Abstract
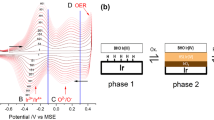
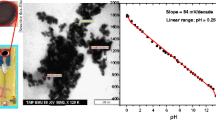
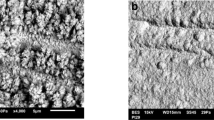
A new iridium-based planar pH sensor for bioanalytical purposes is introduced. The fabrication of the sensor was carried out by a two-stage coating process of different iridium solutions on a platinum thick film surface. The pH response behaviour and the Nernstian characteristics of the double-layer electrode exhibited better results than the single iridium depositions. An almost theoretical Nernstian slope could be obtained as well as a pH response time of about 3 to 5 min in a pH range of 4.01 to 9.18. Furthermore, a biofilm growth of different microorganisms onto the iridium-coated electrodes could be achieved. Afterwards, the viability of the microorganisms was demonstrated via cell plating studies.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Spitzer P, Pratt KW (2011) The history and development of a rigorous metrological basis for pH measurements. J Solid State Electrochem 15:69–76
Deublein D, Steinhauser A (2011) Biogas from waste and renewable resources: an introduction. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Second Edition, Weinheim
Gründler P (2007) Chemical sensors: an introduction for scientists and engineers. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Scheper T (2008) Biosensing for the 21st century. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Ulber R, Frerichs J-G, Beutel S (2003) Optical sensor systems for bioprocess monitoring. Anal Bioanal Chem 376:342–348
Magnusson EB, Halldorsson S, Fleming RMT, Leosson K (2013) Real-time optical pH measurement in a standard microfluidic cell culture system. Biomed Optics Express 4(9):1749–1758
Rajan DK, Patrikoski M, Verho J, Sivula J, Ihalainen H, Miettinen S, Lekkala J (2016) Optical non-contact pH measurement in cell culture with sterilizable, modular parts. Talanta 161:755–761
Kühl M, Jørgensen BB (1992) Microsensor measurements of sulfate reduction and sulfide oxidation in compact microbial communities of aerobic biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 58(4):1164–1174
Santegoeds CM, Schramm A, de Beer D (1998) Microsensors as a tool to determine chemical microgradients and bacterial activity in wastewater biofilms and flocs. Biodegradation 9(3):159–167
Ohle C, Gieseke A, Nistico L, Decker EM, de Beer D, Stoodley P (2010) Real-time microsensor measurement of local metabolic activities in ex vivo dental biofilms exposed to sucrose and treated with chlorhexidine. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(7):2326–2334
Vonau W, Guth U (2006) pH Monitoring: a review. J Solid State Electrochem 10:746–752
Kahlert H (2008) Functionalized carbon electrodes for pH determination. J Solid State Electrochem 12:1255–1266
Alizadeh T, Jamshidi F (2015) Synthesis of nanosized sulfate-modified α-Fe2O3 and its use for the fabrication of all-solid-state carbon paste pH sensor. J Solid State Electrochem 19:1053–1062
Samsonova EN, Lutov VM, Mikhelson KN (2009) Solid-contact ionophore-based electrode for determination of pH in acidic media. J Solid State Electrochem 13:69–75
Shuk P, Guth U, Greenblatt M (2002) Ion-selective sensors based on molybdenum bronzes. J Solid State Electrochem 6:374–383
Razmi H, Heidari H, Habibi E (2008) pH-sensing properties of PbO2 thin film electrodeposited on carbon ceramic electrode. J Solid State Electrochem 12:1579–1587
Prats-Alfonso E, Abad L, Casan-Pastor N, Gonzalo-Ruiz J, Baldrich E (2013) Iridium oxide pH sensor for biomedical applications. Case urea-urease in real urine samples. Biosens Bioelectron 39(1):163–169
Ianniello RM, Yacynych AM (1983) Urea sensor based on iridium dioxide electrodes with immobilized urease. Anal Chim Acta 146:249–253
Kinoshita E, Ingman F, Edwall G, Thulin S, Glab S (1986) Polycrystalline and monocrystalline antimony, iridium and palladium as electrode material for pH-sensing electrodes. Talanta 33(2):125–134
Kurzweil P (2009) Metal oxides and ion-exchanging surfaces as pH sensors in liquids: state-of-the-art and outlook. Sensors 9(6):4955–4985
Cruz AM, Abad L, Carretero NM, Moral-Vico J, Fraxedas J, Lozano P, Subías G, Padial V, Carballo M, Collazos-Castro J, Casan-Pastor N (2012) Iridium oxohydroxide, a significant member in the family of iridium oxides. Stoichiometry, characterization, and implications in bioelectrodes. J Phys Chem C 116:5155–5168
Silva TM, Rito JE, Simoes AMP, Ferreira MGS, da Cunha BM, Watkins KG (1998) Electrochemical characterisation of oxide films formed on Ti-6A1-4V alloy implanted with Ir for bioengineering applications. Electrochim Acta 43(1–2):203–211
Weiland JD, Anderson DJ (2000) Chronic neural stimulation with thin-film, iridium oxide electrodes. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 47(7):911–918
Wang K, Liu C-C, Durand DM (2009) Flexible nerve stimulation electrode with iridium oxide sputtered on liquid crystal polymer. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 56(1):6–14
Yamanaka K (1989) Anodically electrodeposited iridium oxide films (AEIROF) from alkaline solutions for electrochromic display devices. Jpn J Appl Phys 28(4):632–637
Yano J, Noguchi K, Yamasaki S, Yamazaki S (2004) Novel color change of electrochromic iridium oxide in a matrix aramid resin film. Electrochem Commun 6(2):110–114
Bezbaruah AN, Zhang TC (2002) Fabrication of anodically electrodeposited iridium oxide film pH microelectrodes for microenvironmental studies. Anal Chem 74(22):5726–5733
Katsube T, Lauks I, Zemel JN (1982) pH-sensitive sputtered iridium oxide films. Sensors Actuators 2:399–410
Kim TY, Yang S (2014) Fabrication method and characterization of electrodeposited and heat-treated iridium oxide films for pH sensing. Sensors Actuators B Chem 196:31–38
Kreider KG, Tarlov MJ, Cline JP (1995) Sputtered thin-film pH electrodes of platinum, palladium, ruthenium, and iridium oxides. Sensors Actuators B Chem 28(3):167–172
Olthuis W, Robben MAM, Bergveld P, Bos M, van der Linden WE (1990) pH-sensor properties of electrochemically grown iridium oxide. Sensors Actuators B Chem 2(4):247–256
Wang M, Yao S, Madou M (2002) A long-term stable iridium oxide pH electrode. Sensors Actuators B Chem 81(2–3):313–315
Thanawala S, Georgiev DG, Baird RJ, Auner G (2007) Characterization of iridium oxide thin films deposited by pulsed-direct-current reactive sputtering. Thin Solid Films 515(18):7059–7065
Ryynänen T, Nurminen K, Hämäläinen J, Leskelä M, Lekkala J (2010) pH electrode based on ALD deposited iridium oxide. Procedia Eng 5:548–551
Elzanowska H, Abu-Irhayem E, Skrzynecka B, Birss VI (2004) Hydrogen peroxide detection at electrochemically and Sol-Gel derived Ir oxide films. Electroanalysis 16(6):478–490
de Oliveira-Sousa A, da Silva MAS, Machado SAS, Avaca LA, de Lima-Neto P (2000) Influence of the preparation method on the morphological and electrochemical properties of Ti/IrO2-coated electrodes. Electrochim Acta 45(27):4467–4473
Nguyen CM, Rao S, Yang X, Dubey S, Mays J, Cao H, Chiao J-C (2015) Sol-Gel deposition of iridium oxide for biomedical micro-devices. Sensors 15(2):4212–4228
Huang W-D, Cao H, Deb S, Chiao M, Chiao JC (2011) A flexible pH sensor based on the iridium oxide sensing film. Sensors Actuators A Phys 169(1):1–11
Wang M, Yao S (2003) Carbonate-melt oxidized iridium wire for pH sensing. Electroanalysis 15(20):1606–1615
Petit MA, Plichon V (1998) Anodic electrodeposition of iridium oxide films. J Electroanal Chem 444:247–252
Baur JE, Spaine TW (1998) Electrochemical deposition of iridium(IV) oxide from alkaline solutions of iridium(III) oxide. J Electroanal Chem 443:208–216
Juodkazyte J, Sebeka B, Valsiunas I, Juodkazis K (2005) Iridium anodic oxidation to Ir(III) and Ir(IV) hydrous oxides. Electroanalysis 17(11):947–952
VanHoudt P, Lewandowski Z, Little B (1992) Iridium oxide pH microelectrode. Biotechnol Bioeng 40:601–608
Burke LD, Whelan DP (1984) A new interpretation of the charge storage and electrical conductivity behaviour of hydrous iridium oxide. J Electroanal Chem Interfacial Elecrtochem 162(1–2):121–141
Acknowledgements
Financial support by the Bundesministerium für Wirtschaft und Energie (BMWi) through the federation for industrial research (AiF) (IGF-project: 18150BG) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bause, S., Decker, M., Gerlach, F. et al. Development of an iridium-based pH sensor for bioanalytical applications. J Solid State Electrochem 22, 51–60 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-017-3721-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-017-3721-1