Abstract
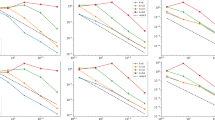
We study the acoustic Helmholtz equation with impedance boundary conditions formulated in terms of velocity, and analyze the stability and convergence properties of lowest-order Raviart-Thomas finite element discretizations. We focus on the high-wavenumber regime, where such discretizations suffer from the so-called “pollution effect”, and lack stability unless the mesh is sufficiently refined. We provide wavenumber-explicit mesh refinement conditions to ensure the well-posedness and stability of discrete scheme, as well as wavenumber-explicit error estimates. Our key result is that the condition “\(k^2 h\) is sufficiently small”, where k and h respectively denote the wavenumber and the mesh size, is sufficient to ensure the stability of the scheme. We also present numerical experiments that illustrate the theory and show that the derived stability condition is actually necessary.









Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The result is actually stated for \(s=1\), but the general case easily follows by interpolation. See also [14].
Theorem 3.2 does not explicitly treat the adjoint problem, but one easily sees that \(\varvec{\xi }\) can be equivalently defined as the unique element of \(\varvec{{\mathcal {X}}}\) such that \(b({\overline{\varvec{\xi }}},{\varvec{v}}) = ({\overline{{\varvec{q}}}},{\varvec{v}})_\varOmega \) for all \({\varvec{v}}\in \varvec{{\mathcal {X}}}\).
References
Adams, R.A., Fournier, J.J.: Sobolev Spaces, 2nd edn. Academic Press, Cambridge (2003)
Babuška, I., Sauter, S.A.: Is the pollution effect of the FEM avoidable for the Helmholtz equation considering high wave numbers? SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 34(6), 2392–2423 (1997)
Chaumont-Frelet, T., Nicaise, S.: High-frequency behaviour of corner singularities in Helmholtz problems. ESAIM Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 5, 1803–1845 (2018)
Chaumont-Frelet, T., Nicaise, S.: Wavenumber explicit convergence analysis for finite element discretizations of general wave propagation problems, IMA J. Numer. Anal. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1093/imanum/drz020
Chaumont-Frelet, T., Nicaise, S., Pardo, D.: Finite element approximation of electromagnetic fields using nonfitting meshes for Geophysics. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 56(4), 2288–2321 (2018)
Ciarlet, P.G.: The Finite Element Method for Elliptic Problems. SIAM, Philadelphia (2002)
Colton, D., Kress, R.: Inverse Acoustic and Electromagnetic Scattering Theory. Springer, New York (2012)
Colton, D., Kress, R.: Integral Equation Methods in Scattering Theory. SIAM, Philadelphia (2013)
Costabel, M.: A remark on the regularity of solutions of Maxwell’s equations on Lipschitz domains. Math. Meth. Appl. Sci. 12, 365–368 (1990)
Dauge, M.: Elliptic Boundary Value Problems on Corner Domains. Springer, New York (1988)
Dhia, A.B.-B., Duclairoir, E., Legendre, G., Mercier, J.: Time-harmonic acoustic propagation in the presence of a shear flow. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 204, 428–439 (2007)
Diaz, J.: Approches analytiques et numériques de problèmes de transmission en propagation d’ondes en régime transitoire. Application au couplage fluide-structure et aux méthodes de couches parfaitement adaptées, Ph.D. Thesis, Paris 6, (2005)
Engquist, B., Majda, A.: Absorbing boundary conditions for the numerical simulation of waves. Math. Comput. 31(139), 629–651 (1977)
Ern, A., Guermond, J.L.: Mollification in strongly Lipshitz domains with application to continuous and discrete De Rham complexes. Comput. Methods Appl. Math. 16(1), 51–75 (2016)
Ern, A., Guermond, J.L.: Analysis of the edge finite element approximation of the Maxwell equations with low regularity solutions. Comput. Math. Appl. 75, 918–932 (2018)
Gastaldi, L.: Mixed finite element methods in fluid structure systems. Numer. Math. 74, 153–176 (1996)
Girault, V., Raviart, P.A.: Finite Element Methods for Navier–Stokes Equations. Springer, New York (1986)
Grisvard, P.: Elliptic Problems in Nonsmooth Domains. Pitman, Boston (1985)
Hetmaniuk, U.: Stability estimates for a class of Helmholtz problems. Commun. Math. Sci. 5(3), 665–678 (2007)
Ihlenburg, F., Babuška, I.: Finite element solution of the Helmholtz equation with high wave number. Part I: the \(h\)-version of the FEM. Comput. Math. Appl. 30(9), 9–37 (1995)
Melenk, J.M., Sauter, S.: Wavenumber explicit convergence analysis for Galerkin discretizations of the Helmholtz equation. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 49(3), 1210–1243 (2011)
Monk, P.: Finite Element Methods for Maxwell’s Equations. Oxford Science Publications, Oxford (2003)
Nédélec, J.C.: Mixed finite elements in \(\mathbb{R}^3\). Numer. Math. 35, 315–341 (1980)
Payne, L.E., Weinberger, H.F.: An optimal Poincaré inequality for convex domains. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal. 5(1), 286–292 (1960)
Raviart, P.A., Thomas, J.M.: A Mixed Finite Element Method for 2nd Order Elliptic Problems, Mathematical Aspect of Finite Element Methods. Springer, New York (1977)
Retka, S., Marburg, S.: An infinite element for the solution of Galbrun equation. Z. Angew. Math. Mech. 93(2–3), 154–162 (2013)
Schatz, A.H.: An observation concerning Ritz–Galerkin methods with indefinite bilinear forms. Math. Comput. 28(128), 959–962 (1974)
Schoberl, J.: Commuting quasi-interpolation operators for mixed finite elements, Technical report preprint ISC-01-10-MATH, Texas A & M Univertsity (2001)
Singer, I., Turkel, E.: High-order finite difference methods for the Helmholtz equation. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 163, 343–358 (1998)
Tartar, L.: An Introduction to Sobolev Spaces and Interpolation Spaces. Springer, New York (2007)
Wang, X., Bathe, K.: On mixed elements for acoustic fluid–structure interactions. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 7(3), 329–343 (1997)
Zhong, L., Shu, S., Wittum, G., Xu, J.: Optimal error estimates for Nédélec edge elements for time-harmonic Maxwell’s equations. J. Comput. Math. 27(5), 563–572 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaumont-Frelet, T. Mixed finite element discretizations of acoustic Helmholtz problems with high wavenumbers. Calcolo 56, 49 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10092-019-0346-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10092-019-0346-z