Abstract
Electrostatic potentials and average local ionization energies on the molecular surfaces of 19 phenols, 17 benzoic acids and their respective conjugate bases were computed at the HF/STO-5G(d)//B3LYP/6-311G(d,p) level. Good correlations were found between pK as and the V S,max values of the neutral acids and the V S,min and \( \bar{I}_{{{\text{S,min}}}} \) of the conjugate bases for both sets of molecules. V S,max is the most positive value of the electrostatic potential on the molecular surface and is an indicator of the ease with which the phenols and benzoic acids lose their acidic hydrogens. V S,min and \( \bar{I}_{{{\text{S,min}}}} \) are the minimum values of the electrostatic potential and the local ionization energy computed on the molecular surface; the V S,min and \( \bar{I}_{{{\text{S,min}}}} \) of the conjugate bases of the phenoxides and benzoates are indicative, respectively, of the tendencies of electrophiles to approach the anions (V S,min) and to react with the anions (\( \bar{I}_{{{\text{S,min}}}} \)) to reform the original acids. The correlations observed between the computed molecular surface quantities, taken as single parameters, and the experimental pK a values ranged from R=0.938 to R=0.970 for the two classes of compounds.
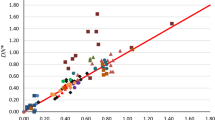
Figure Correlation between pK a and the computed V S,max of the benzoic acids listed in Table 2. The linear correlation coefficient is 0.970



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haeberlein M, Murray JS, Brinck T, Politzer P (1992) Can J Chem 70:2209–2214
Gross KC, Seybold PG (2000) Int J Quantum Chem 80:1107–1115
Gross KC, Seybold PG, Peralta-Inga Z, Murray JS, Politzer P (2001) J Org Chem 66:6919-6925
Gross KC, Seybold PG (2001) Int J Quantum Chem 85:569–579
Hollingsworth CA, Seybold PG, Hadad CM (2002) Int J Quantum Chem 90:1396–1403
Murray JS, Politzer P (1998) Average local ionization energies: significance and applications. In: Parkanyi C (ed) Theoretical organic chemistry. Elsevier, Amsterdam, chapter 7
Politzer P, Daiker KC (1981) In: Deb BM (ed) The force concept in chemistry. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, pp 294–387
Politzer P, Murray JS (1991) In: Lipkowitz KB, Boyd DB (eds) Reviews in computational chemistry II. VCH, New York, chapter 7
Murray JS, Politzer P (1998) Molecular electrostatic potentials. In: Schleyer PvR (ed) Encyclopedia of computational chemistry. Wiley, New York
Murray JS, Politzer P (1992) J Chem Res (S) 110–111
Murray JS, Brinck T, Grice ME, Politzer P (1992) J Mol Struct (Theochem) 256:29–45
Sjoberg P, Murray JS, Brinck T, Politzer P (1990) Can J Chem 68:1440–1443
Koopmans TA (1933) Physica 1:104–113
Brinck T, Murray JS, Politzer P (1991) J Org Chem 56:5012–5015
Brinck T, Murray JS, Politzer P, Carter RE (1991) J Org Chem 56:2934–2936
Murray JS, Seminario JM, Politzer P, Sjoberg P (1990) Int J Quantum Chem, Quantum Chem Symp 24:645–653
Brinck T, Murray JS, Politzer P (1993) Int J Quantum Chem 48:73–88
Murray JS, Abu-Awwad F, Politzer P (2000) J Mol Struct (Theochem) 501–502:241–250
Politzer P, Murray JS, Concha MC (2002) Int J Quantum Chem 88:19–27
Jin P, Murray JS, Politzer P (2004) Int J Quantum Chem 96:394–401
Scrocco E, Tomasi J (1973) In: Topics in current chemistry. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 95-170
Politzer P, Truhlar DG (eds) (1981) Chemical applications of atomic and molecular electrostatic potentials. Plenum, New York
Naray-Szabo G, Ferenczy GG (1995) Chem Rev 95, pp 829–847
Murray JS, Sen K (eds) (1996) Molecular electrostatic potentials. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Hagelin H, Murray JS, Brinck T, Berthelot M, Politzer P (1995) Can J Chem 73:483–488
Pathak RK, Gadre SR (1990) J Chem Phys 93:1770–1773
SAS. SAS Institute Inc, Cary, NC, 27511
Albert A, Serjeant EF (1962) Ionization constants of acids and bases. Methuen, London
Murray JS, Peralta-Inga Z, Politzer P, Ekanayake K, LeBreton P (2001) Int J Quantum Chem: Biophys Q 83:245–254
Murray JS, Peralta-Inga Z, Politzer P (1999) Int J Quantum Chem 75:267–273
Hussein W, Walker CG, Peralta-Inga Z, Murray JS (2001) Int J Quantum Chem 82:160–169
Acknowledgement
We thank Dr. Peter Politzer for many helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Y., Gross, K.C., Hollingsworth, C.A. et al. Relationships between aqueous acidities and computed surface-electrostatic potentials and local ionization energies of substituted phenols and benzoic acids. J Mol Model 10, 235–239 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-004-0185-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-004-0185-x