genet 30:418–426
van Heel AJ, de Jong A, Song C, Viel JH, Kok J, Kuipers OP (2018) BAGEL4: a user-friendly web server to thoroughly mine RiPPs and bacteriocins. Nucleic Acids Res 46:W278–W281
Vynne NG, Månsson M, Nielsen KF, Gram L (2011) Bioactivity, chemical profiling, and 16S rRNA-based phylogeny of Pseudoalteromonas strains collected on a global research cruise. Mar Biotechnol (NY) 13:1062–1073
Wang G, Chen G, Qin S, Hu D, Awakawa T, Li S, Lv J, Wang C, Yao X, Abe I, Gao H (2018) Biosynthetic pathway for furanosteroid demethoxyviridin and identification of an unusual pregnane side-chain cleavage. Nature Communications 9:1838
Wang J, Peng L, Guo X, Yoshida A, Osatomi K, Li Y, Yang J, Liang X (2019) Complete genome of Pseudoalteromonas atlantica ECSMB14104, a Gammaproteobacterium inducing mussel settlement. Mar Genomics 46:54–57
Wick RR, Judd LM, Holt KE (2019) Performance of neural network basecalling tools for Oxford nanopore sequencing. Genome Biol 20:129
Williamson NR, Fineran PC, Leeper FJ, Salmond GP (2006) The biosynthesis and regulation of bacterial prodiginines. Nat Rev Microbiol 4:887–899
Xu L, Zhaobin D, Lu F, Yongjiang L, Zhaoyuan W, Hailong G, Guoqing Z, Yong QG, Devin C, Qingyou X, Yi W (2019) OrthoVenn2: a web server for whole-genome comparison and annotation of orthologous clusters across multiple species. Nucleic Acids Res 47:52–58
Yip CH, Yarkoni O, Ajioka J, Wan KL, Nathan S (2019) Recent advancements in high-level synthesis of the promising clinical drug, prodigiosin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103:1667–1680
Yoon V, Nodwell JR (2014) Activating secondary metabolism with stress and chemicals. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 41:415–424
Yu M, Tang K, Shi X, Zhang XH (2012) Genome sequence of Pseudoalteromonas flavipulchra JG1, a marine antagonistic bacterium with abundant antimicrobial metabolites. J Bacteriol 194:3735
Zhao C, Jing-Jing L, Ting G, Xiang-Ling H, De-Zan Y, Zhua-hua L (2014) Pseudoalteromonas xiamenensis sp. nov. a marine bacterium isolated from coastal surface water. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:444–448
Zhong Z, He B, Li J, Li Y (2020) Challenges and advances in genome mining of ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides (RiPPs). Synth Syst Biotechnol 5:155–172
Zhu XM, Stefanie H, Maulik NT, Lindsay K, Claudia W et al (2015) Biosynthesis of the fluorinated natural product nucleocidin in Streptomyces calvus is dependent on the bldA-specified Leu-tRNAUUA molecule. Chem Bio Chem 16:2498–2506
Funding
Part of the work in this research was financially supported by the Global Alliance for TB Drug Development (TB ALLIANCE), PMDSU program of the KEMENRISTEKDIKTI Republic of Indonesia, and KRUPT program of the KEMENRISTEKDIKTI Republic of Indonesia (contract number: 3847/UN1/DITLIT/DIT-LIT/PT/2020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Desy Putri Handayani: designed the experiment method, conducted the experiments, prepared the figures and/or tables, analyzed the data, and wrote the paper. Alim Isnansetyo: prepared and submitted a proposal for the research grant, designed the experiment method, analyzed the data, reviewed the paper, and approved for the final draft. Indah Istiqomah: analyzed the data, reviewed the paper, and gave approval for the final draft. Jumina: reviewed the paper and approved the final draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human or animals performed by any of the authors. All authors have approved the final version of the publication manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Handayani, D.P., Isnansetyo, A., Istiqomah, I. et al. New Report: Genome Mining Untaps the Antibiotics Biosynthetic Gene Cluster of Pseudoalteromonas xiamenensis STKMTI.2 from a Mangrove Soil Sediment. Mar Biotechnol 24, 190–202 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-022-10096-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-022-10096-1