Abstract
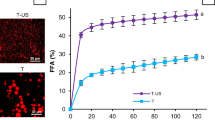
This study was performed to examine the effect of emulsifiers used to coat emulsion droplets containing β-carotene on the behavior of lipid digestion and bioaccessibility. Different emulsifiers (whey protein isolate, soy protein isolate, sodium caseinate, Tween 20, and soy lecithin) were used to prepare emulsions with similar sized droplets (200–400 nm). Protein-stabilized emulsions showed a similar behavior of digestion, and morphological change in the simulated gastrointestinal conditions. Soy lecithin-stabilized emulsions showed the lowest rate and extent of lipid digestion probably due to the low emulsifying capability of soy lecithin, showing coalesced droplets occurring after exposure to the gastric phase. Tween 20-stabilized emulsions had a lower rate and extent of lipid digestion than that of protein-stabilized emulsions, even though Tween 20-stabilized emulsions had a more stable structure to resistant to aggregation in gastric phase. Even though the difference in the digestion rate and extent, β-carotene bioaccessibility was not significantly different among emulsions stabilized by different emulsifiers at p < 0.05.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.L. Tang, J. Sun, Z.G. He, Curr. Drug Ther. 2, 85 (2007)
R. Liang, C.F. Shoemaker, X. Yang, F. Zhong, Q. Huang, J. Agr. Food Chem. 61, 1249 (2013)
D.J. McClements, Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 10, 1621 (2013)
E. Reboul, Nutrients 5, 3563 (2013)
I.J. Joye, D.J. McClements, Curr. Opin. Colloid In. 19, 417 (2014)
A. Maltais, G.E. Remondetto, M. Subirade, Food Hydrocoll. 23, 1647 (2009)
D.J. McClements, Y. Li, Adv. Colloid Interfac. Sci. 159, 213 (2010)
Z. Hou, Y. Liu, F. Lei, Y. Gao, LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 59, 867 (2014)
L. Mao, S. Miao, Food Eng. Rev. 7, 439 (2015)
R. Zhang, Z. Zhang, H. Zhang, E.A. Decker, D.J. McClements, Food Hydrocoll. 45, 175 (2015)
S.J. Hur, E.A. Decker, D.J. McClements, Food Chem. 114, 253 (2009)
J. Yi, Y. Li, F. Zhong, W. Yokoyama, Food Hydrocoll. 35, 19 (2014)
C. Qiu, M. Zhao, E.A. Decker, D.J. McClements, Food Chem. 175, 249 (2015)
T.L. Salvia, C. Qian, B.O. Martín, D.J. McClements, Food Chem. 139, 878 (2013)
T.L. Salvia, C. Qian, B.O. Martín, D.J. McClements, Food Chem. 141, 1472 (2013)
S.H. Mun, Y.R. Kim, D.J. McClements, Food Chem. 173, 454 (2015)
C.L. Lopez-Pena, B. Zheng, D.A. Sela, E.A. Decker, H. Xiao, D.J. McClements, Food Chem. 192, 857 (2016)
A. Sarkar, K.K.T. Goh, H. Singh, Food Hydrocoll. 23, 1270 (2009)
C. Qian, E.A. Decker, H. Xiao, D.J. McClements, Food Chem. 135, 1440 (2012)
E. Troncoso, J.M. Aguilera, D.J. McClements, J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 382, 110 (2012)
D.J. McClements, Food emulsions: Principles, practices and techniques (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2005)
L. Chen, J. Chen, J. Ren, M. Zhao, Food Hydrocoll. 25, 887 (2011)
C.H. Tang, X.R. Li, Food Res. Int. 52, 419 (2013)
E. Silletti, M.H. Vingerhoeds, W. Norde, G.A. van Aken, Food Hydrocoll. 21, 596 (2007)
J. Li, A. Ye, S.J. Lee, H. Singh, Colloid Surf. B. 111, 80 (2013)
C. Yucel, V. Quagliariello, R.V. Iaffaioli, G. Ferrari, F. Donsì, Int. J. Pharm. 494, 357 (2015)
H. Singh, A.Q. Ye, D. Horne, Prog. Lipid Res. 48, 92 (2009)
C.H. Tang, Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 57, 2636 (2017)
S. Damodaran, J. Food Sci. 70, R54 (2005)
G.A. Van Aken, E. Bomhof, F.D. Zoet, M. Verbeek, A. Oosterveld, Food Hydrocoll. 25, 781 (2011)
S.H. Mun, Y.R. Kim, M.S. Shin, D.J. McClements, Food Hydrocoll. 44, 380 (2015)
S.H. Mun, E.A. Decker, D.J. McClements, Food Res. Int. 40, 770 (2007)
H. Singh, A. Sarkar, Adv. Colloid Interfac. Sci. 165, 47 (2011)
Y. Chang, D.J. McClements, Food Hydrocoll. 61, 92 (2016)
G.A. Torcello, V.J. Maldonado, R.A. Martín, D.J. McClements, Soft Matter 7, 6167 (2011)
J.Ø. Christensen, K. Schultz, B. Mollgaard, H.G. Kristensen, A. Mullertz, Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 23, 287 (2004)
T.A.J. Verrijssen, K.H.G. Smeets, S. Christiaens, S. Palmers, A.M. Van Loey, M.E. Hendrickx, Food Res. Int. 67, 60 (2015)
A. Tapal, P.K. Tiku, Food Chem. 130, 960 (2013)
Acknowledgements
This research was partly supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grants funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT, and Future Planning (NRF-2015R1A1A3A04001485). This work was also partly supported by Korea Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (IPET) through High value-added Food Technology Development Program, funded by Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFRA), Republic of Korea (Project No. 315065-3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, S., Mun, S. & Kim, YR. Emulsifier Dependent in vitro Digestion and Bioaccessibility of β-Carotene Loaded in Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Food Biophysics 13, 147–154 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-018-9520-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-018-9520-0