Abstract
Evidence on the utilization of simple fatty acids by sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) at extremely haloalkaline conditions are practically absent, except for a single case of syntrophy by Desulfonatronum on acetate. Our experiments with sediments from soda lakes of Kulunda Steppe (Altai, Russia) showed sulfide production with sulfate as electron acceptor and propionate and butyrate (but not acetate) as an electron donor at a pH 10–10.5 and a salinity 70–180 g l−1. With propionate as substrate, a highly enriched sulfidogenic culture was obtained in which the main component was identified as a novel representative of the family Syntrophobacteraceae. With butyrate as substrate, a pure SRB culture was isolated which oxidized butyrate and some higher fatty acids incompletely to acetate. The strain represents the first haloalkaliphilic representative of the family Desulfobacteraceae and is described as Desulfobotulus alkaliphilus sp. nov.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
The sulfur cycle is one of the most active element cycles in soda lakes, which are extremely alkaline and saline habitats. Most of these lakes are characterized by high primary productivity and high sulfate concentrations. These factors and the limited oxygen solubility at high salinity create potentially favorable conditions for sulfidogenesis in the anoxic sediments. This is indeed evident from the high free sulfide and FeS content of soda lake sediments and from direct measurements of the sulfate reduction rates (Gorlenko et al. 1999; Sorokin et al. 2004; Foti et al. 2007; Kulp et al. 2006).
Despite the evidence of sulfate-reducing activity, little is known on the identity of SRB in soda lakes. Until now, only representatives of the Desulfovibrionales have been obtained in pure culture represented by three genera. Two low-to-moderate salt-tolerant alkaliphilic SRB groups include the genera Desulfonatronovibrio (Zhilina et al. 1997) and Desulfonatronum (Pikuta et al. 1998, 2003; Zhilina et al. 2005a, b), and the extremely natronophilic SRB group is represented by the genus Desulfonatronospira (Sorokin et al. 2008). Members of all three genera utilize acetate as a sole carbon source, but cannot use any fatty acids as an electron donor. Their electron donors are H2, formate, pyruvate, lactate, and ethanol (Desulfonatronum). The only known case of sulfate-dependent acetate oxidation under anaerobic haloalkaline conditions is by a syntrophic co-culture of a clostridium “Candidatus Contubernalis alkalaceticum” and Desulfonatronum cooperativum (Zhilina et al. 2005a, b). However, culture-independent molecular studies on soda lake sediments indicated the presence of other SRB groups, including members of the Desulfobacteraceae, which might be functionally different from the ones available in culture (Scholten et al. 2005; Foti et al. 2007).
The obvious knowledge gap on heterotrophic SRB in haloalkaline habitats prompted us to look specifically at the possibility of fatty acid-dependent sulfate reduction in soda lake sediments. Propionate and butyrate were found to stimulate sulfate reduction due to activity of two novel haloalkaliphilic SRB groups outside the Desulfovibrionales. One of them is described here as a novel species of the genus Desulfobotulus.
Methods
Samples
Sediment samples (0–20 cm depth) were obtained from 2 soda lakes with moderate and high salt content in Kulunda Steppe (south-eastern Siberia, Altai, Russia) in July 2007. Some of the brine and pore water properties of the lakes are given in Table 1.
Potential sulfate reduction rate measurements
Potential rates of sulfidogenesis from sulfate were measured in sediment slurries. For this, one part of the sediments from the top 10 cm layer was mixed with 2 parts of the near-bottom brine and incubated anaerobically under argon in duplicate with various electron donors (5 mM) at natural sulfate concentrations and 30°C. 100 μl samples were taken regularly with a syringe for sulfide analysis. The maximum rates of sulfidogenesis were calculated for the linear period of sulfide production over a time period between 24 and 72 h.
Enrichment and cultivation of SRB
Anaerobic enrichment and routine cultivation of SRB from soda lake sediments was performed at 30°C on a mineral medium containing in total 0.6 M Na+ and strongly buffered at pH 10: 22 g l−1 of Na2CO3, 8 g l−1 of NaHCO3, 0.1 M NaCl, and 0.5 g l−1 of K2HPO4. After sterilization, the medium was supplemented with 4 mM NH4Cl, 1 mM MgSO4, 20 mg l−1 of yeast and 1 ml l−1 each of trace metal and vitamin solutions (Pfennig and Lippert 1966). Sodium acetate and propionate were used at 20 mM concentration and butyrate at 10 mM. Electron acceptors were supplied at 10 mM concentrations. 1 mM HS− was added as a reductant. Routine cultivation was performed in 15 ml Hungate tubes with 10 ml medium made anoxic by several cycles of flushing with argon. Growth was monitored by sulfide production. When the sulfide concentration in the enrichments exceeded 5 mM, the cultures were transferred into new medium at 1:100 dilution. After 2–3 successful transfers, the enrichments were serially diluted up to 10−11. Colonies were obtained only in case of butyrate-utilizing SRB. The alkaline solid medium was prepared by 1:1 mixing of the liquid alkaline medium with 4% (w/v) washed agar at 50°C. After cooling to 45°C the medium was supplied with 2 mM HS−/100 μM dithionite, inoculated and poured into Petry dishes in an anaerobic chamber. After cooling, the Petri dishes were placed into closed jars and were incubated outside the chamber. The final culture composition was checked by microscopy, DGGE and sequencing.
The pH dependence was examined at Na+ content of 0.6 M, using the following filter-sterilized mineral media: for pH 6–8, 0.1 M HEPES and NaCl; for pH 8–11, a mixture of sodium bicarbonate/sodium carbonate containing 0.1 M NaCl (Sorokin 2005). Growth resulted in a shift of initial pH values, especially in highly alkaline region. Therefore, final pH values were taken to indicate a suitable range for growth. To study the influence of salt concentration on growth, mineral bases containing 0.1 and 2.0 M of total Na+ were mixed in different proportions.
Analyses
Sulfide was precipitated in 10% (w/v) Zn acetate and analyzed by the methylene blue method after separation from the supernatant (Trüper and Schlegel 1964). VFA were analyzed by anion chromatography (Biotronic IC-1000, Germany; column BT III OS; conductivity detection; 1 mM HCl as eluant, 0.8 ml min−1) after acidic distillation at pH 2 (Christensen and Blackburn 1982). Cell protein was measured by the Lowry method (Lowry et al. 1951) after removal of interfering FeS from the cell pellet by double wash with 0.5 M NaCl, pH 4. Phase contrast photomicrographs were obtained with a Zeiss Axioplan Imaging 2 microscope (Göttingen, Germany). For electron microscopy of total cells they were suspended in 0.1–0.5 M NaCl, fixed with glutaraldehyde (final 3% v/v) and contrasted with 1% (w/v) neutralized phospotungstic acid.
Genetic and phylogenetic analysis
Isolation of genomic DNA and determination of the G + C content of the DNA from pure cultures was performed according to Marmur (1961) and Marmur and Doty (1962). For molecular analysis, the DNA was extracted from the cells using the UltraClean Microbial DNA Isolation kit (MoBio Laboratories Inc., Carlsbad, CA, USA) following the manufacturer’s instructions. The nearly complete 16S rRNA gene was obtained from pure cultures using general bacterial primers GM3f (5′-AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3′) and GM4r (5′-TACGGTTAC-CTTGTTACGACTT-3′) (Schäfer and Muyzer 2001) and the partial 550 bp fragment for the DGGE analysis with the primers 341f + GC/907r (Schäfer and Muyzer 2001). DGGE analysis of the propionate-oxidizing mix culture was performed according to Schäfer and Muyzer (2001), using 30–70% denaturing gradient. The PCR products were purified using the Qiagen Gel Extraction Kit (Qiagen, the Netherlands). The sequences were first compared to sequences stored in GenBank using the BLAST algorithm. Subsequently, the sequences were imported into the ARB software program (Ludwig et al. 2004), automatically aligned, and added to a phylogenetic tree using the Quick-add tool. Sub-trees were then built using the Neighbor Joining algorithm with automatic selected correction settings.
Results and discussion
Potential activity of sulfate reduction in soda lake sediments
Among the simple fatty acids detected in the sediment pore water (Table 1), propionate was definitely the most abundant species indicating a more active accumulation in comparison with its oxidation in the anoxic sediments. This fact is in line with our previous data on the presence of propionigenic bacteria in the sediments of Kulunda soda lakes (Foti et al. 2008), although at present there is no knowledge on any culturable haloalkaliphilic representatives from this group. Basic activity of sulfate reduction (without spiking with an electron donor) was significantly higher in a moderately saline lake (i.e., Tanatar-5) as compared with a hypersaline lake (i.e., Bitter-1) (Fig. 1).
Influence of various electron donors on potential rates of sulfate reduction in sediment slurries from 2 soda lakes in Kulunda Steppe. Hypersaline lake Bitter-1 (black bars), moderately saline lake Tanatar-5 (gray bars). The results are mean from duplicate with deviation in rates less than 10%. Sulfate was present at native concentrations of around 10 mM. Electron donors were added at 5 mM concentration. Dashed lines cut off indicate the basic rates without external electron donor
In both cases, formate and glucose (most probably indirectly through fermentation products) had a maximum stimulating effect on sulfate reduction. Acetate addition had no or only slightly positive effect, which made it difficult to explain basically low acetate content of the pore waters. Most probably, there must be another major sink for anaerobic acetate oxidation in this system. At present, we have evidences that sulfur reduction might be such a sink in anoxic soda lake sediments (unpublished). Propionate significantly stimulated sulfate reduction in the sediment slurries from the Bitter-1 lake and butyrate—in the Tanatar-5 lake. Based on these data, the propionate-amended sediment slurry from Bitter-1 and the butyrate-amended slurry from Tanatar-5 were used to further enrich for fatty acid-utilizing SRB.
Enrichment and identification of a propionate-utilizing SRB
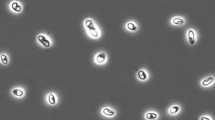
The propionate enrichment with sulfate as electron acceptor after several serial dilutions resulted in a stable sulfidogenic mixed culture dominated by large lemon-shaped coccobacilli, often in chains (Supplementary Figure). The culture formed up to 15 mM sulfide and 8 mM acetate in the presence of 10 mM propionate. Because colony formation was not observed, an attempt was made to separate the dominant organism from a rod-shaped satellite by centrifugation in density gradient using 70% (w/v) Percoll. However, despite successful physical separation, the purified cells of the dominant organism did not grow, due to either inactivation during the long exposure (3 hrs) to Percoll or the obligate syntrophism with the ‘satellite’ bacterium. Replacement of propionate or sulfate by fumarate did not change the outcome. A DGGE analysis showed one dominant and 2 weak bands (not shown). The latter belonged to uncultured Clostridiales, while the dominant band sequence was a member of the Syntrophobacteracea within the Deltaproteobacteria with Syntrophobacter species as closest cultured relatives (93–94% sequence similarity; Fig. 2). The genus Syntrophobacter currently includes four species, mostly from methanogenic bioreactors, with the characteristic potential to utilize propionate as electron donor in presence of sulfate. None of them is either halo- or alkali-philic. From these results, we can conclude that members of the Syntrophobacteraceae are involved in anaerobic sulfate-dependent propionate oxidation at extremely haloalkaline conditions in soda lake sediments.
Phylogenetic position based on 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis of propionate and butyrate-oxidizing haloalkaliphilic SRB from soda lake sediments within the Deltaproteobacteria. ASP1 is a partial sequence from the dominant DGGE band obtained from the propionate-utilizing culture. ASO4-4 is a nearly complete sequence from the pure culture utilizing butyrate. The tree was constructed using maximum likelihood method. The scale bar represents 1 nucleotide changes per 100 nucleotides. The percentage of bootstraps was derived from 1,000 resampling using neighbor-joining algorithm, only values greater than 90% are indicated as black nodes on the branches
Isolation and description of a butyrate-utilizing SRB
An enrichment culture with butyrate as electron donor and sulfate as electron acceptor (initiated from the slurry experiment with sediments from the soda lake Tanatar-5) after several rounds of serial dilution resulted in a binary culture consisted of motile vibrios accumulating PHB-like granules and crescent-shaped long rods. The latter was easily separated by using pyruvate as the sole substrate (acetogenic fermentation) and identified as Tindallia magadii by partial 16S rRNA sequencing (99% sequence similarity). It did not grow with butyrate. The vibrio-shaped bacterium formed separate colonies on original medium with butyrate and sulfate and was isolated from a single colony by using the agar-shake technique. It was designated as strain ASO4-4.
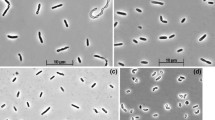
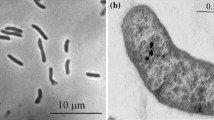
Strain ASO4-4 is a large vibrio motile by means of a single polar flagellum. While growing on fatty acids, it accumulated large amount of PHB-like storage material (Fig. 3a, c). 16S rRNA gene sequencing placed ASO4-4 into the family Desulfobacteraceae within the Deltaproteobacteria with Desulfobotulus sapovorans as the nearest relative. The species name of the latter is indicative of its specialization on utilization of fatty acids. Since the 16S rRNA gene sequence of Db. sapovorans in the GenBank database (M34402) had many nucleotides missing, it was resequenced by us. The sequence identity of strain ASO4-4 to the newly obtained sequence of Db. sapovorans (FJ789839) was 98%, indicating that these two organisms are members of the same genus (Fig. 2). Such close relation warranted a direct phenotypic comparison which demonstrated a general similarity (utilization of straight chain fatty acids), but also many differences between these SRB species. Results of the comparison are presented in Table 2. Obviously, the cells of Db. sapovorans are much thicker than those of ASO4-4 (Fig. 4b, d). Next, the capacity for utilization of various fatty acids in ASO4-4 was more restricted than in Db. sapovorans being limited to C4, C8 and C9. And last, and probably most essential, was the difference in salt and pH tolerance (see Fig. 5 below). The results of DNA–DNA hybridization between the two strains (47% similarity) were in line with the substantial phenotypic difference and indicates that the alkaliphilic isolate is a novel species.
Growth and metabolic characteristics of ASO4-4
When grown at pH 10 with butyrate and sulfate, strain ASO4-4 produced acetate and sulfide as final products parallel to an increase in biomass (Fig. 4) indicating an incomplete mode of butyrate oxidation, similar to Db. sapovorans. The maximum specific growth rate with butyrate was 0.03 h−1. Only sulfate served as an electron acceptor with butyrate and other fatty acids utilized (i.e., caproate, caprilate and nanoate), while with pyruvate, which was the only other electron donor utilized, also thiosulfate and sulfite could serve as electron acceptors. Pyruvate can be fermented with formation of acetate and, presumably, CO2 (high alkalinity prevented its measurement). Addition of sulfate resulted in a twofold increase in final biomass yield on pyruvate accompanied by double decrease in acetate production (after complete utilization of pyruvate). Resting cells of strain ASO4-4 grown with butyrate and sulfate, were able to reduce sulfate, sulfite, thiosulfate and elemental sulfur to sulfide in the presence of butyrate with comparable rates [15–30 nmol HS− (min mg protein)−1] at pH 10.
The pH profile for growth of strain ASO4-4 measured at 0.6 M total Na+ with butyrate and sulfate was indicative of obligate alkaliphilic type with a pH range from 8.7 to 10.7 and an optimum at 9.9–10.1, while washed cells were active within a broader pH range with the same pH optimum (Fig. 5a). The sodium carbonate tolerance both for culture growth and for activity of washed cells at pH 10 was around 2 M Na+ (Fig. 5b), which characterizes strain ASO4-4 as a low salt-tolerant alkaliphile.
In conclusion, this work demonstrated for the first time that soda lake sediments harbor fatty acid-utilizing haloalkaliphilic SRB outside the order Desulfovibrionales. On the basis of distinct phylo(genetic) and phenotypic properties, a butyrate-utilizing SRB isolate, strain ASO4-4, is proposed to be assigned into the new species Desulfobotulus alkaliphilus sp. nov.
Description of Desulfobotulus alkaliphilus sp. nov. alkaliphilus (al.ka.li.phi′lus N. L. n. alkali soda ash; Gr. adj. phylos loving; N. L. masc. adj. alkaliphilus loving alkaline conditions)
Cells are vibrio-shaped, 1 × 3–6 μm, motile by means of a single polar flagellum. Strictly anaerobic with respiratory metabolism. Utilize butyrate (C4), caproate (C6), caprilate (C8) and nanoate (C9) as electron donor with sulfate as electron acceptor. The product of fatty acid utilization is acetate. In addition, it can ferment pyruvate or respire it in the presence of sulfate, thiosulfate and sulfite as electron acceptor. The following electron donors are not utilized: H2, formate, acetate, propionate, valerate, lactate, fumarate, ethanol, isobutyrate, malate, succinate, butanol, isobutanol. Obligately alkaliphilic with a pH range for growth between 8.7 and 10.7 and an optimum at pH 9.9–10.1. Moderately salt-tolerant with a total Na+ range for growth from 0.1 to 1.75 M (optimum at 0.6 M). Mesophilic, with a maximum temperature for growth at 40°C (optimum 32°C). The G + C content of the genomic DNA is 51.3 mol% (T m). The type strain is ASO4-4T (DSM 22078T = UNIQEM U759T). Isolated from sediments of hypersaline soda lake Bitter-1 in Kulunda Steppe (Altai, Russia). The GenBank 16S rRNA gene sequence accession number is FJ788523.
References
Christensen D, Blackburn TH (1982) Turnover of 14C-labelled acetate in marine sediments. Mar Biol 71:113–119
Devereux R, Delaney M, Widdel F, Stahl DA (1989) Natural relationships among sulfate-reducing eubacteria. J Bacteriol 171:6689–6695
Foti M, Sorokin DY, Lomans B, Mussman M, Zakharova EE, Pimenov NV, Kuenen JG, Muyzer G (2007) Diversity, activity and abundance of sulfate-reducing bacteria in saline and hypersaline soda lakes. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:2093–2100
Foti M, Sorokin DY, Zacharova EE, Pimenov NV, Kuenen JG, Muyzer G (2008) Bacterial diversity and activity along a salinity gradient in soda lakes of the Kulunda Steppe (Altai, Russia). Extremophiles 12:133–145
Gorlenko VM, Namsaraev BB, Kulyrova AV, Zavarzina DG, Zhilina TN (1999) Activity of sulfate-reducing bacteria in the sediments of the soda lakes in south-east Transbaikal area. Mikrobiology (Moscow, English Translation) 68:580–586
Kuever J, Rainey FA, Widdel F (2005) Genus IV Desulfobotulus gen. nov. In: Brenner DJ, Kreig NR, Staley JT (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, 2nd edn, vol 2, part C: The Proteobacteria. Springer, USA, p 970
Kulp TR, Hoeft SE, Miller LG, Saltikov C, Murphy JN, Han S, Lanoil B, Oremland RS (2006) Dissimilatory arsenate and sulfate reduction in sediments of two hypersaline, arsenic-rich soda lakes: Mono and Searles Lakes, California. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:6514–6526
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Ludwig W, Strunk O, Westram R, Richter L, Meier H, Yadhukumar BA, Lai T, Steppi S, Jobb G, Forster W, Brettske I, Gerber S, Ginhart W, Gross O, Grumann S, Hermann S, Jost R, Konig A, Liss T, Lûmann R, May M, Nonhoff B, Reichel B, Strehlow R, Stamatakis A, Stuckmann N, Vilbig A, Lenke M, Ludwig T, Bode A, Schleifer KH (2004) ARB: a software environment for sequence data. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1363–1371
Marmur J (1961) A procedure for isolation of DNA from microorganisms. J Mol Biol 3:208–214
Marmur J, Doty P (1962) Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from microorganisms. J Mol Biol 5:109–118
Pfennig N, Lippert KD (1966) Über das Vitamin B12—bedürfnis phototropher Schwefel bacterien. Arch Microbiol 55:245–256
Pikuta EV, Zhilina TN, Zavarzin GA, Kostrikina NA, Osipov GA, Rainey FA (1998) Desulfonatronum lacustre gen. nov., sp. nov.: a new alkaliphilic sulfate-reducing bacterium utilizing ethanol. Microbiology (Moscow, English translation) 67:105–113
Pikuta EV, Hoover RB, Bej AK, Marsic D, Whitman WB, Cleland D, Krader P (2003) Desulfonatronum thiodismutans sp. nov., a novel alkaliphilic, sulfate-reducing bacterium capable of lithoautotrophic growth. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:1327–1332
Schäfer H, Muyzer G (2001) Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis in marine microbial ecology. In: Paul JH (ed) Methods in microbiology. Academic, New York
Scholten JCM, Joye SB, Hollibaugh JT, Murrell JC (2005) Molecular analysis of the sulfate reducing and archaeal community in a meromictic soda lake (Mono Lake, California) by targeting 16S rRNA, mcrA, apsA, and dsrAB genes. Microb Ecol 50:29–39
Sorokin DY (2005) Is there a limit for high-pH growth? Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1405–1406
Sorokin DY, Gorlenko VM, Namsaraev BB, Namsaraev ZB, Lysenko AM, Eshinimaev BT, Khmelenina VN, Trotsenko YA, Kuenen JG (2004) Prokaryotic communities of the north-eastern Mongolian soda lakes. Hydrobiologia 522:235–248
Sorokin DY, Tourova TP, Henstra AM, Stams AJM, Galinski EA, Muyzer G (2008) Sulfidogenesis at extremely haloalkaline conditions by Desulfonatronospira thiodismutans gen. nov., sp. nov., and Desulfonatronospira delicata sp. nov.—a novel lineage of Deltaproteobacteria from hypersaline soda lakes. Microbiology (UK) 154:1444–1453
Trüper HG, Schlegel HG (1964) Sulfur metabolism in Thiorhodaceae. 1. Quantitative measurements on growing cells of Chromatium okenii. Ant van Leeuwenhoek 30:225–238
Zhilina TN, Zavarzin GA, Rainey FA, Pikuta EN, Osipov GA, Kostrikina NA (1997) Desulfonatronovibrio hydrogenovorans gen. nov., sp. nov., an alkaliphilic, sulfate-reducing bacterium. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:144–149
Zhilina TN, Zavarzina DG, Kolganova TV, Tourova TP, Zavarzin GA (2005a) “Candidatus Contubernalis alkalaceticum”, an obligately syntrophic alkaliphilic bacterium capable of anaerobic acetate oxidation in a coculture with Desulfonatronum cooperativum. Microbiology (Moscow, English Translation) 74:695–703
Zhilina TN, Zavarzina DG, Kuever J, Lysenko AM, Zavarzin GA (2005b) Desulfonatronum cooperativum sp.nov., a novel hydrogenotrophic, alkaliphilic, sulfate-reducing bacterium, from a syntrophic culture growing on acetate. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1001–1006
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by RFBR (10-04-00152). We are grateful to A. Galushko and F. Widdel for providing active culture of Desulfobotulus sapovorans and to I. I. Rusanov for analysis of fatty acids in the sediments.
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by A. Oren.
Nucleotide sequence accession number: The GenBank/EMBL accession numbers of the 16S rRNA gene sequences determined in this study are FJ788523, FJ789839 and GQ423597.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/2.0), which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
About this article
Cite this article
Sorokin, D.Y., Detkova, E.N. & Muyzer, G. Propionate and butyrate dependent bacterial sulfate reduction at extremely haloalkaline conditions and description of Desulfobotulus alkaliphilus sp. nov.. Extremophiles 14, 71–77 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-009-0288-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-009-0288-5