Abstract
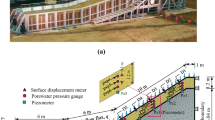
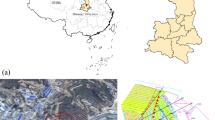
To investigate slope stability under alternating excavation and rainfall disturbance and to reveal the intrinsic mechanism of the slope stress diffusion process caused by stress-seepage coupling, a method consisting of separate simulation of the excavation stress field and rainfall seepage field and superposition analysis is proposed. Meanwhile, the distribution of the pore water pressure and transient saturation zone in the AK2 + 210 ~ AK2 + 610 section slope of a highway in Guangdong Province, China, is comprehensively analysed by calculating the rainfall seepage field during the excavation process. The effects of the rainfall seepage and slope stresses are further studied by applying the changing natural/saturated physical and mechanical parameters and pore water pressure values obtained by physical testing and parameter inversion. Moreover, the safety and stability of the highway slope during each stage is computed numerically using the strength reduction method, and the slope failure process, instability-inducing factors and failure mechanism are discussed in detail. The results indicate that the proposed separate simulation and superposition analysis method is effective and of considerable practical value in slope engineering. Additionally, a comprehensive slope stability treatment is suggested, which can be used as a reference for other slope projects experiencing alternating excavation and rainfall disturbance.























Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Available on reasonable request.
References
Bishop AW (1959) The principle of effective stress. Tecknisk Ukeblad 106(39):859–863
Bishop AW, Blight GE (1963) Some aspects of effective stress in saturated and unsaturated soil. Geotech 13(3):177–197
Fredlund D G (1998) Bringing unsaturated soil mechanics into engineering practice. Proceedings of the 2nd international conference on unsaturated soil 2(36):2-51
Fu CD, Sheng Q, Li G, Zhang ZP, Zhou YQ, Du YX (2020) Analysis of landslide stability under seismic action and subsequent rainfall: a case study on the Ganjiazhai giant landslide along the Zhaotong-Qiaojia road during the 2014 Ludian earthquake, Yunnan. China Bull Eng Geol Environ 79(10):5229–5248
Han H, Shi B, Zhang L (2021) Prediction of landslide sharp increase displacement by SVM with considering hysteresis of groundwater change. Eng Geol 280(2021):105876
Ishii Y, Ota K, Kuraoka S, Tsunaki R (2012) Evaluation of slope stability by finite element method using observed displacement of landslide. Landslides 9(3):335–348
Jiang ZM, Wu ZC, Feng SC, Zhong HY, Wang JY, Wang GY (2015) Limit equilibrium method for stability analysis of slope with transient saturated area. J Hydraul Eng 46(7):773–782
Jotisankasa A, Coop M, Ridley A (2009) The mechanical behaviour of an unsaturated compacted silty clay. Geotechnique 59(5):415–428
Kim Y, Jeong S, Kim J (2016) Coupled infiltration model of unsaturated porous media for steady rainfall. Soils Found 56(6):1071–1081
Li CD, Fu ZY, Wang Y, Tang HM, Yan JF, Gong WP, Yao WM, Criss RE (2019) Susceptibility of reservoir-induced landslides and strategies for increasing the slope stability in the Three gorges reservoir area: Zigui basin as an example. Eng Geol 261:105279
Lin F, Wu LZ, Huang RQ, Zhang H (2018) Formation and characteristics of the Xiaoba landslide in Fuquan, Guizhou. China Landslides 15(4):669–681
Li Q, Wang YM, Zhang KB, Yu H, Tao ZY (2020) Field investigation and numerical study of a siltstone slope instability induced by excavation and rainfall. Landslides 17(6):1485–1499
Liu JM, Qiu Y, Guo TT, Song WZ, Gu C (2020) Comparative experimental study on static shear strength and postcyclic strength of saturated silty clay. Rock Soil Mech 41(3):773–780
Liu JX, Yang C, Gan J, Liu Y, Wei L, Xie Q (2017) Stability analysis of road embankment slope subjected to rainfall considering runoff-unsaturated seepage and unsaturated fluid–solid coupling. Int J Civ Eng 15(6):865–876
Li ZQ, Xue YG, Li SC, Zhang LW, Wang D, Li B, Zhang W, Ning K, Zhu JY (2017) Deformation features and failure mechanism of steep rock slope under the mining activities and rainfall. J Mt Sci-Engl 14(1):31–45
Lu N, Sener-Kaya B, Wayllace A, Godt JW (2012) Analysis of rainfall-induced slope instability using a field of local factor of safety. Water Resour Res 48(9):9524
Nguyen VU (1984) Back calculations of slope failures by the secant method. Geotechnique 34(3):423–427
Oh S, Lu N (2015) Slope stability analysis under unsaturated conditions: case studies of rainfall-induced failure of cut slopes. Eng Geol 184:96–103
Potts DM, Zdravkovic L (1999) Finite element analysis in geotechnical engineering: theory. Thomas Telford, London, UK:72-73.
Qiu X, Jiang HB, Ou J (2020) Numerical analysis of formation conditions and evolution characteristics of transient saturation zone of a slope under rainfall conditions. J Hydraul Eng 51(12):1525–1535
Robinson JD, Vahedifard F, AghaKouchak A (2017) Rainfall-triggered slope instabilities under a changing climate: comparative study using historical and projected precipitation extremes. Can Geotech J 54(1):117–127
Shinoda M, Miyata Y, Kurokawa U, Kondo K (2019) Regional landslide susceptibility following the 2016 Kumamoto earthquake using back-calculated geomaterial strength parameters. Landslides 16(8):1497–1516
Sun HY, Pan P, Lu Q, Wei ZL, Xie W, Zhan W (2019) A case study of a rainfall-induced landslide involving weak interlayer and its treatment using the siphon drainage method. Bull Eng Geol Environ 78(6):4063–4074
Taga H, Turkmen S, Kacka N (2015) Assessment of stability problems at southern engineered slopes along mersin-tarsus motorway in turkey. Bull Eng Geol Environ 74(2):379–391
Tang X, Chen JP, Liu DG, Xu N (2015) The relationship between microstructure characteristics and shear strength of tuff soil landslide zone. Electron J Geotech Eng 20(10):4151–4163
Tan HD, Jian WX, Lu Y, Song Y (2018) Hedro-mechanical Interaction Characteristics of the Tuff Residual Soil in South Jiangxi Province of China. Safety and Environ Eng 25(1):18–22
Wang H, Wang XD, Pan J (2017) A case study of super-high cut slope I: simulation and analysis of instability mechanism of slopes. Chin J Rock Mech Eng-En 4:125–135
Wang JJ, Liang Y, Zhang HP, Wu Y, Lin X (2014) A loess landslide induced by excavation and rainfall. Landslides 11(1):141–152
Yang DH, Yan RT, Wei CF, Zhang M, Zhang Q (2016) A study of water chemical sensitivity of strength indices of silty clay. Rock Soil Mech 37(12):3529–3536
Zhang CY, Zhang M, Zhang TL, Dai ZW, Wang LQ (2020) Influence of intrusive granite dyke on rainfall-induced soil slope failure. Bull Eng Geol Environ 79(10):5259–5276
Zhao L, Li D, Tan H, Cheng X, Zuo S (2019) Characteristics of failure area and failure mechanism of a bedding rockslide in Libo county, Guizhou. China Landslides 16(7):1367–1374
Zhao RX, Yin YP, Li B, Wang WP (2017) Research on the colluvial landslide stability during reservoir water level fluctuation. J Hydraulic Eng 48(4):435–445
Zhuang JQ, Peng JB (2014) A coupled slope cutting-a prolonged rainfall-induced loess landslide: a 17 October 2011 case study. Bull Eng Geol Environ 73(4):997–1011
Zuo C, Liu D, Ding S, Chen J (2016) Micro-characteristics of strength reduction of tuff residual soil with different moisture. KSCE J Civ Eng 20(2):639–646
Funding
This work was financially supported by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2020M680950) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51627804), for which the authors are grateful.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, X., Gong, B. & Tang, C. Study of the slope deformation characteristics and landslide mechanisms under alternating excavation and rainfall disturbance. Bull Eng Geol Environ 80, 7171–7191 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02371-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02371-7