Abstract
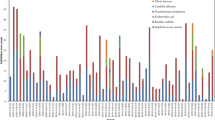
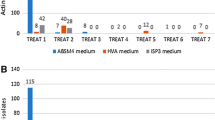
A total of 168 actinomycete colonies were isolated from 14 sediment samples of the northern parts of the Oman Sea and were screened for cytotoxic and antimicrobial activity. Among four media and two treatments, the glucose arginine agar medium (18%) and heat treatment (28.3%) showed maximum isolation rate of actinomycetes. Preliminary characterization revealed that the members of Streptomycetaceae were widely distributed (66%) in the most of the sampling stations followed by Micromonosporaceae (14%), Nocardiaceae (6%), and Pseudonocardiaceae (4%), respectively. Approximately, 23.8% of the isolates inhibited the growth of at least one of the microbial test strains, while the majority of them belonged to the Streptomycetaceae family. Minimum inhibitory concentrations of the ethyl acetate culture extracts of the five most putative isolates varied from 64 μg/mL against Micrococcus luteus and Candida albicans to 1 mg/mL against Aspergillus niger. These extracts showed significant cytotoxic activity at18.74–193.5 μg/mL on the human breast (MCF7), colon (HCT 116), and liver (HepG2) tumor cell lines while exhibited less or no cytotoxicity on the normal cell line (HUVEC). Interestingly, IFSRI 193 extract selectively inhibited the growth of HCT 116 cell line and gram-positive bacteria. 16S rRNA gene sequencing revealed that the potent isolates have 97 to 99% similarity with S. chartreusis, S. cacaoi, S. sampsonii, S. qinglanensis, and S. diastaticus. These results suggested that the five Streptomyces strains could be considered candidates for discovering the antitumor antibiotics.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arakawa K (2018) Manipulation of metabolic pathways controlled by signaling molecules, inducers of antibiotic production, for genome mining in Streptomyces spp. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 111:743–751
Balouiri M, Sadiki M, Ibnsouda SK (2016) Methods for in vitro evaluating antimicrobial activity: a review. J Pharm Anal 6:71–79
Blunt JW, Carroll AR, Copp BR, Davis RA, Keyzers RA, Prinsep MR (2018) Marine natural products. Nat Prod Rep 35:8–53
Chróst RJ (2012) Microbial enzymes in aquatic environments. Springer Science & Business Media
CLSI (2015) Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically; approved standard—Tenth Edition. CLSI document M07-A10. Wayne, PA. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute
Dhaneesha M, Benjamin Naman C, Krishnan KP, Sinha RK, Jayesh P, Joseph V, Bright Singh IS, Gerwick WH, Sajeevan TP (2017) Streptomyces artemisiae MCCB 248 isolated from Arctic fjord sediments has unique PKS and NRPS biosynthetic genes and produces potential new anticancer natural products. 3 Biotech 7:32
Duncan K, Haltli B, Gill K, Correa H, Berrué F, Kerr R (2015) Exploring the diversity and metabolic potential of actinomycetes from temperate marine sediments from Newfoundland, Canada. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 42:57–72
Edrada-Ebel R et al. (2018) SeaBioTech: from seabed to test-bed: harvesting the potential of marine biodiversity for industrial biotechnology. In: Grand challenges in marine biotechnology. Springer, pp 451–504
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution. 39:783–791
Genilloud O (2017) Actinomycetes: still a source of novel antibiotics. Nat Prod Rep 34(10):1203–1232
Goodfellow M, Kämpfer P, Busse H-J, Trujillo ME, Suzuki K-i, Ludwig W, Whitman WB (2012) Bergey’s manual® of systematic bacteriology: volume five the Actinobacteria, part a. Springer New York
Gozari M, Mortazavi M, Bahador N, Rabbaniha M (2016) Isolation and screening of antibacterial and enzyme producing marine actinobacteria to approach probiotics against some pathogenic vibrios in shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Iran J Fish Sci 15:630–644
Gozari M, Bahador N, Jassbi A, Mortazavi M, Eftekhar E (2018) Antioxidant and cytotoxic activities of metabolites produced by a new marine Streptomyces sp. isolated from the sea cucumber Holothuria leucospilota. Iran J Fish Sci 17:413–426
Hamedi J, Poorinmohammad N, Wink J (2017) The role of actinobacteria in biotechnology. In: Biology and biotechnology of actinobacteria. Springer, pp 269–328
Heuer H, Krsek M, Baker P, Smalla K, Wellington E (1997) Analysis of actinomycete communities by specific amplification of genes encoding 16S rRNA and gel-electrophoretic separation in denaturing gradients. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3233–3241
Hu H, Lin H-P, Xie Q, Li L, Xie X-Q, Hong K (2012) Streptomyces qinglanensis sp. nov., isolated from mangrove sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:596–600
Jensen PR, Gontang E, Mafnas C, Mincer TJ, Fenical W (2005) Culturable marine actinomycete diversity from tropical Pacific Ocean sediments. Environ Microbiol 7:1039–1048
Jensen PR, Moore BS, Fenical W (2015) The marine actinomycete genus Salinispora: a model organism for secondary metabolite discovery. Nat Prod Rep 32:738–751
Kalinovskaya N, Romanenko LA, Kalinovsky AI, Ermakova SP, Dmitrenok PS, Afiyatulov S (2017) The antitumor antibiotics complex of aureolic acids from the marine sediment-associated strain of Streptomyces sp. KNIM 9048. Nat Prod Commun 12:571–577
Karamouz M, Nazif S, Falahi M (2012) Hydrology and hydroclimatology: principles and applications. CRC Press
Kieser T (2000) Practical streptomyces genetics. John Innes Foundation, Norwich, England
Kim S-K (2015) Handbook of anticancer drugs from marine origin vol 22–98. Springer
Kruter L, Saggar V, Akhavan A, Patel P, Umanoff N, Viola KV, Stebbins W, Smith E, Akhavan A, Cohen JV, Cohen SR (2015) Intralesional bleomycin for warts: patient satisfaction and treatment outcomes. J Cutan Med Surg 19:470–476
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33(7):1870–1874
Maldonado LA, Stach JE, Pathom-aree W, Ward AC, Bull AT, Goodfellow M (2005) Diversity of cultivable actinobacteria in geographically widespread marine sediments. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 87:11–18
Mincer TJ, Jensen PR, Kauffman CA, Fenical W (2002) Widespread and persistent populations of a major new marine actinomycete taxon in ocean sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5005–5011
Ng ZY, Tan GYA (2018) Selective isolation and characterisation of novel members of the family Nocardiopsaceae and other actinobacteria from a marine sediment of Tioman Island. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 111:727–742
Niu G (2018) Genomics-driven natural product discovery in Actinomycetes. Trends Biotechnol 36:238–241
Olano C, Méndez C, Salas JA (2009) Antitumor compounds from marine actinomycetes. Mar Drugs 7:210–248
Oliveira GH, Al-Kindi SG, Caimi PF, Lazarus HM (2016) Maximizing anthracycline tolerability in hematologic malignancies: treat to each heart’s content. Blood Rev 30:169–178
Osada N, Kosuge Y, Ishige K, Ito Y (2013) Mithramycin, an agent for developing new therapeutic drugs for neurodegenerative diseases. J Pharmacol Sci 122:251–256
Overmann J, Lepleux C (2016) Marine bacteria and archaea: diversity, adaptations, and culturability. In: The marine microbiome. Springer, pp 21–55
Patin NV, Schorn M, Aguinaldo K, Lincecum T, Moore BS, Jensen PR (2017) Effects of actinomycete secondary metabolites on sediment microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 83(4):e02676–e02616
Peng S, Zhao M (2009) Pharmaceutical bioassays: methods and applications. John Wiley & Sons
Quintero M, Velásquez A, Jutinico LM, Jiménez-Vergara E, Blandón LM, Martinez K, Lee HS, Gómez-León J (2018) Bioprospecting from marine coastal sediments of Colombian Caribbean: screening and study of antimicrobial activity. J Appl Microbiol 125:753–765
Rao KVR, Mani P, Satyanarayana B, Rao TR (2017) Purification and structural elucidation of three bioactive compounds isolated from Streptomyces coelicoflavus BC 01 and their biological activity. 3 Biotech 7:24
Seidel V (2005) Initial and bulk extraction of natural products isolation. In Natural products isolation. Humana Press, pp 27–41
Shirling E, Gottlieb D (1966) Methods for characterization of Streptomyces species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 16:313–340
Staneck JL, Roberts GD (1974) Simplified approach to identification of aerobic actinomycetes by thin-layer chromatography. Appl Microbiol 28:226–231
Teicher BA (2013) Anticancer drug development guide: preclinical screening, clinical trials, and approval. Springer Science & Business Media
Vengoji R, Macha MA, Batra SK, Shonka NA (2018) Natural products: a hope for glioblastoma patients. Oncotarget 9:22194
Weaver MS, Navid F, Huppmann A, Meany H, Angiolillo A (2015) Vincristine and dactinomycin in infantile myofibromatosis with a review of treatment options. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 37:237–241
Williams S (1989) Genus Streptomyces Waksman and Henrici 1943 BERGEY’s manual of syntematic bacteriology 4:2452–2492
Zhang Z, Schwartz S, Wagner L, Miller W (2000) A greedy algorithm for aligning DNA sequences. J Comput Biol 7:203–214
Zhang H, Zhang W, Jin Y, Jin M, Yu X (2008) A comparative study on the phylogenetic diversity of culturable actinobacteria isolated from five marine sponge species. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 93:241–248
Zotchev S, Sekurova O, Kurtboke D (2017) Metagenomics of marine actinomycetes: from functional gene diversity to biodiscovery. In: Marine OMICS: prinicples and applications. CRC Press, pp 165–186
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 80 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gozari, M., Zaheri, A., Jahromi, S.T. et al. Screening and characterization of marine actinomycetes from the northern Oman Sea sediments for cytotoxic and antimicrobial activity. Int Microbiol 22, 521–530 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-019-00083-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-019-00083-3