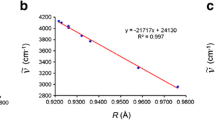
Abstract
Optimized hydrogen-bond descriptors are provided for 21 primary and secondary alcohols, 16 phenols, 10 anilines and 4 amides derived from experimental chromatographic and liquid partition data analyzed using the solvation parameter model with the Solver method. Solver is an optimization package in Microsoft Excel that simultaneously adjusts the descriptor values to minimize the sum of the standard deviation of the residuals for the dependent experimental variable for a set of model equations using a Simplex algorithm. For the full data set the optimized hydrogen-bond acid descriptors are approximately 1.27 times larger than Abraham’s descriptors and the hydrogen-bond base descriptors roughly equivalent. For an isolated aliphatic primary hydroxyl group the hydrogen-bond acidity was estimated as A = 0.340 and hydrogen-bond basicity B = 0.539 and compared with a secondary hydroxyl group is a stronger hydrogen-bond acid and similar hydrogen-bond base, A = 0.26 and B = 0.54. For alcohols of the type C6H5(CH2)mOH the A and B descriptors are linearly related to m for at least m = 1 to 3. In unsubstituted phenols the hydroxyl group is more hydrogen-bond acidic, A = 0.740, and less hydrogen-bond basic, B = 0.158, than a primary aliphatic hydroxyl group. Ortho substituents reduce the hydrogen-bond acidity of a phenolic hydroxyl group in the order –CH3 < –Cl < < –NO2 with 2-nitrophenol almost non-hydrogen-bond acidic, A = 0.062, due to favorable intramolecular hydrogen-bonding. For para-substituted phenols hydrogen-bond acidity increases in the order –CH3 < –Br < –C6H5 < –CN ≈ –Cl < < –NO2 with a range for A from 0.673 to 0.975 and for hydrogen-bond basicity –Cl ≈ –Br < –NO2 < –CH3 < –CN < –C6H5 with a range for B from 0.775 to 1.267. The ranking order is not simply explained by consideration of inductive or mesomeric effects acting individually. The –NH2 group in aniline is a weaker hydrogen-bond acid, A = 0.238, and stronger hydrogen-bond base than phenol. A single methyl group in any ring position for anilines simultaneously increases the hydrogen-bond basicity and reduces the hydrogen-bond acidity of the –NH2 group. A single nitro group in any ring position has the opposite effect on the hydrogen-bonding properties of the –NH2 group. Primary amides are relatively strong hydrogen-bond acids and bases compared with primary alcohols and anilines and occupy the same descriptor space as phenols. An NMR correlation model is developed to estimate the optimized A descriptor using chemical shift differences for acidic protons in DMSO and CDCl3. The principle of additivity is not a good model for estimating the A and B descriptors for compounds with more than one hydrogen-bond acid/base site, although it provides acceptable results in some cases.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All experimental data is in the public domain and can be retrieved from the cited sources without hinderance for free.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Abraham, M.H.: Scales of solute hydrogen-bonding: their construction and approach to physicochemical and biochemical processes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 22, 73–83 (1993)
Abraham, M.H., Platts, J.A.: Hydrogen bond structural group constants. J. Org. Chem. 66, 3484–3491 (2001)
Abraham, M.H., Gola, J.M.R., Cometto-Muniz, J.E., Acree, W.E.: Hydrogen bonding between solutes in solvents octan-1-ol and water. J. Org. Chem. 75, 7651–7658 (2010)
Abraham, M.H., Poole, C.F., Poole, S.K.: Classification of stationary phases and other materials by gas chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 842, 79–114 (1999)
Abraham, M.H., Ibrahim, A., Zissimos, A.M.: Determination of sets of solute descriptors from chromatographic measurements. J. Chromatogr. A 1037, 29–47 (2004)
Poole, C.F., Ariyasena, T.C., Lenca, N.: Estimation of the environmental properties of compounds from chromatographic measurements and the solvation parameter model. J. Chromatogr. A 1317, 85–104 (2013)
Abraham, M.H., Whiting, G.S., Doherty, R.M., Shuely, W.J.: Hydrogen bonding 13. A new method for the characterization of GC stationary phases—the Laffort data set. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, 1451–1460 (1990)
Abraham, M.H., Whitting, G.S., Doherty, R.M., Shuely, W.J.: Hydrogen-bonding 16: a new solute solvation parameter, π2H, from gas chromatographic data. J. Chromatogr. 587, 213–228 (1991)
Martin, S.D., Poole, C.F., Abraham, M.H.: Synthesis and gas chromatographic evaluation of a high-temperature hydrogen-bond acid stationary phase. J. Chromatogr. A 805, 217–235 (1998)
Abraham, M.H.: Hydrogen-bonding 31: construction of a scale of solute effective or summation hydrogen-bond basicity. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 6, 660–684 (1993)
ADME suite 5.0, Advanced Chemistry Development, Toronto, ON.
Ulrich, N., Endo, S., Brown, T.N., Watanabe, N., Bronner, C., Abraham, M.H., Goss, K.-H.: UFZ-LSER Database v. 3.2.1 [internet]. Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research-UFZ, Leipzig (2017)
Poole, C.F.: Wayne State University experimental descriptor database for use with the solvation parameter model. J. Chromatogr. A 1617, 460841 (2020)
Poole, C.F.: Selection of calibration compounds for selectivity evaluation of wall-coated, open-tubular columns for gas chromatography by the solvation parameter model. J. Chromatogr. A 1629, 461500 (2020)
Poole, C.F.: Selection of calibration compounds for selectivity evaluation of siloxane-bonded silica columns for reversed-phase liquid chromatography by the solvation parameter model. J. Chromatogr. A 1633, 461652 (2020)
Poole, C.F., Atapattu, S.N.: Selectivity evaluation of core-shell silica columns for reversed-phase liquid chromatography using the solvation parameter model. J. Chromatogr. A 1634, 461692 (2020)
Poole, C.F.: Evaluation of the solvation parameter model as a quantitative structure-retention relationship model for gas and liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1626, 461308 (2020)
Poole, C.F., Atapattu, S.N., Bell, A.K.: Determination of solute descriptors by chromatographic methods. Anal. Chim. Acta 652, 32–53 (2009)
Poole, C.F., Ahmed, H., Kiridena, W., Patchett, C.C., Koziol, W.W.: Revised solute descriptors for characterizing retention properties of open-tubular columns in gas chromatography and their application to a carborane-siloxane copolymer stationary phase. J. Chromatogr. A 1104, 299–312 (2006)
Poole, C.F.: Solvation parameter model: tutorial on its application to separation systems for neutral compounds. J. Chromatogr. A 1645, 462108 (2021)
Poole, C.F.: Gas chromatography system constant database for 52 wall-coated, open-tubular columns covering the temperature range 60–140 °C. J. Chromatogr. A 1604, 460482 (2019)
Poole, C.F.: Gas chromatography system constant database over an extended temperature range for nine open-tubular columns. J. Chromatogr. A 1590, 130–145 (2019)
Lenca, N., Poole, C.F.: A system map for the ionic liquid stationary phase 1,9-Di(3-vinylimidazolium)nonane Bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide. Chromatographia 78, 81–88 (2015)
Lenca, N., Poole, C.F.: A system map for the ionic liquid stationary phase tri(tripropylphosphoniumhexanamido)triethylamine bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide for gas chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1524, 210–214 (2017)
Lenca, N., Poole, C.F.: A system maps for the ionic liquid stationary phase 1,12-di(tripropylphosphonium)dodecane bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide for gas chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1525, 138–144 (2017)
Lenca, N., Poole, C.F.: A system maps for the ionic liquid stationary phase 1,12-di(tripropylphosphonium)dodecane bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide trifluoromethanesulfonate for gas chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1559, 164–169 (2018)
Abraham, M.H., Andonian-Haftvan, J., Hamerton, I., Poole, C.F., Kollie, T.O.: Comparison of the solvation theories of Abraham and Poole, using a new acidic GLC stationary phase. J. Chromatogr. 646, 351–360 (1993)
Poole, C.F.: Reversed-phase liquid chromatography system constant database over an extended mobile phase composition range for 25 siloxane-bonded silica-based columns. J. Chromatogr. A 1600, 112–126 (2019)
Atapattu, S.N.: Solvation properties of acetone–water mobile phases in reversed-phase liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1650, 462252 (2021)
Poole, C.F.: Partition constant database for totally organic biphasic systems. J. Chromatogr. A 1527, 18–32 (2017)
Ariyasena, T.C., Poole, C.F.: Models for liquid–liquid partition in the system ethanolamine–organic solvent and their use for estimating descriptors for organic compounds. Chromatographia 76, 157–164 (2013)
Ariyasena, T.C., Poole, C.F.: Evaluation of triethylamine as a counter solvent in totally organic biphasic liquid–liquid partition systems. Chromatographia 76, 1031–1039 (2013)
Hansch, C., Leo, A., Hoekman, D.: Q.S.A.R. Exploring Hydrophobic, Electronic, and Steric Constraints. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC (1995)
Abraham, M.H., Platts, J.A., Hersey, A., Leo, A.J., Taft, R.W.: Correlation and estimation of gas–chloroform and water–chloroform partition coefficients by a linear free energy relationship method. J. Pharm. Sci. 88, 670–679 (1999)
Sprunger, L.M., Gibbs, J., Acree, W.E., Abraham, M.H.: Correlation and prediction of partition coefficients for solute transfer to 1,2-dichloroethane from both water and from the gas phase. Fluid Phase Equilibr. 273, 78–86 (2008)
Qian, J., Poole, C.F.: Distribution model for Folch partition. J. Sep. Sci. 30, 2326–2331 (2007)
Abraham, M.H., Chadha, H.S., Whiting, G.S., Mitchell, R.C.: Hydrogen bonding 32. An analysis of water–octanol and water–alkane partitioning and the Δlog P parameter of Seller. J. Pharm. Sci. 83, 1085–1100 (1994)
Platts, J.A., Butina, D., Abraham, M.H., Hersey, A.: Estimation of molecular linear free energy relation descriptors using a group contribution approach. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 39, 825–845 (1999)
Ariyasena, T.C., Poole, C.F.: Determination of descriptors for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and related compounds by chromatographic methods and liquid–liquid partition in totally organic biphasic systems. J. Chromatogr. A 1361, 240–254 (2014)
Sheldon, T.J., Adjiman, C.S., Cordiner, J.L.: Pure component properties from group contribution: hydrogen-bond basicity, Hildebrand solubility parameter, macroscopic surface tension, dipole moment, refractive index and dielectric constant. Fluid Phase Equilibr. 231, 27–37 (2005)
Schuurmann, G., Ebert, R.-U., Kuehne, R.: Prediction of physicochemical properties of organic compounds from 2D molecular structure—fragment methods vs. LFER models. Chimia 60, 691–698 (2006)
Cacelli, I., Campanile, S., Giolitt, A., Molin, D.: Theoretical prediction of the Abraham hydrogen bond acidity and basicity factors from a reaction field method. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 45, 327–333 (2005)
Devereux, M., Popelier, P.L.A., Mclay, I.M.: A refined model for prediction of hydrogen bond acidity and basicity parameters from quantum chemical molecular descriptors. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 11, 1595–1603 (2009)
Schwobel, J.A.H., Ebert, R.-U., Kuhne, R., Schuurmann, G.: Prediction models for Abraham hydrogen bond donor strength: comparison of semi-empirical, ab initio, and DFT methods. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 24, 1072–1080 (2011)
Rahaman, O., Doren, D.J., Di Toro, D.M.: Quantum mechanical estimation of Abraham hydrogen bond parameters using 1:1 donor-acceptor complexes. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 27, 783–793 (2014)
Liang, Y.-Z., Xiong, R.C., Sandler, S.I., Di Toro, D.M.: Quantum chemically estimated Abraham solute parameters using multiple solvent–water partition coefficients and molecular polarizability. Environ. Sci. Technol. 51, 9887–9898 (2017)
Lenca, N., Atapattu, S.N., Poole, C.F.: Estimation of descriptors for hydrogen-bonding compounds from chromatographic and liquid–liquid partition measurements. J. Chromatogr. A 1526, 13–22 (2017)
Abraham, M.H., Du, C.M., Platts, J.A.: Lipophilicity of nitrophenols. J. Org. Chem. 65, 7114–7118 (2000)
Abraham, M.H., Dearden, J.C., Bresnen, G.M.: Hydrogen bonding steric effects and thermodynamics of partitioning. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 19, 242–248 (2006)
Abraham, M.H., Abraham, R.J., Acree, W.E., Aliev, A.E., Leo, A., Whaley, W.L.: An NMR method for the quantitative assessment of intermolecular hydrogen bonding: application to physicochemical, environmental, and biochemical properties. J. Org. Chem. 79, 11075–11083 (2014)
Abraham, M.H., Abraham, R.J., Aliev, A.E., Tormena, C.F.: Is there an intramolecular bond in 2-halophenols? A theoretical and spectroscopic investigation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17, 25151–25159 (2015)
Abraham, M.H., Acree, W.E., Earp, C.E., Vladimirova, A., Whaley, W.L.: Studies on the hydrogen bond acidity and other descriptors and properties for hydroxyflavones and hydroxyisoflavones. J. Mol. Liq. 208, 363–372 (2015)
Acree, W.E., Smart, K., Abraham, M.H.: Abraham model solute descriptors reveal strong intramolecular hydrogen bonding in 1,4-dihydroxyanthraquinone and 1,8-dihydroxyanthraquinone. Phys. Chem. Liq. 56, 416–420 (2018)
Abraham, M.H., Abraham, R.J., Aghamohammadi, A., Afarinkia, K., Liu, X.L.: The assessment of intramolecular hydrogen bonding in ortho-substituted anilines by an NMR method. J. Mol. Liq. 315, 113730 (2020)
Abraham, M.H., Abraham, R.J.: A simple and facile NMR method for the determination of hydrogen bonding by amide N-H protons in protein models and other compounds. New J. Chem. 41, 6064–6066 (2017)
Atapattu, S.N., Poole, C.F.: Solute descriptors for characterizing retention properties of open-tubular columns of different selectivity in gas chromatography at intermediate temperatures. J. Chromatogr. A 1195, 136–145 (2008)
Abraham, M.H., Abraham, R.J., Byrne, J., Griffiths, L.: NMR method for the determination of solute hydrogen bond acidity. J. Org. Chem. 71, 3389–3394 (2006)
Abraham, M.H., Gil-Lostes, J., Cometto-Muniz, J.E., Cain, W.S., Poole, C.F., Atapattu, S.N., Abraham, R.J., Leonard, P.: The hydrogen-bond acidity and other descriptors for oximes. New J. Chem. 33, 76–81 (2009)
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CFP is the sole author of this article and responsible for all elements of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author has no financial or proprietary interest in any of the material discussed in this article.
Ethical Approval
Not applicable. No human or animal data used in writing this manuscript.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Wayne State University agrees to the submission of this article by the author.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poole, C.F. Structural Effects on the Hydrogen-Bonding Descriptors of the Solvation Parameter Model. J Solution Chem 51, 1056–1080 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-021-01133-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-021-01133-z