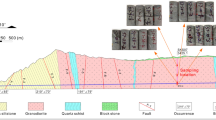
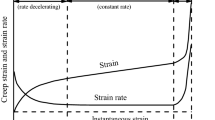
Abstract
The local fracture and instability of granite in deep caverns have obvious time-dependent behaviors. In the present study, a coupled mechanism of granite nonlinear creep damage and strain softening was proposed, based on deep mine roadway engineering as the research background. Laboratory experiments were used to investigate the strain-softening and creep damage characteristics of granite, and the model parameters were then obtained by nonlinear fitting. A nonlinear Burgers model and viscoplastic strain-softening model were connected in series to construct a coupled model of granite nonlinear creep damage and strain softening, and the numerical solution was then obtained using the FLAC3D software. The results show that the accelerated creep curve calculated by the creep damage model was in good agreement with the experimental results. The proposed unified variable for granite strength damage and attenuation can characterize the evolution law of rock creep damage and strength attenuation. The coupled model was used to analyze the local fracture characteristics of surrounding rock in a deep cavern, and the calculation results were similar to the findings of practical engineering. The proposed coupled model is suitable for analyzing the deformation and fracture instability of surrounding rock in deep hard rock cavern engineering.



















Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The data and material used to support the findings of this study cannot be shared at this time because the data also form part of an ongoing study.
Code availability
The code used to support the findings of this study cannot be shared at this time because the code also forms part of an ongoing study.
References
Ahmed Z, Wang SH, Hashmi MZ, Zhang ZS, Zhu CJ (2020) Causes, characterization, damage models, and constitutive modes for rock damage analysis: a review. Arab J Geosci 13(16):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05755-3
Alejano LR, Alonso E, Rodriguez-Dono A, Fernandez-Manin G (2010) Application of the convergence-confinement method to tunnels in rock masses exhibiting Hoek-Brown strain-softening behaviour. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 47:150–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2009.07.008
Alejano LR, Rodríguez-Dono A, Veiga M (2012) Plastic radii and longitudinal deformation profiles of tunnels excavated in strain-softening rock masses. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 30:169–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2012.02.017
Bui TA, Wong H, Deleruyelle F, Xie LZ, Tran DT (2017) A thermodynamically consistent model accounting for viscoplastic creep and anisotropic damage in unsaturated rocks. Int J Solids Struct 117:26–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2017.04.015
Cao P, Wen Y, Wang Y, Yuan H, Yuan B (2016) Study on nonlinear damage creep constitutive model for high-stress soft rock. Environ Earth Sci 75:900. https://doi.org/10.1007/x12665-016-5699-x
Darabi MK, Al-Rub RK, Little DN (2012) A continuum damage mechanics framework for modeling micro-damage healing. Int J Solids Struct 49:492–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2011.10.017
Feng WL, Qiao CS, Niu SJ (2019) Study on sandstone creep properties of Jushan Mine affected by degree of damage and confining pressure. Bull Eng Geol Environ 79(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01615-x
Feng WL, Qiao CS, Wang T, Yu MY, Niu SJ, Jia ZQ (2020) Strain-softening composite damage model of rock under thermal environment. Bull Eng Geol Environ 79:4321–4333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-020-01808-9
Feng XT, Pei SF, Jiang Q, Zhou YY, Li SJ, Yao ZB (2017) Deep fracturing of the hard rock surrounding a large underground cavern subjected to high geostress: in situ observation and mechanism analysis. Rock Mech Rock Eng 50:2155–2175. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-017-1220-4
Golshani A, Oda M, Okui Y, Takemura T, Munkhtogoo E (2007) Numerical simulation of the excavation damaged zone around an opening in brittle rock. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 44:835–845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2006.12.005
Hoek E, Brown ET (1997) Practical estimates of rock mass strength. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 34:1165–1186. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1365-1609(97)80069-X
Itasca (2012) FLAC3D (Fast Lagrangian Analysis of Continua in 3 Dimensions) Version 5.0. Itasca Consulting Group, Minneapolis, MN
Kabwe E, Karakus M, Chanda EK (2020) Isotropic damage constitutive model for time-dependent behaviour of tunnels in squeezing ground. Comput Geotech 127:103738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2020.103738
Li G, Ma F, Liu G, Zhao H, Guo J (2019) A strain-softening constitutive model of heterogeneous rock mass considering statistical damage and its application in numerical modeling of deep roadways. Sustainability 11:2399. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11082399
Li SC, Wang Q, Wang HT, Jiang B, Wang DC, Zhang B, Li Y, Ruan GQ (2015) Model test study on surrounding rock deformation and failure mechanisms of deep roadways with thick top coal. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 47:52–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2014.12.013
Li X, Cao WG, Su YH (2012) A statistical damage constitutive model for softening behavior of rocks. Eng Geol 143:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2012.05.005
Oge IF (2021) Revisiting the assessment of squeezing condition and energy absorption of flexible supports: a mine development case. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2020.103712
She CX (2009) Research on nonlinear viscoelasto-plastic creep model of rock. Chinese J Rock Mech Eng 28:2006–2011 ((in Chinese))
Shen P, Tang H, Ning Y, Xia D (2019) A damage mechanics based on the constitutive model for strain-softening rocks. Eng Fract Mech 216:106521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2019.106521
Song F, Rodriguez-Dono A, Olivella S, Zhong Z (2020) Analysis and modelling of longitudinal deformation profiles of tunnels excavated in strain-softening time-dependent rock masses. Comput Geotech 125:103643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2020.103643
Sterpi D, Gioda G (2009) Visco-plastic behaviour around advancing tunnels in squeezing rock. Rock Mech Rock Eng 42:319–339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-007-0137-8
Sun C, Ao Y, Wang L (2020) The research on strain-softening characteristics and local fracture law of deep granite roadway. Complexity 2020:1064016. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/1064016
Takemura T, Oda M, Kirai H, Golshani A (2012) Microstructural based time-dependent failure mechanism and its relation to geological background. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 53:76–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2012.03.012
Wang X, Hu B, Tang H, Hu X, Wang J, Huang L (2016) A constitutive model of granite shear creep under moisture. J Earth Sci 27:677–685. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-016-0709-1
Wang ZL, Li YC, Wang JG (2007) A damage-softening statistical constitutive model considering rock residual strength. Comput Geosci 33:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2006.02.011
Wu X, Jiang Y, Guan Z (2018) A modified strain-softening model with multi-post-peak behaviours and its application in circular tunnel. Eng Geol 240:21–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.03.031
Xu GW, He C, Yan J, Ma GY (2019) A new transversely isotropic nonlinear creep model for layered phyllite and its application. Bull Eng Geol Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01462-w
Xu Y, Ren FY, Ahmed Z, Wang KY (2020) Mechanical and fatigue damage evolution properties of cracked sandstone under cyclic loading: damage evolution law of sandstone. Proceedings of the Pakistan Academy of Sciences: A. Physical and Computational Sciences 57(1):59–72. http://www.ppaspk.org/index.php/PPAS-A/article/view/53
Xu Y, Ren FY, Ahmed Z, Wang KY, Wang ZH (2021) Mechanical characteristics and damage evolution law of sandstone with prefabricated cracks under cyclic loading. Arab J Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05460-7
Xue Y, Mishra B, Gao D (2017) Using the relaxation test to study variation in the time-dependent property of rock and the consequent effect on time-dependent roof failure. Rock Mech Rock Eng 50:2521–2533. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-017-1232-0
Yang W, Zhang Q, Li S, Wang S (2014) Time-dependent behavior of diabase and a nonlinear creep model. Rock Mech Rock Eng 47:1211–1224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-013-0478-4
Zhang C, Wang Z, Wang Q (2015) Deformation and failure characteristics of the rock masses around deep underground caverns. Math Probl Eng 2015:230126. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/230126
Zhao XG, Cai M (2010) A mobilized dilation angle model for rocks. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 47:368–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2009.12.007
Zhao YL, Tang JZ, Fu CC, Wan W, Wang WJ, Luo SL (2016) Rheological test of separation between viscoelastic-plastic strains and creep damage model. Chinese J Rock Mech Eng 35(07):1297–1308. https://doi.org/10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2015.1178. (in Chinese)
Zhao YL, Wang YX, Wang WJ, Wan W, Tang JZ (2017) Modeling of non-linear rheological behavior of hard rock using triaxial rheological experiment. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 93:66–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2017.01.004
Zhu YG, Liu Q, Kang YS, Liu K (2011) Study of creep damage constitutive relation of granite considering thermal effect. Chinese J Rock Mech Eng 30:1882–1888 ((in Chinese))
Acknowledgements
We thank Esther Posner, PhD, and Sara J. Mason, MSc, ELS, from Liwen Bianji, Edanz Editing China (www.liwenbianji.cn/ac), for editing the English text of drafts of this manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program (grant number 2017YFC1503101), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 51704144), the Talent Project of Revitalizing Liaoning Funding Project (grant number XLYC1807107), and the Project supported by discipline innovation team of Liaoning Technical University (grant number LNTU20TD08).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation and laboratory tests were performed by CJ and YA. Data collection and theoretical analysis were performed by CS, LW, and JZ. The first draft of the manuscript was written by CS and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, C., Jin, C., Wang, L. et al. Creep damage characteristics and local fracture time effects of deep granite. Bull Eng Geol Environ 81, 79 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-02578-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-02578-2