Abstract
The Xiangjiaba (XJB) hydropower station is the most downstream dam among the cascade hydropower projects in the lower reach of the Jinsha River. Reservoir-induced seismicity (RIS) has been detected in the XJB region since the initiation of the reservoir impoundment in October 2012. This study investigates the correlations between the spatiotemporal evolution of seismicity and the impoundment process using regional permanent network data in the XJB area. Various statistical parameters, including seismic b-values, are estimated to identify the typical stages of earthquake occurrence from January 2009 to May 2022, showing a temporal correlation with reservoir water levels. The epidemic-type aftershock sequence (ETAS) model reveals that the proportion of the seismicity conforming to Omori’s law is higher than that before impoundment, indicating a tectonic influence on RIS. Notably, major seismic clusters recognized via the double-difference location method demonstrate a spatiotemporal migration corresponding to the impoundment. Focal solutions for \(M3.0\) earthquakes are obtained utilizing the full moment tensor inversion, presenting a dominantly strike-slip mechanism inconsistent with surrounding faults. The distribution of their relocated aftershocks implies an unmapped 5-km-long fault with striking S30\(^{\circ }\)E-S10\(^{\circ }\)E and dipping \(\sim 80^{\circ }\) to the west. Considering geological context, we propose that shallow karst structures probably facilitate hydraulic channel development and effective stress reduction for the inferred fault, thereby inducing earthquakes due to fault dislocation. This study strengthens the understanding of RIS occurrence with artificial impoundment process and signifies that seismicity in the tail area of the XJB reservoir still warrants attention.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
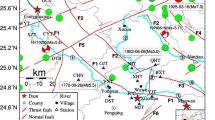
The datasets in Fig. 1 incorporate block boundary data from Zhang et al. (2005a), GPS data from Wang and Shen (2020) with a 70% confidence error ellipse in the legend, focal mechanisms of \(M > 3\) earthquakes from Guo et al. (2022b) and gas reservoir outlines modified from Lei et al. (2020). The Red lines in Fig. 1 show the azimuth of the maximum horizontal stress (https://www.world-stress-map.org/). The water level data in Fig. 2 are modified from Yang et al. (2019b). The 1:50000 geological data in Fig. 8 are sourced from https://www.ngac.cn/. The precise relocation catalog and waveform data of the three M3 earthquakes will be made available on request from the first author.
Change history
01 April 2024
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-024-03656-3
References
Carder DS (1945) Seismic investigations in the boulder dam area, 1940–1944, and the influence of reservoir loading on local earthquake activity. Bull Seismol Soc Am 35(4):175–192. https://doi.org/10.1785/BSSA0350040175
Chen R, Zhu J, Li S et al (2023) Characteristics and mechanisms of human-induced earthquakes in China from the QuakeQuake database. Geol J 58(5):2099–2131. https://doi.org/10.1002/gj.4713
Cui Y, Deng J, Hu W et al (2021) 36Cl exposure dating of the Mahu Giant landslide (Sichuan Province, China). Eng Geol 285(6):106039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106039
Diao G, Wang Y, Feng X et al (2014) Analysis of characteristics of focal mechanism in reservoir head region of Xiluodu Reservoir after impoundment. Seismol Geol 36(3):644–657. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2014.03.008
Dong S, Li L, Zhao L et al (2022) Seismic evidence for fluid-driven pore pressure increase and its links with induced seismicity in the Xinfengjiang Reservoir, South China. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 127:e2021JB023548. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021JB023548
Feng X, Yue X, Wang Y et al (2015a) Discussion on genesis of induced earthquake based on focal mechanism in Xiangjiaba Reservoir region. Seismol Geol 37(2):565–575. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2015.02.018
Feng Z, Cheng W, Diao G et al (2015b) Seismicity of the Xiangjiaba Reservoir after impoundment. Earthq Res China 32(2):319–328. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-4683.2015.02.016
Foulger GR, Wilson MP, Gluyas JG et al (2018) Global review of human-induced earthquakes. Earth Sci Rev 178:438–514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.07.008
Ge S, Liu M, Lu N et al (2009) Did the Zipingpu Reservoir trigger the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake? Geophys Res Lett 36(20). https://doi.org/10.1029/2009GL040349
Gough D, Gough W (1970) Load-induced earthquakes at lake Kariba-II. Geophys J Int 21(1):79–101. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.1970.tb01768.x
Guo W, Zhao C, Zuo K et al (2022a) Characteristics of seismicity before and after impoundment of Baihetan Dam in the lower reaches of Jinsha River. Chin J Geophys 65(12):4659–4671. https://doi.org/10.6038/cjg2022Q0119
Guo X, Jiang C, Han L et al (2022b) Focal mechanism data set in Chinese mainland and its adjacent area (2009-2021). https://data.earthquake.cn
Gupta HK (2022a) Artificial water reservoir-triggered seismicity (RTS): most prominent anthropogenic seismicity. Surv Geophys 43(2):619–659. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10712-021-09675-z
Gupta HK (2022b) Koyna, India: a very prominent site of artificial water reservoir-triggered seismicity. J Earth Syst Sci 131(1):30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-021-01780-2
Gupta HK, Rastogi B, Narain H (1972) Some discriminatory characteristics of earthquakes near the Kariba, Kremasta, and Koyna artificial lakes. Bull Seismol Soc Am 62(2):493–507. https://doi.org/10.1785/BSSA0620020493
Heidbach O, Rajabi M, Cui X et al (2018) The world stress map database release 2016: crustal stress pattern across scales. Tectonophysics 744(0040–1951):484–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2018.07.007
Keranen KM, Weingarten M, Abers GA et al (2014) Sharp increase in central Oklahoma seismicity since 2008 induced by massive wastewater injection. Science 345(6195):448–451. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1255802
Lei X (2011) Possible roles of the Zipingpu Reservoir in triggering the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake. J Asian Earth Sci 40(4):844–854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.05.004
Lei X, Satoh T (2007) Indicators of critical point behavior prior to rock failure inferred from pre-failure damage. Tectonophysics 431(1):97–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2006.04.023
Lei X, Xie C, Fu B (2011) Remotely triggered seismicity in Yunnan, Southwestern China, following the 2004 \(m_{w}9.3\) Sumatra earthquake. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 116:B08303. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011JB008245
Lei X, Ma S, Chen W et al (2013) A detailed view of the injection-induced seismicity in a natural gas reservoir in Zigong, Southwestern Sichuan basin, China. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 118(8):4296–4311. https://doi.org/10.1002/jgrb.50310
Lei X, Su J, Wang Z (2020) Growing seismicity in the Sichuan basin and its association with industrial activities. Sci China Earth Sci 63:1633–1660. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-020-9646-x
Li N, Zhang P, Chen Y et al (2003) Fatigue properties of cracked, saturated and frozen sandstone samples under cyclic loading. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 40(1):145–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1365-1609(02)00111-9
Li T, Cai MF, Cai M (2007) A review of mining-induced seismicity in China. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 44(8):1149–1171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2007.06.002
Liu A, Zheng L, Deng J et al (2018) Landslide susceptibility of the Xiangjiaba Reservoir area associated with the Yaziba fault. Bull Eng Geol Environ 77:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1053-0
Marsan D, Lengline O (2008) Extending earthquakes’ reach through cascading. Science 319(5866):1076–1079. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1148783
Michas G, Pavlou K, Vallianatos F et al (2020) Correlation between seismicity and water level fluctuations in the Polyphyto Dam, North Greece. Pure Appl Geophys 177:3851–3870. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-020-02465-5
Ogata Y (1992) Detection of precursory relative quiescence before great earthquakes through a statistical model. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 97(B13):19845–19871. https://doi.org/10.1029/92JB00708
Papazachos B (1974) On the relation between certain artificial lakes and the associated seismic sequences. Eng Geol 8(1–2):39–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-7952(74)90010-6
Qiao L, Yao H, Lai YC et al (2018) Crustal structure of Southwest China and Northern Vietnam from ambient noise tomography: implication for the large-scale material transport model in SE Tibet. Tectonics 37:1492–1506. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018TC004957
Rong H, Lupei Z, John E et al (2018) Seismic and geologic evidence of water-induced earthquakes in the three gorges reservoir region of China. Geophys Res Lett 45:5929–5936. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018GL077639
Royden LH, Burchfiel BC, King RW et al (1997) Surface deformation and lower crustal flow in eastern Tibet. Science 276(5313):788–790. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.276.5313.788
Sebastian H, Ogata Y (2005) Detecting fluid signals in seismicity data through statistical earthquake modeling. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 110(B5):B05S07. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004JB003247
Shashidhar D, Mallika K, Gahalaut K et al (2019) A new earthquake sequence at Koyna-Warna, India, and its implication for migration of the reservoir triggered seismicity short note. Bull Seismol Soc Am 109(2):827–831. https://doi.org/10.1785/0120180295
Simpson DW (1976) Seismicity changes associated with reservoir loading. Eng Geol 10(2–4):123–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-7952(76)90016-8
Stein S, Wiens DA, Fujita K (1982) The 1966 Kremasta Reservoir earthquake sequence. Earth Planet Sci Lett 59(1):49–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-821X(82)90117-0
Tao W, Masterlark T, Shen ZK et al (2015) Impoundment of the Zipingpu Reservoir and triggering of the 2008 mw 7.9 Wenchuan earthquake, China. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 120(10):7033–7047. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014JB011766
Waldhauser F, Ellsworth W (2000) A double-difference earthquake location algorithm: method and application to the Northern Hayward fault, California. Bull Seismol Soc Am 90(6):1353–1368. https://doi.org/10.1785/0120000006
Wang J, Walter BA, Yao F et al (2022) Geodar: georeferenced global dams and reservoirs dataset for bridging attributes and geolocations. Earth Syst Sci Data 14(4):1869–1899. https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-14-1869-2022
Wang M, Shen ZK (2020) Present-day crustal deformation of continental China derived from GPS and its tectonic implications. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 125(2):e2019JB018774. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JB018774
Wells DL, Coppersmith KJ (1994) New empirical relationships among magnitude, rupture length, rupture width, rupture area, and surface displacement. Bull Seismol Soc Am 84(4):974–1002. https://doi.org/10.1785/BSSA0840040974
Wen X, Du F, Yi G et al (2013) Earthquake potential of the Zhaotong and Lianfeng fault zones of the Eastern Sichuan-Yunnan border region. Chin J Geophys 56(10):3361–3372. https://doi.org/10.6038/cjg20131012
Wessel P, Smith WHF, Scharroo R et al (2013) Generic mapping tools: improved version released. Eos Trans Am Geophys Union 94(45):409–410. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013EO450001
Wiemer S, Wyss M (2000) Minimum magnitude of completeness in earthquake catalogs: examples from Alaska, the Western United States, and Japan. Bull Seismol Soc Am 99(4):859–869. https://doi.org/10.1785/0119990114
Wilson MP, Foulger GR, Gluyas JG et al (2017) Hiquake: the human-induced earthquake database. Seismol Res Lett 88(6):1560–1565. https://doi.org/10.1785/0220170112
Xu X, Jiang G, Yu G et al (2014) Discussion on seismogenic fault of the Ludian \(m_{s}\)6.5 earthquake and its tectonic attribution. Chin J Geophys 57(9):3060–3068. https://doi.org/10.6038/cjg20140931
Xu X, Chen G, Wang Q et al (2017) Discussion on seismogenic structure of Jiuzhaigou earthquake and its implication for current strain state in the Southeastern Ginghai-Tibet Plateau. Chin J Geophys 60(10):4018–4026. https://doi.org/10.6038/cjg20171028
Yang L, Li B, Chang T (2019a) Research and application of reservoir induced earthquakes focal depth checking method. J Geod Geodyn 39(11):1194–1197. https://doi.org/10.14075/j.jgg.2019.11.018
Yang L, Li B, Chang T (2019b) Seismicity characteristics of Xiangjiaba Reservoir region before and after the impoundment. J Geod Geodyn 39(9):919–923. https://doi.org/10.14075/j.jgg.2019.09.009
Yao Y, Wang Q, Liao W et al (2017) Influences of the three gorges project on seismic activities in the reservoir area. Sci Bull 62(15):1089–1098. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2017.07.014
Yin G, Zhang H, Shi Y (2023) Cascade effects of triggered earthquakes of cascade dams: taking Xiluodu and Xiangjiaba Reservoirs as examples. Chin J Geophys 66(6):2470–2488. https://doi.org/10.6038/cjg2022Q0063
Yin X, Jiang C, Zhai H et al (2021) Review of induced seismicity and disaster risk control in dry hot rock resource development worldwide. Chin J Geophys 64(11):3817–3836. https://doi.org/10.6038/cjg2021O0448
Zhang G, Ma H, Wang H et al (2005a) Boundaries between active-tectonic blocks and strong earthquakes in China mainland. Chin J Geophys 48(3):662–671. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1674-7240.2004.07.001
Zhang L, Lei X, Liao W et al (2019) Statistical parameters of seismicity induced by the impoundment of the three gorges reservoir, central China. Tectonophysics 751:13–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2018.12.022
Zhang M, Ge S, Yang Q et al (2021) Impoundment-associated hydro-mechanical changes and regional seismicity near the Xiluodu Reservoir, Southwestern China. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 126(9):e2020JB021590. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020JB021590
Zhang S, Nie G, Liu X et al (2005b) Kinematical and structural patterns of Yingjing-Mabian-Yanjin fault zone, southeast of Tibetan Plateau, and its segmentation from earthquakes. Seismol Geol 27(2):221–233. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2005.02.005
Zhao C, Zhao C, Lei H et al (2022) Seismic activities before and after the impoundment of the Xiangjiaba and Xiluodu Reservoirs in the lower Jinsha river. Earthq Sci 35(5):355–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eqs.2022.10.003
Zhou H, Nie D, Li X (2012) On influence analysis after impoundment of Xiangjiaba hydropower station to great gorge hot spring. J Hunan Univ Sci Technol (Nat Sci Edition) 27(1):55–62. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1672-9102.2012.01.011
Zhou L, Zhao C, Zhang M et al (2021) Machine-learning-based earthquake locations reveal the seismogenesis of the 2020 \(m_{w}5.0\) Qiaojia, Yunnan earthquake. Geophys J Int 228(3):1637–1647. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggab420
Zhu L, Ben-Zion Y (2013) Parametrization of general seismic potency and moment tensors for source inversion of seismic waveform data. Geophys J Int 194(2):839–843. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggt137
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. Xinglin Lei for his provision and kind guidance in the use of GeoTaos_map software (http://bemlar.ism.ac.jp/lxl/), which was utilized to conduct ETAS modeling, HypoDD relocation and moment tensor inversion of this study. The earthquake catalog and phase datasets are sourced from the China Earthquake Data Center (https://data.earthquake.cn/). Waveform data of regional permanent stations for moment tensor inversion in this study are provided by the Earthquake Administration of Sichuan Province. The maps and plots were created using the Generic Mapping Tools (Wessel et al. 2013) and GeoTaos_map and finished with the software CorelDRAW 2021.
Funding
The study was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province of China (NSFSC) grants No.42007272, No.2023NSFSC0384, No.U19A2098, No.2019QZKK0905.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised: Originally, the article was published with error in Funding. A funding source numbered 2023NSFSC0384 was misstated. It should be corrected as Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province of China (NSFSC) instead of National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, Z., Chen, F., Deng, J. et al. Statistical investigation of induced seismicity associated with the impoundment of the Xiangjiaba Reservoir, Southwestern China. Bull Eng Geol Environ 83, 106 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-024-03562-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-024-03562-8