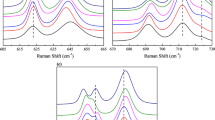
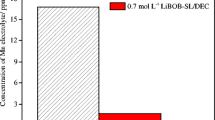
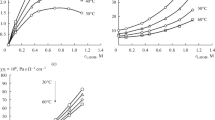
Abstract
The effect of lithium bis(oxalato)borate (LiBOB) on the physicochemical properties of lithium perchlolate solutions in sulfolane and the cycling time of lithium metal electrode is studied. It is found that the introduction of a small amount (0.24 M) of LiBOB into sulfolane solutions of LiClO4 increases insignificantly the solution viscosity but does not decrease the specific ion conductivity. The larger amounts of LiBOB decrease the electrolyte solution specific ion conductivity and increase both its viscosity and the activation energies of conductivity and viscous flow. The corrected conductivity of the solution containing two salts with the overall concentration 1.54 М is shown to far exceed the corrected conductivity of 1.5 М LiClO4 solution in sulfolane, which can be explained by the formation of ion associates of the higher order in the presence of LiBOB. The introduction of lithium bis(oxalato)borate into sulfolane solutions of lithium perchlorate increases the resistance of surface layers on the lithium metal electrode and the electrode cycling time. The main factor that determines the cycling time of lithium metal electrode is associated with protective properties of surface layers formed on the lithium electrode rather than with their conductivity.

Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Varzi, A., Thanner, K., Scipioni, R., Di Lecce, D., Hassoun, J., D¨orfler, S., Altheus, H., Kaskel, S., Prehal, C., and Freunberger, S.A., Current status and future perspectives of lithium metal batteries, J. Power Sources, 2020, vol. 480, p. 228803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2020.228803
Wu, X., Pan, K., Jia, M., Ren, Y., He, H., Zhang, L., and Zhang, S., Electrolyte for lithium protection: From liquid to solid, Green Energy Environ., 2019, vol. 4, p. 360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gee.2019.05.003
Wang, Q., Wang, H., Wu, J., Zhou, M., Liu, W., and Zhou, H., Advanced electrolyte design for stable lithium metal anode: From liquid to solid, Nano Energy, 2021, vol. 80, p. 105516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.105516
Peled, E., The electrochemical behavior of alkali and alkaline earth metals in nonaqueous battery Systems – The solid electrolyte interphase model, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1979, vol. 126, p. 2047.
Von Aspern, N., Rçschenthaler, G.-V., Winter, M., and Cekic-Laskovic, I., Fluorine and lithium: ideal partners for high-performance rechargeable battery electrolytes, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2019, vol. 58, p. 15978. https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.201901381
Guo, J., Wen, Z., Wu, M., Jin, J., and Liu, Y., Vinylene carbonate–LiNO3: A hybrid additive in carbonic ester electrolytes for SEI modification on Li metal anode, Electrochem. Commun., 2015, vol. 51, p. 59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2014.12.008
Xu, R., Cheng, X.-B., Yan, C., Zhang, X.-Q., Xiao, Y., Zhao, C.Z., Huang, J.-Q., and Zhang, Q., Artificial interphases for highly stable lithium metal anode, Matter, 2019, vol. 1, p. 317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matt.2019.05.016
Cheng, X.-B., Zhang, R., Zhao, C.-Z., and Zhang, Q., Toward safe lithium metal anode in rechargeable batteries: A review, Chem. Rev., 2017, vol. 117, p. 10403. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00115
Park, S.-J., Hwang, J.-Y., Yoon, C. S., Jung, H.G., and Sun, Y.-K., Stabilization of lithium-metal batteries based on in-situ formation of stable solid electrolyte interphase layer, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, vol. 10, no. 21, p. 17985.
Zhang, X.-Q., Cheng, X.-B., Chen, X., Yan, C., and Zhang, Q., Fluoroethylene carbonate additives to render uniform Li deposits in lithium metal batteries, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2017, 1605989. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201605989
Li, S., Yang, L., Wang, P., Li, Z., Li, W., Liu, H., and Cui, X., Targeted research on the single role of lithium bis(oxalate)borate in the film-forming process through a novel lithium salt-free electrolyte system, J. Power Sources, 2020, vol. 471, p. 228426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2020.228426
Li, C., Wang, P., Li, S., Zhao, D., Zhao, Q., Liu, H., and Cui, X., Active mechanism of the interphase film-forming process for an electrolyte based on a sulfolane solvent and a chelato-borate complex, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, vol. 10, no. 30, p. 25744.
Ding, F., Xu, W., Chen, X., Zhang, J., Engelhard, M.H., Zhang, Y., Johnson, B.R., Crum J.V., Blake, T.A., Liu, X., and Zhang, J.-G., Effects of carbonate solvents and lithium salts on morphology and coulombic efficiency of lithium electrode, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2013, vol. 160, no. 10, p. A1894. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.100310jes
Li, S.Y., Cui, X.L., Xu, X.L., Shi, X.M., and Li, G.X., Electrochemical performances of two kinds of ternary electrolyte mixtures with lithium bis(oxalate)borate, Russ. J. Electrochem., 2012, vol. 48, p. 518. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193511090126
Bushkova, O.V., Yaroslavtseva, T.V., and Dobrovolsky, Y.A., New lithium salts in Electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries (review), Russ. J. Electrochem., 2017, vol. 53, p. 677. https://doi.org/10.7868/S0424857017070015
Fan, L.-Z., Xing, T., Awan, R., and Qiu, W., Studies on lithium bis(oxalato)-borate/propylene carbonate-based electrolytes for Li-ion batteries, Ionics, vol. 17, p. 491. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-011-0551-5
Hofmann, A. and Hanemann, T., Novel electrolyte mixtures based on dimethyl sulfone, ethylene carbonate and LiPF6 for lithium-ion batteries, J. Power Sources, 2015, vol. 298, p. 322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.08.071
Santee, S., Xiao, A., Yang, L., Gnanaraj, J., and Lucht, B.L., Effect of combinations of additives on the performance of lithium ion batteries, J. Power Sources, 2009, vol. 194, p. 1053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2009.06.012
Zhang, S.S., An unique lithium salt for the improved electrolyte of Li-ion battery, Electrochem. Commun., 2006, vol. 8, p. 1423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2006.06.016
Flamme, B., Haddad, M., Phansavath, P., Ratovelomanana-Vidal, V., and Chagnes, A., Anodic stability of new sulfone-based electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries, ChemElectroChem., 2018, vol. 5, p. 2279. https://doi.org/10.1002/celc.201701343
Shao, N., Sun, X.-G., Dai, S., and Jiang, D., Electrochemical windows of sulfone-based electrolytes for high-voltage Li-ion batteries, Phys. Chem. B, 2011, vol. 115, p. 12120. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp204401t
Wu, F., Zhou, H., Bai, Y., Wang, H., and Wu, C., Toward 5 V Li-ion batteries: Quantum chemical calculation and electrochemical characterization of sulfone-based high-voltage electrolytes, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2015, vol. 7, no. 27, p. 15098. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b04477
Ivanov, A.L., Electrochemistry of lithium electrode in electrolyte systems containing lithium polysulfides, Cand. Sci. (Chem.) Dissertation, Ufa, 2011.
Kolosnitsyn, V.S., Ivanov, A.L., and Karaseva, E.V., Cathodic deposition of lithium on stainless steel from sulfolane electrolyte systems, Elektrokhim. Energ., 2009, vol. 9, no. 1, p. 25.
Kolosnitsyn, V.S., Karaseva, E.V., and Ivanov, A.L., Electrochemistry of a lithium electrode in lithium polysulfide solutions, Russ. J. Electrochem., 2008, vol. 44, p. 564. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193508050091
Kolosnitsyn, V.S., Ivanov, A.L., Karaseva, E.V., Mochalov, S.E., and Kuz’mina, E.V., The effect of lithium polysulfides on cycling of lithium electrode in 1 M LiClO4 in sulfolane, Elektrokhim. Energ., 2013, vol. 13, no. 3, p. 144.
Liu, X., Shen, C., Gao, N., Hou, Q., Song, F., Tian, X., He, Y., Huang, J., Fang, Z., and Xie, K., Concentrated electrolytes based on dual salts of LiFSI and LiODFB for lithium–metal battery, Electrochim. Acta, 2018, vol. 289, p. 422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2018.09.085
Qian, J.F., Henderson, W.A., Xu, W., et al., High rate and stable cycling of lithium metal anode, Nat. Commun., 2015, vol. 6, p. 6362. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms7362
Sheina, L.V., Physicochemical and electrochemical properties of electrolyte systems based on sulfones, Cand. Sci. (Chem.) Dissertation, Ufa, 2009, p. 60.
Sheina, L.V., Ivanov, A.L., Karaseva, E.V., and Kolosnitsyn, V.S., Physico-chemical and electrochemical properties of lithium bis(oxalate)borate solutions in sulfolane, Russ. J. Electrochem., 2021, vol. 57, no. 12, p. 1138. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193521120065
Mochalov, S.E., Antipin, A.V., and Kolosnitsyn, V.S., Multichannel test system for secondary chemical current sources and electrochemical cells, Nauchn. Priborostr., 2009, vol. 19, no. 3, p. 88. URL: http:// 213.170.69.26/en/magazine.php.
Evans, J., Vincent, C.A., and Bruce, P.G., Electrochemical measurement of transference number in polymer electrolytes, Polymer., 1987, vol. 28, p. 2324. https://doi.org/10.1016/0032-3861(87)90394-6
Bruce, P.G., Evans, J., and Vincent, C.A., Conductivity and transference number measurements on polymer electrolytes, Solid State Ionics, 1988, vols. 28–30, p. 918. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-2738(88)90304-9
Ishikawa, M., Machino, S., and Morita, M., Electrochemical control of a Li metal anode interface: improvement of Li cyclability by inorganic additives compatible with electrolytes, J. Electroanal. Chem., 1999, vol. 473, nos. 1–2, p. 279.
Erkabaev, A.M., Yaroslavtseva, T.V., and Bushkova, O.V., Quantum-chemical and IR spectroscopic study of ionic association in solutions of LiCF3SO3 in acetonitrile, Russ. J. Phys. Chem., 2020, vol. 94, p. 933.] https://doi.org/10.31857/S0044453720050064
Kolosnitsyn, V.S., Sheina, L.V., and Mochalov, S.E., Physicochemical and electrochemical properties of sulfolane solutions of lithium salts, Russ. J. Electrochem., 2008, vol. 44, p. 575. https://doi.org/10.1134/S102319350805011X
Kolosnitsyn, V.S., Slobodchikova, N.V., and Sheina, L.V., Electroconduction of lithium perchlorate solutions in sulfones, Russ. J. Electrochem., 2001, vol. 37, p. 599. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016666517462
Karaseva, E.V., Kuzmina, E.V., Kolosnitsyn, D.V., Shakirova, N.V., Sheina, L.V., and Kolosnitsyn, V.S., The mechanism of effect of support salt concentration in electrolyte on performance of lithium–sulfur cells, Electrochim. Acta, 2019, vol. 296, no. 10, p. 1102.] https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2018.11.019
Funding
This study was carried out within government assignment no. AAAA-A20-120012090022-1 “Development of Methods for Enhancing the Efficiency of Electric Energy Accumulation in Electrochemical Systems of Various Types. Development of New Electrolytes and Electrode Materials for Supercapacitors, Lithium and Lithium-Ion Batteries Aimed at Increasing Their Specific Energy, Power, and Service Life.” The study was carried out by using the equipment of the Center of Collective Use “Chemistry.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Translated by T. Safonova
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sheina, L.V., Ivanov, A.L., Karaseva, E.V. et al. The Effect of Lithium Bis(oxalato)borate on the Galvanostatic Charge–Discharge Cycling of Lithium Electrode in Sulfolane Solutions of Lithium Perchlorate. Russ J Electrochem 58, 210–215 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S102319352201013X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S102319352201013X