Abstract
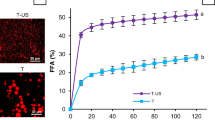
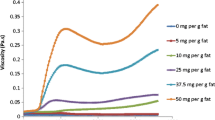
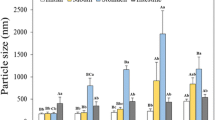
Hydrolysis of the oil phase in a water-in-oil-in-water (W/O/W) emulsion was studied using pancreatic lipase. The influence of the W/O volume fraction, lipase concentration, and concentration of emulsifiers used to prepare W/O/W emulsions on lipid digestion and release of encapsulated material were investigated. The extent of lipid digestion differed depending on the W/O volume and lipase concentration, and the amount of dye released was not dependent on the W/O content or lipase concentration. The concentration of emulsifiers did not affect the extent of digestion. The information obtained in this study will be useful for design of W/O/W emulsion formulations with controlled release profiles and lipid digestion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Matalanis A, Jones OG, McClements DJ. Structured biopolymer-based delivery systems for encapsulation, protection, and release of lipophilic compounds. Food Hydrodolloid. 25: 1865–1880 (2011)
Matalanis A, McClement DJ. Impact of encapsulation within hydrogel microspheres on lipid digestion: An in vitro study. Food Biophys. 7: 145–154 (2012)
McClements DJ, Decker EA, Park Y. Controlling lipid bioavailability through physicochemical and structural approaches. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 49: 48–67 (2009)
Qian C, Decker EA, Xiao H, McClements DJ. Impact of lipid nanoparticle physical state on particle aggregation and β-carotene degradation: Potential limitations of solid lipid nanoparticles. Food Res. Int. 52: 342–349 (2013)
Singh H, Ye AQ, Horne D. Structuring food emulsions in the gastrointestinal tract to modify lipid digestion. Prog. Lipid Res. 48: 92–100 (2009)
Troncoso E, Aguilera JM, McClements DJ. Fabrication, characterization and lipase digestibility of food-grade nanoemulsion. Food Hydrocolloid. 27: 355–363 (2012)
Leal-Calderon F, Homer S, Goh A, Lundin L. W/O/W emulsions with high internal droplet volume fraction. Food Hydrocolloid. 27: 30–41 (2012)
Garti N. Double emulsions-scope, limitations, and new achievements. Colloid. Surface. A. 123–124: 233–246 (1997)
Benichou A, Aserin A, Garti N. Double emulsions stabilized with hybrids of natural polymers for entrapment and slow release of active matters. Adv. Colloid Interfac. 108–109: 29–41 (2004)
Benichou A, Aserin A, Garti N. W/O/W double emulsions stabilized with WPI-polysaccharide complexes. Colloid. Surface. A. 294: 20–32 (2007)
Weiss J, Scherze I, Muschiolik G. Polysaccharide gel with multiple emulsion. Food hydrocolloid. 19: 605–615 (2005)
Su J, Flanagan J, Hemar Y, Singh H. Synergistic effects of polyglycerol ester of polyricinoleic acid and sodium caseinate on the stabilisation of water-oil-water emulsions. Food Hydrocolloid. 20: 261–268 (2006)
Silva-Cunha A, Grossiord JL, Puisieux F, Seiller M. Insulin in w/o/w multiple emulsions: Preparation, characterization, and determination of stability towards protease in vitro. J. Microencapsul. 14: 311–319 (1997)
Silva-Cunha A, Grossiord JL, Puisieux F, Seiller M. Insulin in w/o/w multiple emulsions: Biological activity after oral administration in normal and diabetic rats. J. Microencapsul. 14: 321–333 (1997)
Silva-Cunha A, Chéron M, Grossiord JL, Puisieux F, Seiller M. W/O/W multiple emulsions of insulin containing a protease inhibitor and an absorption enhancer: Biological activity after oral administration to normal and diabetic rats. Int. J. Pharm. 169: 33–44 (1998)
Surh J, Vladisavljeviæ GT, Mun SH, McClements DJ. Preparation and characterization of water/oil and water/oil/water emulsions containing biopolymer-gelled water droplets. J. Agr. Food Chem. 55: 175–184 (2007)
Tokgoz NS, Grossiord JL, Fructus A, Seiller M, Prognon P. Evaluation of two fluorescent probes for the characterization of W/O/W emulsions. Int. J. Pharm. 141: 27–37 (1996)
Adachi S, Imaoka H, Hasegawa Y, Matsuno R. Preparation of a water-in-oil-in-water (W/O/W) type microcapsules by a single-droplet-drying method and change in encapsulation efficiency of a hydrophilic substance during storage. Biosci. Biotech. Bioch. 67: 1376–1381 (2003)
Li Y, Hu M, McClements DJ. Factors affecting lipase digestibility of emulsified lipids using an in vitro digestion model: Proposal for a standardised pH-stat method. Food Chem. 126: 498–505 (2011)
Mun S, Decker EA, McClements DJ. Influence of emulsifier type on in vitro digestibility of lipid droplets by pancreatic lipase. Food Res. Int. 40: 770–781 (2007)
Nik AM, Wright AJ, Corredig M. Impact of interfacial composition on emulsion digestion and rate of lipid hydrolysis using different in vitro digestion models. Colloid. Surface. B. 83: 321–330 (2011)
Euston SR, Baird WG, Campbell L, Kuhns M. Competitive adsorption of dihydroxy and trihydroxy bile salts with whey protein and casein in oil-in-water emulsions. Biomacromolecules 14: 1850–1858 (2013)
Bellesi FA, Ruiz-Henestrosa VMP, Pilosof AMR. Behavior of protein interfacial films upon bile salts addition. Food Hydrocolloid. 36: 115–122 (2014)
McClements DJ. Food emulsions: Principles, practices, and techniques. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, USA. pp. 310–324 (2005)
Ahmed K, Li Y, McClements DJ, Xiao H. Nanoemulsion-and emulsion-based delivery systems for curcumin: Encapsulation and release properties. Food Chem. 132: 799–807 (2012)
Salvia-Trujillo L, Qian C, Martín-Belloso O, McClements DJ. Modulating β-carotene bioaccessibility by controlling oil composition and concentration in edible nanoemulsions. Food Chem. 139: 878–884 (2013)
Hu M, Li Y, Decker EA, McClements DJ. Role of calcium and calcium-binding agents on the lipase digestibility of emulsified lipids using an in vitro digestion model. Food Hydrocolloid. 24: 719–725 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mun, S., Choi, Y. & Kim, YR. Lipase digestibility of the oil phase in a water-in-oil-in-water emulsion. Food Sci Biotechnol 24, 513–520 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-015-0067-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-015-0067-2