Abstract
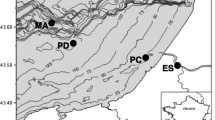
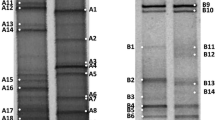
Here we describe the diversity and activity of sulfate reducing bacteria along a salinity gradient in four different soda lakes from the Kulunda Steppe (South East Siberia, Russia). For this purpose, a combination of culture-dependent and independent techniques was applied. The general bacterial and SRB diversity were analyzed by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) targeting the 16S rDNA gene. DNA was used to detect the microbial populations that were present in the soda lake sediments, whereas ribosomal RNA was used as a template to obtain information on those that were active. Individual DGGE bands were sequenced and a phylogenetic analysis was performed. In addition, the overall activity of SRB was obtained by measuring the sulfate reduction rates (SRR) and their abundance was estimated by serial dilution. Our results showed the presence of minor, but highly active microbial populations, mostly represented by members of the Proteobacteria. Remarkably high SRR were measured at hypersaline conditions (200 g L−1). A relatively high viable count indicated that sulfate reducing bacteria could be highly active in hypersaline soda lakes. Furthermore, the increase of sodium carbonate/bicarbonate seemed to affect the composition of the microbial community in soda lakes, but not the rate of sulfate reduction.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benlloch S, Lopez-Lopez A, Casamayor EO, Ovreas L, Goddard V, Daae FL, Smerdon G, Massana R, Joint I, Thingstad F, Pedros-Alio C, Rodriguez-Valera F (2002) Prokaryotic genetic diversity throughout the salinity gradient of a coastal solar saltern. Environ Microbiol 4:349–360
Braid MD, Daniels ML, Kitts CL (2003) Removal of PCR inhibitors from soil DNA by chemical flocculation. J Microbiol Methods 52:389–393
Brandt KK, Vester F, Jensen AN, Ingvorsen K (2001) Sulfate reduction dynamics and enumeration of sulfate-reducing bacteria in hypersaline sediments of the Great Salt Lake (Utah, USA). Microb Ecol 41:1–11
Brinkhoff T, Santegoeds CM, Sahm K, Kuever J, Muyzer G (1998) Polyphasic approach to study the diversity and vertical distribution of sulfur-oxidizing Thiomicrospira species in coastal sediments of the German Wadden Sea. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4650–4657
Casamayor EO, Massana R, Benlloch S, Ovreas L, Diez B, Goddard VJ, Gasol JM, Joint I, Rodriguez-Valera F, Pedros-Alio C (2002) Changes in archaeal, bacterial and eukaryal assemblages along a salinity gradient by comparison of genetic fingerprinting methods in a multipond solern saltern. Environ Microbiol 4:338–348
Crump BC, Hopkinson CS, Sogin ML, Hobbie JE (2004) Microbial biogeography along an estuarine salinity gradient: combined influences of bacterial growth and residence time. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:1494–1505
Daly K, Sharp RJ, McCarthy AJ (2000) Development of oligonucleotide probes and PCR primers for detecting phylogenetic subgroups of sulfate-reducing bacteria. Microbiology 146:1693–1705
Dar SA, Kuenen JG, Muyzer G (2005) Nested PCR-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis approach to determine the diversity of sulfate-reducing bacteria in complex microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:2325–2330
Duckworth AW, Grant WD, Jones BE, van Steenbergen R (1996) Phylogenetic diversity of soda lake alkaliphiles. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 19:181–191
Foti M, Sorokin DY, Lomans B, Mussmann M, Zacharova EE, Pimenov NV, Kuenen JK, Muyzer G (2007) Diversity, activity and abundance of sulfate-reducing bacteria in saline and hypersaline soda lakes. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:2093–2100
Freitas M, Rainey FA, Nobre MF, Silvestre AJD, da Costa MS (2003) Tepidimonas aquatica sp. nov., a new slightly thermophilic β-proteobacterium isolated from a hot water tank. Syst Appl Microbiol 26:376–381
Gorlenko V, Tsapin A, Namsaraev Z, Teal T, Tourova T, Engler D, Mielke R, Nealson K (2004) Anaerobranca californiensis sp.nov., an anaerobic, alkalithermophilic , fermentative bacterium isolated froma hot spring on Mono lake. Int J Syst Evol Micriobiol 54:739–743
Häse CC, Fedorova ND, Galperin MY, Dibrov PA (2001) Sodium ion cycle in bacterial pathogens: evidences from cross-genome comparison. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 65:353–370
Humayoun SB, Bano N, Hollibaugh JT (2003) Depth distribution of microbial diversity in Mono Lake, a meromictic soda lake in California. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1030–1042
Imhoff JF, Sahl HG, Soliman GSH, Truper HG (1979) The Wadi Natrun: chemical composition and microbial mass developments in alkaline brines of eutrophic desert lakes. Geomicrobiol J 1:219–234
Issachenko BL (1951) Chloride, sulfate and soda lakes of Kulunda steppe and its biogenic processes. In: Selected works, vol 2. Academy of Sciences USSR, Leningrad (in Russian), pp 143-162
Jones BE, Grant WD, Duckworth AW, Owenson GG (1998) Microbial diversity of soda lakes. Extremophiles 2:191–200
Kjeldsen KU, Loy A, Jakobsen TF, Thomsen TR, Wagner M, Ingvorsen K (2007) Diversity of sulfate-reducing bacteria from an extreme hypersaline sediment, Great Salt Lake (Utah). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 60:287–298
Kulp TR, Han S, Saltikov XW, Lanoil BD, Zargar K, Oremland RS (2007) Effects of imposed salinity gradient on dissimilatory arsenate reduction, sulphate reduction and other microbial processed in sediments from two California soda lakes. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5130–5137
Lein A, Pimenov N, Guillou C, Martin J-M, Lancelot C, Rusanov I, Yusupov S, Miller Y, Ivanov M (2002) Seasonal dynamics of the sulfate reduction rate on the north-western Black Sea shelf. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 54:385–401
Ludwig W, Strunk O, Westram R, Richter L, Meier H, Yadhukumar, Buchner A, Lai T, Steppi S, Jobb G, Forster W, Brettske I, Gerber S, Ginhart W, Gross O, Grumann S, Hermann S, Jost R, Konig A, Liss T, Lûmann R, May M, Nonhoff B,Reichel B, Strehlow R, Stamatakis A ,Stuckmann N, Vilbig A, Lenke M, Ludwig T, Bode A, Schleifer KH (2004) ARB: a software environment for sequence data. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1363–1371
Ma Y, Zhang W, Xue Y, Zhou P, Ventosa A, Grant WD (2004) Bacterial diversity of the Inner Mongolian Baer Soda Lake as revealed by 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis. Extremophiles 8:45–51
Muyzer G, deWaal EC, Uitterlinden A (1993) Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction—amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:695–700
Nübel U, Garcia-Pichel F, Clavero E, Muyzer G (2000) Matching molecular diversity and ecophysiology of benthic cyanobacteria and diatoms in communities along a salinity gradient. Environ Microbiol 2:217–226
Ollivier B, Caumette P, Garcia J, Mah RA (1994) Anaerobic bacteria from hypersaline environments. Microbiol Rev 58:27–38
Oren A (1999) Bioenergetic aspects of halophilism. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63:334–348
Rees HC, Grant WD, Jones BE, Heaphy S (2004) Diversity of Kenyan soda lake alkaliphiles assesses by molecular methods. Extremophiles 8:63–71
Schafer H, Muyzer G (2001) Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis in marine microbial ecology. In: Paul JH (ed) Methods in microbiology. Academic, New York
Scholten JCM, Joye SB, Hollibaugh JT, Murrell JC (2005) Molecular analysis of the sulfate-reducing and archaeal community in a meromictic soda lake (mono Lake, California) by targeting 16SrRNA, mcrA, apsA and dsrAB genes. Microb Ecol 50:29–39
Schultz GE, Ducklow H (2001) Changes in bacterioplankton metabolic capabilities along a salinity gradient in the York River estuary, Virginia, USA. Aquat Microb Ecol 22:167–174
Sörensen KB, Canfield DE, Oren A (2004) Salinity responses of benthic microbial communities in a solar saltern (Eilat, Israel). Appl Environ Microbiol 70:1608–1616
Sorokin DY, Kuenen JK (2005a) Haloalkaliphilic sulphur-oxidizing bacteria in soda lakes. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29:685–702
Sorokin DY, Kuenen JG (2005b) Chemolithotrophic haloalkaliphiles from soda lakes. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 52:287–295
Sorokin DY, Gorlenko VM, Namsaraev BB, Namsaraev ZB, Lysenko AM, Eshinimaev BT, Khmelenina VN, Trotsenko YA, Kuenen JG (2004) Prokaryotic communities of the north-eastern Mongolian soda lakes. Hydrobiologia 522:235–248
Sorokin DY, Foti M, Pinkart HC, Muyzer G (2007a) Sulfur-oxidizing bacteria in Soap Lake (Washington State), a meromictic, halosaline lake with an unprecedented high sulphide content. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:451–455
Sorokin DY, van Pelt S, Tourova TP, Muyzer G (2007b) Microbial isobutyronitrile utilization at haloalkaline conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5574–5579
Suzuki MT, Giovannoni SJ (1996) Bias caused by template annealing in the amplification of mixtures of 16S rRNA genes by PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:625–630
Trüper HG, Schlegel HG (1964) Sulphur metabolism in Thiorhodaceae. Quantitative measurements on growing cells of Chromatium okenii. Antonie van Leeuwenh 30:225–238
Wani AA, Surakasi VP, Siddharth J, Raghavan RG, Patole MS, Ranade D, Shouche YS (2006) Molecular analysis of microbial diversity associated with the Lonar soda lake in India: an impact crater in a basalt area. Res Microbiol 157:928–937
Wu QL, Zwart G, Schauer M, Kamst-van Agterveld MP, Hahn MW (2006) Bacterioplankton community composition along a salinity gradient of sixteen high-mountain lakes on the Tibetan Plateau, China. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:5478–5485
Zavarzin GA, Zhilina TN, Kevbrin VV (1999) The alkaliphilic microbial community and its functional diversity. Microbiology 63:503–521
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Dutch Science Foundation for Applied Research (STW) and by NWO-RFBR (grant 047.011.2004.010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by K. Horikoshi.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Foti, M.J., Sorokin, D.Y., Zacharova, E.E. et al. Bacterial diversity and activity along a salinity gradient in soda lakes of the Kulunda Steppe (Altai, Russia). Extremophiles 12, 133–145 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-007-0117-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-007-0117-7