Abstract
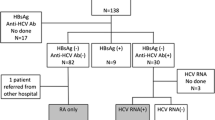
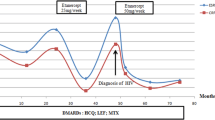
An understanding of the cytokine cascade in a rheumatoid joint has led to the development of new therapeutic options, including drugs targeting tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α). The safety profile of these agents in patients with hepatitis-induced liver disease, however, remains a concern because of risks associated with immune suppression. To examine the effect of three different TNF-α antagonists, infliximab, etanercept, and adalimumab, on serum transaminases and hepatitis viral load in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and concurrent hepatitis B (HBV) or hepatitis C (HCV). Medical records of 11 patients with diagnosis of RA and documented seropositivity for hepatitis B or hepatitis C were retrospectively reviewed for worsening of hepatic inflammation and viral proliferation as measured by a rise in aspartate aminotransferase (AST) or alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and viral load while using these agents. Three patients had RA with concurrent chronic HBV and eight patients had RA with concurrent chronic HCV. Seven patients remained on a single anti-TNF-α agent and four patients switched to a second anti-TNF-α agent due to treatment failure. Two patients showed a transient elevation in AST and/or ALT from normal, but in all 11 patients, AST and ALT levels were within one time the upper range of normal at the conclusion of the study. No significant increase in viral load was seen except one patient who showed a fourfold increase from baseline. Our case series supports results obtained from previous studies examining the safety of anti-TNF-α agents in patients with underlying hepatic disease. Use of these agents in patients with HBV or HCV may be associated with a transient transaminitis but appears to be safe overall. In both groups, frequent monitoring of serum transaminase levels and viral load is essential.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Helmick CG, Felson DT, Lawrence RC, Gabriel S, Hirsch R, Kwoh CK, Liang MH, Kremers HM, Mayes MD, Merkel PA, Pillemer SR, Reveille JD, Stone JH, National Arthritis Data Workgroup (2008) Estimates of the prevalence of arthritis and other rheumatic conditions in the United States. Arthritis Rheum 58(1):15–25
Olsen NJ, Stein CM (2004) New drugs for rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 350:2167–2179
Scott DL, Kingsley GH (2006) Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors for rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 355:704–712
Mok MY, Ng WL, Yuen MF, Wong RW, Lau CS (2000) Safety of disease modifying anti-rheumatic agents in rheumatoid arthritis patients with chronic viral hepatitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 18:363–368
Kallinowski B, Haseroth K, Marinos G, Hanck C, Stremmel W, Theilmann L, Singer MV, Rossol S (1998) Induction of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor type p55 and p75 in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. Clin Exp Immunol 111:269–277
Monsalve-DeCastillo F, Romero TA, Estevez J, Costa LL, Atencio R, Porto L, Callejas D (2002) Concentrations of cytokines, soluble interleukin-2 receptor, and soluble CD30 in sera of patients with hepatitis B virus infection during acute and convalescent phases. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 9:1372–1375
Zylberberg H, Rimaniol AC, Pol S, Masson A, D Groote D, Berthelot P, Bach JF, Brechot C, Zavala F (1999) Soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors in chronic hepatitis C: a correlation with histological fibrosis and activity. J Hepatol 30:185–191
Calabrese LH, Zein N, Vassilopoulos D (2004) Safety of antitumour necrosis factor (anti-TNF) therapy in patients with chronic viral infections: hepatitis C, hepatitis B and HIV infection. Ann Rheum Dis 63:18–24
Aslanidis S, Vassiliadis T, Pyrpasopoulou A, Douloumpakas I, Zamboulis C (2007) Inhibition of TNF-α does not induce viral reactivation in patients with chronic hepatitis C infection: two cases. Clin Rheumatol 26:261–264
Carroll MB, Bond MI (2008) Use of tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors in patients with chronic hepatitis B infection. Semin Arthritis Rheum 38:208–217
Michel M, Duvoux C, Hezode C, Cherqui D (2003) Fulminant hepatitis after Infliximab in a patient with hepatitis B virus treated for an adult onset Still's disease. J Rheumatol 30:1624–1625
Millonig G, Kern M, Ludwiczek O, Nachbaur K, Vogel W (2006) Subfulminant hepatitis B after infliximab in Crohn's disease: need for HBV-screening? World J Gastroenterol 12:974–976
Parke FA, Reveille JD (2004) Anti-tumor necrosis factor agents for rheumatoid arthritis in the setting of chronic hepatitis C infection. Arthritis Rheum 51:800–804
Peterson JR, Hsu FC, Simkin PA, Wener MH (2003) Effect of tumour necrosis factor alpha antagonists on serum transaminases and viraemia in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and chronic hepatitis C infection. Ann Rheum Dis 62:1078–1082
Roux CH, Brocq O, Breuil V, Albert C, Euller-Ziegler L (2006) Safety of anti-TNF-α therapy in rheumatoid arthritis and spondyloarthropathies with concurrent B or C chronic hepatitis. Rheumatology 45:1294–1297
Ferri C, Ferraccioli G, Ferrari D, Galeazzi M, Lapadula G, Montecucco C, Triolo G, Valentini G, Valesini G (2008) Safety of anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and chronic hepatitis C virus infection. J Rheumatol 35:1944–1949
Disclosures
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Kaur, P.P., Chan, V. et al. Use of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) antagonists infliximab, etanercept, and adalimumab in patients with concurrent rheumatoid arthritis and hepatitis B or hepatitis C: a retrospective record review of 11 patients. Clin Rheumatol 28, 787–791 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-009-1149-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-009-1149-4