Abstract
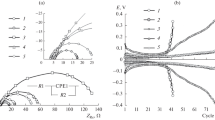
The electrolytic conductivity and viscosity of lithium perchlorate in bis-1,4-dioxapentyl sulfate (IV) [OS22] and 1,4,7-trioxaoctyl sulfate (IV) [OS32] were determined as a function of salt concentration (0.00005–2 M) and temperature (286–318 K). At 298 K, the highest conductivity (κ=2.77×10−3 Ω−1 cm−1) was achieved for OS22 based solutions containing 1–2 M LiClO4. Formation of electrically neutral ion pairs appeared to be the main reason for a continuous decline in the molar conductivity (Λ) observed in dilute solutions with increasing salt concentration. Additionally, an increase in the dynamic viscosity (η) accounted for a decrease in the mobility of charge carriers with increasing length of the oxaalkyl chain in the podand molecules. The temperature dependence of the conductivity and viscosity was found to be of the Arrhenius type for both systems investigated, while the activation energies, E κ # and E η #, varied in parallel with the degree of interionic aggregation. CVs obtained on a polycrystalline Pt electrode indicated the electrochemical stability of OS22 in the potential range between −0.8 V and 4.7 V versus Li+/Li. A linear current density–potential dependence, with the same slope for the anodic and cathodic branches proved the reversibility of lithium electrodeposition and re-dissolution at the Pt/1 M LiClO4+OS22 interface.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gierczyk B, Łęska B (1999) J Incl Phenom 35:327
Schroeder G, Gierczyk B, Łęska B, Wojciechowski G, Pankiewicz R, Brzezinski B, Bartl F (2002) J Mol Struct 607:9
Afanase'ev WN, Grechin AG (2002) Uspekhi Chimii 71:878
Iwahori T, Mitsuishi L, Shiraga S, Nakajima N, Momose H, Ozaki Y, Tanigichi S, Awata H, Ono T, Takeuchi K (2000) Electrochim Acta 45:1509
Wrigh PV (2002) MRS Bull 27:597
McBreen J, Lee HS, Yang XQ, Sun X (2000) J Power Sources 89:163
Lisowska-Oleksiak A, Inerowicz HD (1999) J Power Sources 81–82:813
Lisowska-Oleksiak A, Kazubowska K, Lis M (2000) Symposium of the Polish Supramolecular Chemistry Network, Olsztyn
Morford RV, Kellam EC, Hofmann MA, Baldwin R, Allcock HR (2000) Solid State Ionics 133:171
Saito Y, Yamamoto H, Nakamura O, Kageyama H, Ishikawa H, Miyoshi T, Matsuoka M (1999) J Power Sources 81–81:772
Bełtowska-Brzezinska M (A. Mickiewicz University) (1991) PL Patent 151 145
Biegler T, Rand DAJ, Woods R (1971) J Electroanal Chem 29:269
Fuoss RM (1935) J Am Chem Soc 57:488
Onsager L (1926) Physik Z 27:388
Schroeder G, Gierczyk B (2002) Zastosowanie magnetycznego rezonansu jądrowego w chemii supramolekularnej, In: Chemia supramolekularna. Betagraf, Poznań, p 30
Lo Surdo A, Wirth HE (1979) J Phys Chem 83:879
Tarascon JM, Guyomard D (1994) Solid State Ionics 69:293
Guyomard D, Tarascon JM (1995) J Power Sources 54:92
Chen HP, Fergus JW, Jang BZ (2000) J Electrochem Soc 147:399
Abraham KM, Alamgir M (1993) J Power Sources 43–44:195
Herr R (1990) Electochim Acta 35:1257
Dudley JT, Wilkinson DP, Thomas G, LeVae R, Woo S, Blom H, Horvath C, Juzkow MW, Denis B, Juric P, Aghakian P, Dahn JR (1991) J Power Sources 35:59
Cisak A, Werblan L (1986) Wysokoenergetyczne niewodne ogniwa galwaniczne. PWN, Warsaw
Tobishima S-I, Okada T (1985) Electrochim Acta 30:1715
Tobishima S-I, Arakawa M, Yamaki J-I (1988) Electrochim Acta 33:239
Matsuda Y, Morita M, Yamada K, Hirai K (1985) J Electrochem Soc 132:2538
Morita M, Yamada O, Ishikawa M (1999) J Power Sources 81–82:425
Watanabe H, Nohma T, Nakane I, Yoshimura S, Nishio K, Saito T (1993) J Power Sources 43–44:217
Takahashi M, Yoshimura S, Nakane I, Nishio K, Saito T, Fujimoto M, Narukawa S, Hara M, Furukawa N (1993) J Power Sources 43–44:253
Joho F, Rykart B, Imhof R, Novak P, Spahr ME, Monnier A (1999) J Power Sources 81–82:243
Novak P, Joho F, Imhof R, Panitz J.Ch, Haas O (1999) J Power Sources 81–82:212
Kumai K, Miyashiro H, Kobayashi Yo, Takei K, Ishikawa R (1999) J Power Sources 81–82:715
Aurbach D, Gofer Y, Ben-Zion M, Aped P (1992) J Electroanal Chem 339:451
Kanamura K, Tamura H, Takehara Z (1992) J Electroanal Chem 333:127
Egashira M, Takahashi H, Okada S, Yamaki J (2001) J Power Sources 92:267
Kanamura K (1999) J Power Sources 81–82:123
Johnson BA, White RE (1998) J Power Sources 70:48
Peled E, Yamin H, (1979) Isr J Chem 18:131
Burrows B, Jasinski R (1968) J Electrochem Soc 115:365
Peled E (1979) J Electrochem Soc 126:2049
Peled E (1983) J Power Sources 9:253
Wiesener E, Eckoldt U, Rahner D (1989) Electrochim Acta 34:1277
Acknowledgement
This work was performed within the research project supported by the Committee for Scientific Research (KBN), Poland. The authors wish to express their thanks to Dr hab. Piotr Barczyński (Department of Chemistry, A. Mickiewicz University in Poznań) for the numerical PC program for calculations according to the Fuoss–Krauss method.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bełtowska-Brzezinska, M., Łuczak, T., Węsierski, T. et al. Conductivity and interfacial behaviour of bis-1,4-dioxapentyl sulfate (IV) and 1,4,7-trioxaoctyl sulfate (IV) based electrolyte for lithium batteries. J Solid State Electrochem 7, 539–544 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-003-0435-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-003-0435-3