Abstract
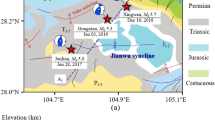
This paper discusses the spatiotemporal pattern of seismicity during the impoundment of the Xiaowan reservoir area, Yunnan Province, China, in the period from May 21, 2005 to December 31, 2012. The filling operations took place in five phases, starting on December 16, 2008. A notable increase in seismicity was only observed during the third filling phase, starting on July 15, 2010. Seismicity increase was mostly localized within two clusters, located to the northwest and west of the dam. Seismicity rates in these clusters showed a significant correlation with the water level increase, with the seismicity starting to increase when the water level reached the area covered by the two clusters, which additionally support they were induced by the reservoir impoundment. We further investigate source parameters for 44 pre-impoundment earthquakes and 164 post-impoundment earthquakes with M L ≥ 2.0. Corner frequencies, seismic moments, and stress drops are obtained based on the spectral analysis of regional data, upon corrections for geometrical spreading, frequency-dependent Q, and site effects. Our results show that during the post-impoundment phase reservoir-induced seismicity (RIS) inside the two clusters have systematically lower stress drops with respect to those occurring at further distance, and surrounding natural tectonic earthquakes, by a factor of about two to three times, suggesting a possible source characteristic that differentiate reservoir-induced seismicity from natural tectonic earthquakes. However, temporal stress drops changes within the clusters cannot be resolved. To compare the difference in stress drop between RIS and natural tectonic earthquakes, not only the difference in stress drop due to different region, but also the temporal change of background stress level even in the same region should be taken into account.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abercrombie RE (1995) Earthquake source scaling relationships from −1 to 5 M L using seismograms recorded at 2.5 km depth. J Geophys Res 100:24,015–24,036
Abercrombie RE, Leary P (1993) Source parameters of small earthquakes recorded at 2.5 km depth, Cajon Pass Southern California: Implications for earthquake scaling. Geophys Res Lett 20:1511–1514
Allmann BP, Shearer PM (2009) Global variations of stress drop for moderate to large earthquakes. J Geophys Res 114:B01310. doi:10.1029/2008JB005821
Andrews DJ (1986) Objective determination of source parameters and similarity of earthquakes of different size, in Earthquake Source Mechanics, S. Das, J. Boatwright, and C. H. Sholtz (Editors), Geophys. Monogr. Ser., Vol. 37, American Geophysical Union, Washington, DC, 259–268
Archuleta RJ, Cranswick E, Mueller C, Spudich P (1982) Source parameters of the 1980 Mammoth Lakes, California, earthquake sequence. J Geophys Res 87:4595–4607
Atkinson GM, Mereu RF (1992) The shape of ground motion attenuation curves in Southeastern Canada. Bull Seismol Soc Am 82:2014–2031
Bell ML, Nur A (1978) Strength changes due to reservoir-induced pore pressure and application to Lake Oroville. J Geophys Res 83:4469–4483
Boatwright J (1994) Regional propagation characteristics and source parameters of earthquakes in northeastern North America. Bull Seismol Soc Am 84:1–15
Brune JN (1970) Tectonic stress and the spectra of seismic waves from earthquakes. J Geophys Res 75:4997–5009
Brune JN (1971) Correction. J Geophys Res 76:5002
Carder DS (1945) Seismic investigations in the Boulder Dam area, 1940–1944, and the influence of reservoir loading on earthquake activity. Bull Seismol Soc Am 35:175–192
Cesca S, Dost B, Oth A (2013a) Preface to the special issue “Triggered and induced seismicity: probabilities and discrimination”. J Seismol 17:1–4
Cesca S, Rohr A, Dahm T (2013b) Discrimination of induced seismicity by full moment tensor inversion and decomposition. J Seismol 17:147–163
Chael E (1987) Spectral scaling of earthquakes in the Miramichi region of New Brunswick. Bull Seismol Soc Am 77:347–365
Chen LY, Talwani P (2001) Mechanism of initial seismicity following impoundment of the Monticello reservoir, South Carolina. Bull Seismol Soc Am 91:1582–1594
Cheng WZ (2013) The reservoir induced earthquake problem in the high seismicity region. Recent Dev World Seismol 4:10–18 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Dahm T, Becker D, Bischoff M, Cesca S, Dost B, Fritschen R, Hainzl S, Klose CD, Kühn D, Lasocki S, Meier T, Ohrnberger M, Rivalta E, Wegler U, Husen S (2013) Recommendation for the discrimination of human-related and natural seismicity. J Seismol 17:197–202
Di Bona M, Rovelli A (1988) Effects of the bandwidth limitation on stress drops estimated from integrals of the ground motion. Bull Seismol Soc Am 78:1818–1825
El Hariri M, Abercrombie RA, Rowe CA, do Nascimento AF (2010) The role of fluids in triggering earthquakes: observations from reservoir induced seismicity in Brazil. Geophys J Int 181(3):1566–1574. doi:10.1111/j.1365-246X.2010.04554.x
Fehler MC, Phillips WS (1991) Simultaneous inversion for Q and source parameters of microearthquakes accompanying hydraulic fracturing in granitic rock. Bull Seismol Soc Am 81:553–575
Frankel A, Kanamori H (1983) Determination of rupture duration and stress drop for earthquakes in southern California. Bull Seismol Soc Am 73:1527–1551
Gibowicz SJ, Young RP, Talebi S, Rawlence DJ (1991) Source parameters of seismic events at the underground research laboratory in Manitoba, Canada: scaling relations for events with moment magnitude smaller than −2. Bull Seismol Soc Am 81:1157–1182
Gupta HK (1992) Reservoir-induced earthquakes, developments in geotechnical engineering. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Gupta HK (2002) A review of recent studies of triggered earthquakes by artificial water reservoirs with special emphasis on earthquakes in Koyna, India. Earth Sci Rev 58(3/4):279–310. doi:10.1016/S0012-8252(02)00063-6
Gupta HK, Rastogi BK, Narain H (1972a) Common features of the reservoir associated seismic activities. Bull Seismol Soc Am 62:481–492
Gupta HK, Rastogi BK, Narain H (1972b) Some discriminatory characteristics of earthquakes near the Kariba, Kremasta and Koyna artificial lakes. Bull Seismol Soc Am 62:493–507
Gutenberg B, Richter CF (1956) Magnitude and energy of earthquakes. Ann Geofis 9:1–15
Holland JH (1975) Adaptation in natural and artificial systems. University of Michigan Press, Ann Arbor, Michigan
Hough S (1996) Observational constraints on earthquake source scaling: understanding the limits in resolution. Tectonophysics 261:83–95
Hough SE (2014) Shaking from injection-induced earthquakes in the Central and Eastern United States. Bull Seismol Soc Am 104(5), doi:10.1785/0120140099
Hua W, Chen ZL, Zheng SH (2013a) Source parameters and scaling relations for reservoir induced seismicity in the Longtan reservoir area. Pure Appl Geophys 170:767–783
Hua W, Zheng SH, Yan CQ, Chen ZL (2013b) Attenuation, site effects and source parameters in the three Gorges reservoir area, China. Bull Seismol Soc Am 103:371–382
Humphrey J, Anderson J (1994) Seismic source parameters from the Guerrero subduction zone. Bull Seismol Soc Am 84:1754–1769
Iwata T, Irikura K (1988) Source parameters of the 1983 Japan earthquake sequence. J Phys Earth 36:155–184
Kanamori H, Rivera L (2004) Static and dynamic scaling relations for earthquakes and their implications for rupture speed and stress drop. Bull Seismol Soc Am 94:314–319
Li YL, Zhao XY, Fu H (2012) Research on variation of wave velocity ratio before and after water storage for Xiaowan reservoir. J Seismol Res 35:464–470 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Mandal P, Rastogi BK, Sarma CSP (1998) Source parameters of Koyna earthquakes, India. Bull Seismol Soc Am 88:833–842
Mao YP, Wang YL, Li CC (2004) Seismo-geological ambiance analyses of reservoir induced earthquake in Xiaowan area. J Seismol Res 27:339–343 (in Chinese with English abstract)
McGarr A (1993) Factors influencing the strong ground motion from mining-induced tremors. In: Young RP (ed) Rockbursts and seismicity in mines. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 3–12
Mori J, Frankel A (1990) Source parameters of aftershocks of the 1986 North Palm Springs earthquake. Bull Seismol Soc Am 80:278–295
Moya CA, Aguirre J, Irikura K (2000) Inversion of source parameters and site effects from strong ground motion records using genetic algorithms. Bull Seismol Soc Am 90:977–992
Oprsal I, Eisner L (2014) Cross-correlation—an objective tool to indicate induced seismicity. Geophys J Int 196:1536–1543
Prieto GA, Shearer PM, Vernon FL, Kilb D (2004) Earthquake source scaling and self-similarity estimation from stacking P and S spectra. J Geophys Res 109, B08310. doi:10.1029/2004JB003084
Ren JW (1993) On the fault structure conditions of Xiaowan reservoir in Lancang river area that induced earthquakes. Inland Earthq 7:30–37 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Roeloffs EA (1988) Fault stability changes induced beneath a reservoir with cyclic variations in water level. J Geophys Res 93:2107–2124
Shearer PM (1999) Introduction to seismology. Cambridge University Press, New York
Shearer PM, Prieto GA, Hauksson E (2006) Comprehensive analysis of earthquake source spectra in southern California. J Geophys Res 111, B06303. doi:10.1029/2005JB003979
Simpson DW, Leith WS, Scholz CH (1988) Two types of reservoir-induced seismicity. Bull Seismol Soc Am 78:2025–2040
Snoke JA (1987) Stable determinations of (Brune) stress drops. Bull Seismol Soc Am 77:530–538
Snow DT (1972) Geodynamics of seismic reservoirs. Proc Sym Percolation Through Fissured Rock Stuttgart Ges Erd und Grundbau T2J: 1–19
Stabile TA, Giocoli A, Lapenna V, Perrone A, Piscitelli S, Telesca L (2014) Evidences of low-magnitude continued reservoir-induced seismicity associated with the Pertusillo artificial lake (southern Italy). Bull Seismol Soc Am 104(4):1820–1828. doi:10.1785/0120130333
Stork AL, Ito H (2004) Source parameter scaling for small earthquakes observed at the western Nagano 800-m-deep borehole, central Japan. Bull Seismol Soc Am 94:1781–1794
Tajima R, Tajima F (2007) Seismic scaling relations and aftershock activity from the sequences of the 2004 mid Niigata and the 2005 west off Fukuoka earthquakes (M w 6.6) in Japan. J Geophys Res 112, B10302. doi:10.1029/2007JB004941
Talwani P (1997a) On the nature of reservoir-induced seismicity. Pure Appl Geophys 150:473–492
Talwani P (1997b) Seismotectonics of the Koyna-Warna Area, India. Pure Appl Geophys 150:511–550
Tomic J, Abercrombie RE, do Nascimento AF (2009) Source parameters and rupture velocity of small M ≤ 2.1 reservoir induced earthquakes. Geophys J Int 179:1013–1023
Wessel P, Smith WHF (1998) New, improved version of generic mapping tools released. EOS Trans Am Geophys Union 79:579
Wu CD, Fu H, Tang SE (2007) Non-elasticity attenuation of seismic wave and site response near Xiaowan reservoir. Earthq Res China 23:259–266 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wu CD, Fu H, Zhao XY (2010) Primary study on source parameters near Xiaowan reservoir. J Seismol Res 33:50–54 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yamada T, Mori JJ, Ide S, Kawakata H, Iio Y, Ogasawara H (2005) Radiation efficiency and apparent stress of small earthquakes in a South African gold mine. J Geophys Res 110(B01305):18. doi:10.1029/2004JB003221
Zhao CP, Chen ZL, Hua W, Wang QC, Li ZX, Zheng SH (2011) Study on source parameters of small to moderate earthquakes in the main seismic active regions, China mainland. Chin J Geophys 54:1478–1489 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Acknowledgments
The reviews and suggestions by two anonymous reviewers for improving the manuscript are greatly appreciated. We are also thankful to editor in chief Mariano Garcia-Fernandez for editing the paper. This research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation (41174051) and the Special Research Project in Earthquake Science, China (201208003). We thank Earthquake Administration of Yunnan Province for providing us these data used in this paper. All of the maps were plotted using Generic Mapping Tools (Wessel and Smith 1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hua, W., Fu, H., Chen, Z. et al. Reservoir-induced seismicity in high seismicity region—a case study of the Xiaowan reservoir in Yunnan province, China. J Seismol 19, 567–584 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-015-9482-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-015-9482-3