Abstract
Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory systemic autoimmune disease. Cytokines regulate a wide range of inflammatory processes involved in RA pathogenesis. Anti-inflammatory cytokines (i.e., TGF-β and lL-10) and pro-inflammatory cytokines, like IL-6, were found to be potentially implicated in RA pathogenesis. Besides, NF-κB and FoxP3 are critical transcription factors regulating the inflammatory events occurring in RA patients. This study intends to assess the plasma levels of IL-6, IL-10, and TGF-β1 cytokines, as well as the expression of NF-κB and FoxP3 genes in RA patients, compared to the healthy controls.
Methods
Peripheral blood was collected from 50 RA patients (25 new case and 25 under-treatment) and 25 age- and gender-matched healthy subjects. The disease activity was determined using the DAS-28 and ESR criteria. Also, plasma levels of TGF-β1, lL-10, and IL-6 were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) technique, and the gene expression of NF-κB and FoxP3 was evaluated using the real-time PCR method.
Results
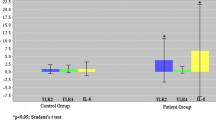
Our results showed a significant up-regulation of Rel-A and NF-κB1, and also a down-regulation of FoxP3 gene expression in under-treatment RA patients compared to the controls (P=0.031, P=0.014, and P=0.011, respectively). Moreover, there was a significant reduction of Rel-A and FoxP3 in the under-treatment RA patients compared to new case RA patients (P=0.005 and P=0.015, respectively). Also, plasma levels of TGF-β1 were significantly increased in both the new case and under-treatment RA patients relative to controls (P<0.001).
Conclusion
In conclusion, classical NF-κB (P65/P50) and FoxP3 may have significant pro- and anti-inflammatory roles in RA pathogenesis, respectively.
Key Point • NF-κB (P65/P50) has a contribution to the early phase of RA. |


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- RA:
-
Rheumatoid arthritis
- FoxP3:
-
Forkhead box P3
- TGF-β:
-
Transforming growth factor-β
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin 6
- Treg cell:
-
Regulatory T cell
- NFAT:
-
Nuclear factor of activated T cells
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor-κB
References
Alunno A, Manetti M, Caterbi S, Ibba-Manneschi L, Bistoni O, Bartoloni E, Valentini V, Terenzi R, Gerli R (2015) Altered immunoregulation in rheumatoid arthritis: the role of regulatory T cells and proinflammatory Th17 cells and therapeutic implications. Mediators Inflamm 2015:751793. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/751793
Alunno A, Carubbi F, Giacomelli R, Gerli R (2017) Cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: new players and therapeutic targets. BMC Rheumatol 1:3. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41927-017-0001-8
Roman-Blas JA, Jimenez SA (2006) NF-kappaB as a potential therapeutic target in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 14(9):839–848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2006.04.008
Nemeth E, Rivera S, Gabayan V, Keller C, Taudorf S, Pedersen BK, Ganz T (2004) IL-6 mediates hypoferremia of inflammation by inducing the synthesis of the iron regulatory hormone hepcidin. J Clin Invest 113(9):1271–1276. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci20945
Scott-Taylor TH, Hourihane JB, Harper J, Strobel S (2005) Patterns of food allergen-specific cytokine production by T lymphocytes of children with multiple allergies. Clin Exp Allergy 35(11):1473–1480. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2222.2005.02355.x
Xiao J, Zhu F, Liu X, Xiong J (2012) Th1/Th2/Th17/Treg expression in cultured PBMCs with antiphospholipid antibodies. Mol Med Rep 6(5):1035–1039. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2012.1055
Nedoszytko B, Lange M, Sokołowska-Wojdyło M, Renke J, Trzonkowski P, Sobjanek M, Szczerkowska-Dobosz A, Niedoszytko M, Górska A, Romantowski J, Czarny J, Skokowski J, Kalinowski L, Nowicki R (2017) The role of regulatory T cells and genes involved in their differentiation in pathogenesis of selected inflammatory and neoplastic skin diseases. Part II: The Treg role in skin diseases pathogenesis. Postepy Dermatol Alergol 34(5):405–417. https://doi.org/10.5114/ada.2017.71105
Okamoto A, Fujio K, Okamura T, Yamamoto K (2011) Regulatory T-cell-associated cytokines in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Biomed Biotechnol 2011:463412. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/463412
Kay J, Upchurch KS (2012) ACR/EULAR 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria. Rheumatology (Oxford) 51(Suppl 6:vi5):9. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kes279
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29(9):e45. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/29.9.e45
McInnes IB, Schett G (2011) The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 365(23):2205–2219. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1004965
Tornatore L, Thotakura AK, Bennett J, Moretti M, Franzoso G (2012) The nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathway: integrating metabolism with inflammation. Trends Cell Biol 22(11):557–566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2012.08.001
Makarov SS (2001) NF-kappa B in rheumatoid arthritis: a pivotal regulator of inflammation, hyperplasia, and tissue destruction. Arthritis Res 3(4):200–206. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar300
Hilliard BA, Mason N, Xu L, Sun J, Lamhamedi-Cherradi SE, Liou HC, Hunter C, Chen YH (2002) Critical roles of c-Rel in autoimmune inflammation and helper T cell differentiation. J Clin Invest 110(6):843–850. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci15254
Das J, Chen CH, Yang L, Cohn L, Ray P, Ray A (2001) A critical role for NF-kappa B in GATA3 expression and TH2 differentiation in allergic airway inflammation. Nat Immunol 2(1):45–50. https://doi.org/10.1038/83158
Majumdar S, Aggarwal BB (2001) Methotrexate suppresses NF-kappaB activation through inhibition of IkappaBalpha phosphorylation and degradation. J Immunol 167(5):2911–2920. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.167.5.2911
Handel ML, McMorrow LB, Gravallese EM (1995) Nuclear factor-kappa B in rheumatoid synovium. Localization of p50 and p65. Arthritis Rheum 38(12):1762–1770. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.1780381209
Le F, Zhang JY, Liu W, Huang XM, Luo WZ (2018) The levels of NF-κB p50 and NF-κB p65 play a role in thyroid carcinoma malignancy in vivo. J Int Med Res 46(10):4092–4099. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300060518785846
Porta C, Ippolito A, Consonni FM, Carraro L, Celesti G, Correale C, Grizzi F, Pasqualini F, Tartari S, Rinaldi M, Bianchi P, Balzac F, Vetrano S, Turco E, Hirsch E, Laghi L, Sica A (2018) Protumor steering of cancer inflammation by p50 NF-κB enhances colorectal cancer progression. Cancer Immunol Res 6(5):578–593. https://doi.org/10.1158/2326-6066.cir-17-0036
Ruan Q, Kameswaran V, Tone Y, Li L, Liou HC, Greene MI, Tone M, Chen YH (2009) Development of Foxp3(+) regulatory t cells is driven by the c-Rel enhanceosome. Immunity 31(6):932–940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2009.10.006
Suzuki K, Setoyama Y, Yoshimoto K, Tsuzaka K, Abe T, Takeuchi T (2011) Decreased mRNA expression of two FOXP3 isoforms in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 24(1):7–14. https://doi.org/10.1177/039463201102400102
Lohr J, Knoechel B, Abbas AK (2006) Regulatory T cells in the periphery. Immunol Rev 212:149–162. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0105-2896.2006.00414.x
Yoshimura A, Wakabayashi Y, Mori T (2010) Cellular and molecular basis for the regulation of inflammation by TGF-beta. J Biochem 147(6):781–792. https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvq043
Marçal JR, Samuel RO, Fernandes D, de Araujo MS, Napimoga MH, Pereira SA, Clemente-Napimoga JT, Alves PM, Mattar R, Rodrigues V Jr, Rodrigues DB (2010) T-helper cell type 17/regulatory T-cell immunoregulatory balance in human radicular cysts and periapical granulomas. J Endod 36(6):995–999. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2010.03.020
Boissier MC, Assier E, Falgarone G, Bessis N (2008) Shifting the imbalance from Th1/Th2 to Th17/treg: the changing rheumatoid arthritis paradigm. Joint Bone Spine 75(4):373–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbspin.2008.04.005
Mieliauskaite D, Venalis P, Dumalakiene I, Venalis A, Distler J (2009) Relationship between serum levels of TGF-beta1 and clinical parameters in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and Sjögren's syndrome secondary to rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmunity 42(4):356–358. https://doi.org/10.1080/08916930902831977
Gerards AH, de Lathouder S, de Groot ER, Dijkmans BAC, Aarden LA (2003) Inhibition of cytokine production by methotrexate. Studies in healthy volunteers and patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 42(10):1189–1196. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keg323
Olsen NJ, Spurlock CF 3rd, Aune TM (2014) Methotrexate induces production of IL-1 and IL-6 in the monocytic cell line U937. Arthritis Res Ther 16(1):R17. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar4444
Strand V, Boklage SH, Kimura T, Joly F, Boyapati A, Msihid J (2020) High levels of interleukin-6 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis are associated with greater improvements in health-related quality of life for sarilumab compared with adalimumab. Arthritis Res Ther 22(1):250. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-020-02344-3
Tanaka T, Narazaki M, Kishimoto T (2014) IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 6(10):a016295. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a016295
Tao JH, Cheng M, Tang JP, Liu Q, Pan F, Li XP (2017) Foxp3, Regulatory T Cell, and Autoimmune Diseases. Inflammation 40(1):328–339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-016-0470-8
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all subjects who eagerly participated in this study. This work was accomplished in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the M.Sc. thesis of Seyed Askar Roghani, in the School of Medicine, Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences (KUMS), Kermanshah, Iran.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the deputy of research and technology of the Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences, Kermanshah, Iran [Grant Number: 95709].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct, and intellectual contribution to the work and approved it for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Roghani, S.A., Lotfi, R., Soleymani, B. et al. Investigating the correlation of the NF-κB and FoxP3 gene expression with the plasma levels of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin Rheumatol 42, 1443–1450 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-023-06521-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-023-06521-y