Abstract
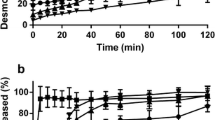
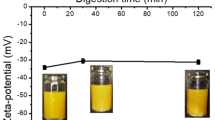
The objective of this study was to determine the influence of encapsulation of protein-coated lipid droplets within biopolymer hydrogel microspheres on their digestibility by lipase. We therefore compared the in vitro lipid digestion of non-encapsulated (“emulsions”) and encapsulated (“filled microspheres”) casein-coated lipid droplets. Filled microspheres were fabricated from a phase separated mixture of pectin and sodium caseinate and emulsified oil to form an oil-in-water-in-water (O/W/W) emulsion. The microspheres were then acidified, cross-linked with transglutaminase, and washed to remove excess pectin. Filled hydrogel microspheres were stable to simulated mouth conditions but formed large flocs under simulated gastric conditions. The casein stabilized emulsion showed modest droplet flocculation under simulated mouth conditions and showed significant flocculation and coalescence under simulated gastric conditions. The structure of both microspheres and emulsions was completely destroyed following in vitro digestion. Digestion profiles revealed similar rates of lipid digestion for both microspheres and emulsions. Since in vitro digestion conditions simulate the small intestine, the region of the body where the majority of lipid digestion and absorption occurs, these results suggest that lipid droplets encapsulated within microspheres would be digested similarly to those in conventional emulsions. Based on these findings, filled hydrogel microspheres appear to be a suitable delivery system for lipophilic bioactives.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Heurtault, P. Saulnier, B. Pech, J. Proust, J. Benoit, Biomaterials 24, 4283 (2003)
S.R.B.M. Eussen, H. Verhagen, O.H. Klungel, J. Garssen, H. van Loveren, H.J. van Kranen, C.J.M. Rompelberg, Eur. J. Pharmacol. 668(Supplement 1), S2 (2011)
C.J. Henry, Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 64, 657 (2010)
D.J. McClements, E.A. Decker, Y. Park, J. Weiss, Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 49, 577 (2009)
P. de Vos, M.M. Faas, M. Spasojevic, J. Sikkema, Int. Dairy J. 20, 292 (2010)
D.J. McClements, E.A. Decker, J. Weiss, J. Food Sci. 72, R109 (2007)
D.J. McClements, Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 1, 241 (2010)
L. Sagalowicz, M.E. Leser, Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 15, 61 (2010)
A. Matalanis, U. Lesmes, E.A. Decker, D.J. McClements, Food Hydrocoll. 24, 689 (2010)
C. H. M. Versantvoort, E. v. d. Kamp, and C. J. M. Rompelberg, Development and applicability of an in vitro digestion model in assessing the bioaccessibility of contaminants from food. (Rijksinstituut voor Volksgezondheid en Milieu, 2004) http://hdl.handle.net/10029/8885. Accessed 14 November 2011.
D.J. McClements, E.A. Decker, Y. Park, Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 49, 48 (2008)
D.J. McClements, Y. Li, Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 159, 213 (2010)
M.M. Bradford, Anal. Biochem. 72, 248 (1976)
M. DuBois, K.A. Gilles, J.K. Hamilton, P.A. Rebers, F. Smith, Anal. Chem. 28, 350 (1956)
S. Iverson, S. Lang, M. Cooper, Lipids 36, 1283 (2001)
A. Sarkar, K.K.T. Goh, H. Singh, Food Hydrocoll. 23, 1270 (2009)
M. Hu, Y. Li, E.A. Decker, D.J. McClements, Food Hydrocoll. 24, 719 (2010)
D.J. McClements, Food emulsions: principles, practice, and techniques (CRC, Boca Raton, 2005), p. 14
E. Dickinson, J. Dairy Sci. 80, 2607 (1997)
M. David Julian, Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 9, 305 (2004)
J. Surh, E.A. Decker, D.J. McClements, Food Hydrocoll. 20, 607 (2006)
M.H. Vingerhoeds, T.B.J. Blijdenstein, F.D. Zoet, G.A. van Aken, Food Hydrocoll. 19, 915 (2005)
R. Bansil, B.S. Turner, Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 11, 164 (2006)
E. Dickinson, Food Hydrocoll. 17, 25 (2003)
E. Silletti, M.H. Vingerhoeds, W. Norde, G.A. van Aken, Food Hydrocoll. 21, 596 (2007)
A. Sarkar, K.K.T. Goh, R.P. Singh, H. Singh, Food Hydrocoll. 23, 1563 (2009)
A. Macierzanka, A.I. Sancho, E.N.C. Mills, N.M. Rigby, A.R. Mackie, Soft Matter 5, 538 (2009)
M. Golding, T.J. Wooster, L. Day, M. Xu, L. Lundin, J. Keogh, P. Clifton, Soft Matter 7, 3513 (2011)
M. Golding, T.J. Wooster, Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 15, 90 (2010)
S.J. Hur, E.A. Decker, D.J. McClements, Food Chem. 114, 253 (2009)
S. Sandra, E.A. Decker, D.J. McClements, J. Agric. Food Chem. 56, 7488 (2008)
Y. Li, D.J. McClements, Food Hydrocoll. 25, 1025 (2011)
A. Dahan, A. Hoffman, Pharm. Res. 23, 2165 (2006)
Y. Li, D.J. McClements, J. Agric. Food Chem. 58, 8085 (2010)
L. Marciani, M. Wickham, G. Singh, D. Bush, B. Pick, E. Cox, A. Fillery-Travis, R. Faulks, C. Marsden, P.A. Gowland, am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 292, G1607 (2007)
L. Marciani, R. Faulks, M.S.J. Wickham, D. Bush, B. Pick, J. Wright, E.F. Cox, A. Fillery-Travis, P.A. Gowland, R.C. Spiller, Br. J. Nutr. 101, 919 (2009)
Acknowledgements
This material is based upon work supported by the United States Department of Agriculture, CREES, NRI Grants. We also acknowledge funding from the University of Massachusetts (CVIP and Hatch).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matalanis, A., McClements, D.J. Impact of Encapsulation Within Hydrogel Microspheres on Lipid Digestion: An In Vitro Study. Food Biophysics 7, 145–154 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-012-9252-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-012-9252-5