Abstract
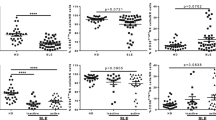
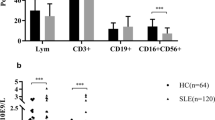
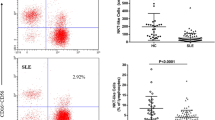
Imbalance of natural killer (NK) cells is associated with the development of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). However, little is known about the dynamic changes on NK cells following therapy. This study aimed at examining the impact of classic therapies on the numbers of different subsets of NK cells in new-onset SLE patients. The numbers of different subsets of peripheral blood NK cells in 24 new-onset SLE patients before, 4 and 12 weeks post the classic therapies, and 7 healthy controls were determined by flow cytometry. The potential correlation between the numbers of NK cells and the values of clinical measures was analyzed. In comparison with that before treatment, the numbers of NK, NKG2C+, and KIR2DL3+ NK cells were significantly increased while the numbers of NKp46+ and NKG2A + NK cells significantly decreased at 4 and/or 12 weeks post the treatment only in the drug well-responding patients, but not in those poor responders (P < 0.05 for all). The numbers of NKG2C + NK cells were correlated positively with the levels of serum C3 while the numbers of KIR2DL3+ NK cells were correlated negatively with the scores of SLEDAI in these patients at 4 weeks post the treatment. The classic therapies modulated the numbers of some subsets of NK cells in drug well-responding SLE patients. The changes in the numbers of some subsets of NK cells may serve as biomarkers for evaluating the therapeutic responses of SLE.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sekigawa I, Naito T, Hira K, Mitsuishi K, Ogasawara H, Hashimoto H, Ogawa H (2004) Possible mechanisms of gender bias in SLE: a new hypothesis involving a comparison of SLE with atopy. Lupus 13(4):217–222
Raulet DH, Vance RE, McMahon CW (2001) Regulation of the natural killer cell receptor repertoire. Annu Rev Immunol 19:291–330. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.19.1.291
Pende D, Parolini S, Pessino A, Sivori S, Augugliaro R, Morelli L, Marcenaro E, Accame L, Malaspina A, Biassoni R, Bottino C, Moretta L, Moretta A (1999) Identification and molecular characterization of NKp30, a novel triggering receptor involved in natural cytotoxicity mediated by human natural killer cells. J Exp Med 190(10):1505–1516
Sivori S, Vitale M, Morelli L, Sanseverino L, Augugliaro R, Bottino C, Moretta L, Moretta A (1997) p46, a novel natural killer cell-specific surface molecule that mediates cell activation. J Exp Med 186(7):1129–1136
Vitale M, Bottino C, Sivori S, Sanseverino L, Castriconi R, Marcenaro E, Augugliaro R, Moretta L, Moretta A (1998) NKp44, a novel triggering surface molecule specifically expressed by activated natural killer cells, is involved in non-major histocompatibility complex-restricted tumor cell lysis. J Exp Med 187(12):2065–2072
Bryceson YT, March ME, Ljunggren HG, Long EO (2006) Activation, coactivation, and costimulation of resting human natural killer cells. Immunol Rev 214:73–91. doi:10.1111/j.1600-065X.2006.00457.x
Moretta L, Moretta A (2004) Unravelling natural killer cell function: triggering and inhibitory human NK receptors. EMBO J 23(2):255–259. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600019
Vivier E, Nunes JA, Vely F (2004) Natural killer cell signaling pathways. Science 306(5701):1517–1519. doi:10.1126/science.1103478
Baxter AG, Smyth MJ (2002) The role of NK cells in autoimmune disease. Autoimmunity 35(1):1–14
Li WX, Pan HF, Hu JL, Wang CZ, Zhang N, Li J, Li XP, Xu JH, Ye DQ (2010) Assay of T- and NK-cell subsets and the expression of NKG2A and NKG2D in patients with new-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol 29(3):315–323. doi:10.1007/s10067-009-1322-9
Ye Z, Ma N, Zhao L, Jiang ZY, Jiang YF (2014) Differential expression of natural killer activating and inhibitory receptors in patients with newly diagnosed systemic lupus erythematosus. Int J Rheum Dis. doi:10.1111/1756-185X.12289
Green MR, Kennell AS, Larche MJ, Seifert MH, Isenberg DA, Salaman MR (2005) Natural killer cell activity in families of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: demonstration of a killing defect in patients. Clin Exp Immunol 141(1):165–173. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02822.x
Hervier B, Beziat V, Haroche J, Mathian A, Lebon P, Ghillani-Dalbin P, Musset L, Debre P, Amoura Z, Vieillard V (2011) Phenotype and function of natural killer cells in systemic lupus erythematosus: excess interferon-gamma production in patients with active disease. Arthritis Rheum 63(6):1698–1706. doi:10.1002/art.30313
Ortaldo JR, Mason AT, O'Shea JJ (1995) Receptor-induced death in human natural killer cells: involvement of CD16. J Exp Med 181(1):339–344
Lauzurica P, Sancho D, Torres M, Albella B, Marazuela M, Merino T, Bueren JA, Martinez AC, Sanchez-Madrid F (2000) Phenotypic and functional characteristics of hematopoietic cell lineages in CD69-deficient mice. Blood 95(7):2312–2320
Shiow LR, Rosen DB, Brdickova N, Xu Y, An J, Lanier LL, Cyster JG, Matloubian M (2006) CD69 acts downstream of interferon-alpha/beta to inhibit S1P1 and lymphocyte egress from lymphoid organs. Nature 440(7083):540–544. doi:10.1038/nature04606
Testi R, D'Ambrosio D, De Maria R, Santoni A (1994) The CD69 receptor: a multipurpose cell-surface trigger for hematopoietic cells. Immunol Today 15(10):479–483. doi:10.1016/0167-5699(94)90193-7
Harigai M, Kawamoto M, Hara M, Kubota T, Kamatani N, Miyasaka N (2008) Excessive production of IFN-gamma in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and its contribution to induction of B lymphocyte stimulator/B cell-activating factor/TNF ligand superfamily-13B. J Immunol 181(3):2211–2219
Viallard JF, Pellegrin JL, Ranchin V, Schaeverbeke T, Dehais J, Longy-Boursier M, Ragnaud JM, Leng B, Moreau JF (1999) Th1 (IL-2, interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma)) and Th2 (IL-10, IL-4) cytokine production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Clin Exp Immunol 115(1):189–195
Zhuang H, Kosboth M, Lee P, Rice A, Driscoll DJ, Zori R, Narain S, Lyons R, Satoh M, Sobel E, Reeves WH (2006) Lupus-like disease and high interferon levels corresponding to trisomy of the type I interferon cluster on chromosome 9p. Arthritis Rheum 54(5):1573–1579. doi:10.1002/art.21800
Martin-Fontecha A, Thomsen LL, Brett S, Gerard C, Lipp M, Lanzavecchia A, Sallusto F (2004) Induced recruitment of NK cells to lymph nodes provides IFN-gamma for T(H)1 priming. Nat Immunol 5(12):1260–1265. doi:10.1038/ni1138
Steimle V, Siegrist CA, Mottet A, Lisowska-Grospierre B, Mach B (1994) Regulation of MHC class II expression by interferon-gamma mediated by the transactivator gene CIITA. Science 265(5168):106–109
Sijts A, Sun Y, Janek K, Kral S, Paschen A, Schadendorf D, Kloetzel PM (2002) The role of the proteasome activator PA28 in MHC class I antigen processing. Mol Immunol 39(3–4):165–169
Snapper CM, Paul WE (1987) Interferon-gamma and B cell stimulatory factor-1 reciprocally regulate Ig isotype production. Science 236(4804):944–947
Acknowledgments
We thank Medjaden Bioscience Limited for assisting in the preparation of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
All authors declared no conflict of interests involved.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, H., Zhao, L., Jiang, Z. et al. Dynamic changes in the numbers of different subsets of peripheral blood NK cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus following classic therapy. Clin Rheumatol 33, 1603–1610 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-014-2712-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-014-2712-1