Abstract
Objectives
Decreased natural killer (NK) cells have been reported in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients. However, the role of NK cells in the pathogenesis of SLE is not well understood. In this study, we aimed to characterize NK cell subsets, phenotypes, and cytokine-secreting functions and investigate the clinical relevance of NK cells in SLE patients.
Methods
Peripheral blood samples from 81 SLE patients and 59 healthy donors (HDs) were collected. The frequency and phenotype of NK cells were measured by flow cytometry. Intracellular interferon-γ (IFN-γ) production by NK cells was evaluated by flow cytometry after stimulation with interleukin-12 (IL-12) and IL-18.
Results
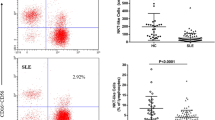
The percentages of NK cells in the peripheral blood of SLE patients were significantly lower than those in HDs, and the percentages of CD56dim NK cells among total NK cells showed a trend toward decrease. The CD56dim NK cells in SLE patients showed increased production of IFN-γ and displayed relatively activated phenotypic characteristics, including significant increases in NKp44, NKp46, and CD69 and decreased expression of CD16 and CD158a/h/g. Furthermore, CD56dim NK cells in active SLE patients had higher percentages of NKp44+ cells and lower percentages of CD158a/h/g+ cells than those in inactive SLE patients. The percentages of CD158a/h/g+ cells among CD56dim NK cells were negatively correlated with the systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index (SLEDAI) and positively correlated with C3 and C4 levels.
Conclusion
CD56dim NK cells in SLE patients show a reduced proportion tendency among total NK cells and are activated, which partially reflects the disease activity. CD158a/h/g expression on CD56dim NK cells may be considered an index of disease activity.
Key Points • In patients with SLE, the proportion of CD56dim NK cells showed a decreased trend and CD56dim NK cells were phenotypically activated which partially reflects the disease activity. • CD158a/h/g expression on CD56dim NK cells were decreased which may be used as an indicator for evaluating disease activity in SLE patients. |





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campbell KS, Hasegawa J (2013) Natural killer cell biology: an update and future directions. J Allergy Clin Immunol 132(3):536–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2013.07.006
Shi FD, Wang HB, Li H, Hong S, Taniguchi M, Link H, Van Kaer L, Ljunggren HG (2000) Natural killer cells determine the outcome of B cell-mediated autoimmunity. Nat Immunol 1(3):245–251. https://doi.org/10.1038/79792
Fogel LA, Yokoyama WM, French AR (2013) Natural killer cells in human autoimmune disorders. Arthritis Res Ther 15(4):216. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar4232
De Maria A, Bozzano F, Cantoni C, Moretta L (2011) Revisiting human natural killer cell subset function revealed cytolytic CD56(dim)CD16+ NK cells as rapid producers of abundant IFN-gamma on activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(2):728–732. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1012356108
Abel AM, Yang C, Thakar MS, Malarkannan S (2018) Natural killer cells: development, maturation, and clinical utilization. Front Immunol 9:1869. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.01869
Poli A, Michel T, Theresine M, Andres E, Hentges F, Zimmer J (2009) CD56bright natural killer (NK) cells: an important NK cell subset. Immunology 126(4):458–465. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.03027.x
Martinet L, Smyth MJ (2015) Balancing natural killer cell activation through paired receptors. Nat Rev Immunol 15(4):243–254. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3799
Bryceson YT, March ME, Ljunggren HG, Long EO (2006) Synergy among receptors on resting NK cells for the activation of natural cytotoxicity and cytokine secretion. Blood 107(1):159–166. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2005-04-1351
Grzywacz B, Kataria N, Verneris MR (2007) CD56dimCD16+ NK cells downregulate CD16 following target cell induced activation of matrix metalloproteinases. Leukemia 21(2):356–359. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404499
Park YW, Kee SJ, Cho YN, Lee EH, Lee HY, Kim EM, Shin MH, Park JJ, Kim TJ, Lee SS, Yoo DH, Kang HS (2009) Impaired differentiation and cytotoxicity of natural killer cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 60(6):1753–1763. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.24556
Hervier B, Beziat V, Haroche J, Mathian A, Lebon P, Ghillani-Dalbin P, Musset L, Debre P, Amoura Z, Vieillard V (2011) Phenotype and function of natural killer cells in systemic lupus erythematosus: excess interferon-gamma production in patients with active disease. Arthritis Rheum 63(6):1698–1706. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.30313
Huang Z, Fu B, Zheng SG, Li X, Sun R, Tian Z, Wei H (2011) Involvement of CD226+ NK cells in immunopathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol 186(6):3421–3431. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1000569
Henriques A, Teixeira L, Ines L, Carvalheiro T, Goncalves A, Martinho A, Pais ML, da Silva JA, Paiva A (2013) NK cells dysfunction in systemic lupus erythematosus: relation to disease activity. Clin Rheumatol 32(6):805–813. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-013-2176-8
Ma H, Zhao L, Jiang Z, Jiang Y, Feng L, Ye Z (2014) Dynamic changes in the numbers of different subsets of peripheral blood NK cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus following classic therapy. Clin Rheumatol 33(11):1603–1610. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-014-2712-1
Ye Z, Ma N, Zhao L, Jiang ZY, Jiang YF (2016) Differential expression of natural killer activating and inhibitory receptors in patients with newly diagnosed systemic lupus erythematosus. Int J Rheum Dis 19(6):613–621. https://doi.org/10.1111/1756-185X.12289
Lin SJ, Kuo ML, Hsiao HS, Lee PT, Chen JY, Huang JL (2017) Activating and inhibitory receptors on natural killer cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosis-regulation with interleukin-15. PLoS One 12(10):e0186223. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0186223
Lin YL, Lin SC (2017) Analysis of the CD161-expressing cell quantities and CD161 expression levels in peripheral blood natural killer and T cells of systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Clin Exp Med 17(1):101–109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-015-0402-1
Spada R, Rojas JM, Perez-Yague S, Mulens V, Cannata-Ortiz P, Bragado R, Barber DF (2015) NKG2D ligand overexpression in lupus nephritis correlates with increased NK cell activity and differentiation in kidneys but not in the periphery. J Leukoc Biol 97(3):583–598. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.4A0714-326R
Huang X, Li J, Dorta-Estremera S, Di Domizio J, Anthony SM, Watowich SS, Popkin D, Liu Z, Brohawn P, Yao Y, Schluns KS, Lanier LL, Cao W (2015) Neutrophils regulate Humoral autoimmunity by restricting interferon-gamma production via the generation of reactive oxygen species. Cell Rep 12(7):1120–1132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2015.07.021
Liu M, Liu J, Hao S, Wu P, Zhang X, Xiao Y, Jiang G, Huang X (2018) Higher activation of the interferon-gamma signaling pathway in systemic lupus erythematosus patients with a high type I IFN score: relation to disease activity. Clin Rheumatol 37(10):2675–2684. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-018-4138-7
Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF, Masi AT, McShane DJ, Rothfield NF, Schaller JG, Talal N, Winchester RJ (1982) The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 25(11):1271–1277
Gladman DD, Ibanez D, Urowitz MB (2002) Systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index 2000. J Rheumatol 29(2):288–291
Franklyn K, Lau CS, Navarra SV, Louthrenoo W, Lateef A, Hamijoyo L, Wahono CS, Chen SL, Jin O, Morton S, Hoi A, Huq M, Nikpour M, Morand EF (2016) Definition and initial validation of a lupus low disease activity state (LLDAS). Ann Rheum Dis 75(9):1615–1621. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-207726
Schepis D, Gunnarsson I, Eloranta ML, Lampa J, Jacobson SH, Karre K, Berg L (2009) Increased proportion of CD56bright natural killer cells in active and inactive systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunology 126(1):140–146. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.02887.x
Hudspeth K, Wang S, Wang J, Rahman S, Smith MA, Casey KA, Manna Z, Sanjuan M, Kolbeck R, Hasni S, Ettinger R, Siegel RM (2019) Natural killer cell expression of Ki67 is associated with elevated serum IL-15, disease activity and nephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol 196(2):226–236. https://doi.org/10.1111/cei.13263
Lajoie L, Congy-Jolivet N, Bolzec A, Gouilleux-Gruart V, Sicard E, Sung HC, Peiretti F, Moreau T, Vie H, Clemenceau B, Thibault G (2014) ADAM17-mediated shedding of FcgammaRIIIA on human NK cells: identification of the cleavage site and relationship with activation. J Immunol 192(2):741–751. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1301024
Zingoni A, Sornasse T, Cocks BG, Tanaka Y, Santoni A, Lanier LL (2004) Cross-talk between activated human NK cells and CD4+ T cells via OX40-OX40 ligand interactions. J Immunol 173(6):3716–3724. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.173.6.3716
Liu R, Van Kaer L, La Cava A, Price M, Campagnolo DI, Collins M, Young DA, Vollmer TL, Shi FD (2006) Autoreactive T cells mediate NK cell degeneration in autoimmune disease. J Immunol 176(9):5247–5254. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.176.9.5247
Segerberg F, Lundtoft C, Reid S, Hjorton K, Leonard D, Nordmark G, Carlsten M, Hagberg N (2019) Autoantibodies to killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors in patients with systemic lupus Erythematosus induce natural killer cell hyporesponsiveness. Front Immunol 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.02164
Liang HL, Ma SJ, Tan HZ (2017) Association between killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) polymorphisms and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in populations: a PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 96(10):e6166. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000006166
Bai Y, Zhang Y, Yang Q, Hou Y, Hu N, Wang D, Sun H (2014) The aberrant expression of stimulatory and inhibitory killer immunoglobulin-like receptors in NK- and NKT-cells contributes to lupus. Clin Lab 60(5):717–727
Hou YF, Zhang YC, Jiao YL, Wang LC, Li JF, Pan ZL, Yang QR, Sun HS, Zhao YR (2010) Disparate distribution of activating and inhibitory killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor genes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 19(1):20–26. https://doi.org/10.1177/0961203309345779
Hou Y, Zhang C, Xu D, Sun H (2015) Association of killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor and human leucocyte antigen-Cw gene combinations with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol 180(2):250–254. https://doi.org/10.1111/cei.12582
Chasset F, Arnaud L (2018) Targeting interferons and their pathways in systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun Rev 17(1):44–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2017.11.009
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31470854) and the Pujiang Talents Plan (16PJ1405600).
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants No. 31470854) and Pujiang Talents Plan (Grants No. 16PJ1405600).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Figure S1
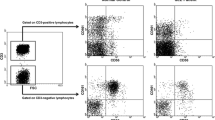
Frequency of CD56dim NK cells in SLE patients before and after treatment or follow-up. (a) Flow cytometry gating strategy for the analysis of NK cells. (b) SLEDAI scores, frequency of total NK cells among lymphocytes and percentages of CD56bright NK cells and CD56dim NK cells among total NK cells from six SLE patients were determined at two points during induction therapy or follow-up (Wilcoxon signed rank test). The first and second measurements are depicted. Data from the same patient before and after treatment or follow-up are denoted by an individual line. (PNG 197 kb).
Figure S2
IFN-γ production by CD56dim NK cells from SLE patients not taking (n = 22) and taking HCQ (n = 25) with IL12/18 stimulation (unpaired t test) (PNG 11 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M., Liu, J., Zhang, X. et al. Activation status of CD56dim natural killer cells is associated with disease activity of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol 40, 1103–1112 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-05306-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-05306-x