Abstract
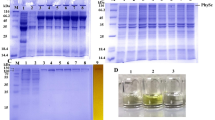
The genome of the hyperthermophilic bacterium Thermotoga maritima contains the genes that encode core subunits of the protein translocase, a complex consisting of the molecular motor SecA and the protein conducting pore SecYE. In addition, we identified an erroneous sequence in the genome encoding for a putative secG gene. The genes of the T. maritima translocase subunits were overexpressed in Escherichia coli and purified to homogeneity. T. maritima SecA showed a basal thermostable ATPase activity that was stimulated up to 4-fold by phospholipids with an optimum at 74°C. Membrane vesicles and proteoliposomes containing SecYE or SecYEG supported 2- to 4-fold stimulation of the precursor dependent SecA ATPase activity. Imaging of small two-dimensional crystals of the SecYE complex using electron microscopy showed square-shaped particles with a side-length of about 6 nm. These results demonstrate that in T. maritima a highly thermostable translocase complex is operational.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Breyton C, Haase W, Rapoport TA, Kuhlbrandt W, Collinson I (2002) Three-dimensional structure of the bacterial protein-translocation complex SecYEG. Nature 418:662–665
Brundage L, Hendrick JP, Schiebel E, Driessen AJM, Wickner W (1990) The purified E. coli integral membrane protein SecY/E is sufficient for reconstitution of SecA-dependent precursor protein translocation. Cell 62:649–657
Cunningham K, Wickner WT (1989) Detergent disruption of bacterial inner membranes and recovery of protein translocation activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:8673–8677
Del Tito BJ Jr, Ward JM, Hodgson J, Gershater CJ, Edwards H, Wysocki LA, Watson FA, Sathe G, Kane JF (1995) Effects of a minor isoleucyl tRNA on heterologous protein translation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 177:7086–7091
Ding H, Hunt JF, Mukerji I, Oliver D (2003) Bacillus subtilis SecA ATPase exists as an antiparallel dimer in solution. Biochemistry 42:8729–8738
van der Does C, den Blaauwen T, De Wit JG, Manting EH, Groot NA, Fekkes P, Driessen AJM (1996) SecA is an intrinsic subunit of the Escherichia coli preprotein translocase and exposes its carboxyl terminus to the periplasm. Mol Microbiol 22:619–629
van der Does C, Manting EH, Kaufmann A, Lutz M, Driessen AJM (1998) Interaction between SecA and SecYEG in micellar solution and formation of the membrane-inserted state. Biochemistry 37:201–210
Driessen AJM, Wickner W (1991) Proton transfer is rate-limiting for translocation of precursor proteins by the Escherichia coli translocase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:2471–2475
Driessen AJM, Manting EH, van der Does C (2001) The structural basis of protein targeting and translocation in bacteria. Nature Struct Biol 8:492–498
Fekkes P, De Wit JG, van der Wolk JP, Kimsey HH, Kumamoto CA, Driessen AJM (1998) Preprotein transfer to the Escherichia coli translocase requires the co-operative binding of SecB and the signal sequence to SecA. Mol Microbiol 29:1179–1190
Fekkes P, De Wit JG, Boorsma A, Friesen RH, Driessen AJM (1999) Zinc stabilizes the SecB binding site of SecA. Biochemistry 38:5111–5116
Hanahan D (1983) Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol 166:557–580
Hendrick JP, Wickner W (1991) SecA protein needs both acidic phospholipids and SecY/E protein for functional high-affinity binding to the Escherichia coli plasma membrane. J Biol Chem 266:24596–24600
Huber R, Langworthy TA, Konig H, Thomm M, Woese CR, Sleytr UB, Stetter KO (1986) Thermotoga maritima sp. nov. represents a new genus of unique extremly thermophilic eubacteria growing up to 90°C. Arch Microbiol 144:324–333
Hunt JF, Weinkauf S, Henry L, Fak JJ, McNicholas P, Oliver DB, Deisenhofer J (2002) Nucleotide control of interdomain interactions in the conformational reaction cycle of SecA. Science 297:2018–2026
Kim R, Sandler SJ, Goldman S, Yokota H, Clark AJ, Kim SH (1998) Overexpression of archaeal proteins in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Lett 20:207–210
Lanzetta PA, Alvarez LJ, Reinach PS, Candia OA (1979) An improved assay for nanomole amounts of inorganic phosphate. Anal Biochem 100:95–97
Lévy D, Mosser G, Lambert O, Moeck GS, Bald D, Rigaud J-L (1999) Two-dimensional crystallization on lipid layer: a successful approach for membrane proteins. J Struct Biol 127:44–52
Lill R, Cunningham K, Brundage LA, Ito K, Oliver D, Wickner W (1989) SecA protein hydrolyzes ATP and is an essential component of the protein translocation ATPase of Escherichia coli. EMBO J 8:961–966
Lill R, Dowhan W, Wickner W (1990) The ATPase activity of SecA is regulated by acidic phospholipids, SecY, and the leader and mature domains of precursor proteins. Cell 60:271–280
Lo SL, Chang EL (1990) Purification and characterization of a liposomal-forming tetraether lipid fraction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 167:238–243
Manting EH, Driessen AJM (2000) Escherichia coli translocase: the unravelling of a molecular machine. Mol Microbiol 37:226–238
Manting EH, van der Does C, Remigy H, Engel A, Driessen AJM (2000) SecYEG assembles into a tetramer to form the active protein translocation channel. EMBO J 19:852–861
Meyer TH, Menetret JF, Breitling R, Miller KR, Akey CW, Rapoport TA (1999) The bacterial SecY/E translocation complex forms channel-like structures similar to those of the eukaryotic Sec61p complex. J Mol Biol 285:1789–1800
Mori H, Tsukazaki T, Masui R, Kuramitsu S, Yokoyama S, Johnson AE, Kimura Y, Akiyama Y, Ito K (2003) Fluorescence resonance energy transfer analysis of protein translocase. SecYE from Thermus thermophilus HB8 forms a constitutive oligomer in membranes. J Biol Chem 278:14257–14264
Nishiyama K, Mizushima S, Tokuda H (1993) A novel membrane protein involved in protein translocation across the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. EMBO J 12:3409–3415
Nishiyama K, Hanada M, Tokuda H (1994) Disruption of the gene encoding p12 (SecG) reveals the direct involvement and important function of SecG in the protein translocation of Escherichia coli at low temperature. EMBO J 13:3272–3277
Saxton WO (1996) Semper: distortion compensation, selective averaging, 3-D reconstruction, and transfer function correction in a highly programmable system. J Struct Biol 116:230–236
Schiebel E, Driessen AJM, Hartl FU, Wickner W (1991) Δ μ H+ and ATP function at different steps of the catalytic cycle of preprotein translocase. Cell 64:927–939
Schleper C, Holz I, Janekovic D, Murphy J, Zillig W (1995) A multicopy plasmid of the extremely thermophilic archaeon Sulfolobus effects its transfer to recipients by mating. J Bacteriol 177:4417–4426
Sharma V, Arockiasamy A, Ronning DR, Savva CG, Holzenburg A, Braunstein M, Jacobs WR Jr, Sacchettini JC (2003) Crystal structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis SecA, a preprotein translocating ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:2243–2248
Van de Vossenberg JLCM, Ubbink-Kok T, Elferink MGL, Driessen AJM, Konings, WN (1995) Ion permeability of the cytoplasmic membrane limits the maximum growth temperature of bacteria and archaea. Mol Microbiol 18:925–932
Van den Berg B, Clemons WM Jr, Collinson I, Modis Y, Hartmann E, Harrison SC, Rapoport TA (2004) X-ray structure of a protein-conducting channel. Nature 427:36–44
Acknowledgements
M. G. Pretz and H. Remigy were supported by the MEMBMACS training network and funded by EU TMR contract HPRN-CT-2000-00075. S.V. Albers was supported by a VENI-grant from the Dutch Science Organization (NWO). We would like to thank to Dr. R Huber and Dr. M. Thomm from the University of Regensburg, Germany, for kindly providing us with T. maritima cells, and Dr. C. van der Does for valuable discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by G. Antranikian
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pretz, M.G., Remigy, H., Swaving, J. et al. Functional and structural characterization of the minimal Sec translocase of the hyperthermophile Thermotoga maritima. Extremophiles 9, 307–316 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-005-0446-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-005-0446-3