Abstract
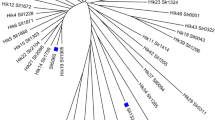
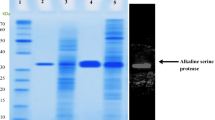
A histidine acid phosphatase (HAP) (PhySc) with 99.50% protein sequence similarity with PHO5 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae was expressed functionally with the molecular mass of ∼110 kDa through co-expression along with the set of molecular chaperones dnaK, dnaJ, GroESL. The purified HAP illustrated the optimum activity of 28.75 ± 0.39 U/mg at pH 5.5 and 40 ˚C. The Km and Kcat values towards calcium phytate were 0.608 ± 0.09 mM and 650.89 ± 3.6 s− 1. The half-lives (T1/2) at 55 and 60 ˚C were 2.75 min and 55 s, respectively. The circular dichroism (CD) demonstrated that PhySc includes 30.5, 28.1, 21.3, and 20.1% of random coils, α-Helix, β-Turns, and β-Sheet, respectively. The Tm recorded by CD for PhySc was 56.5 ± 0.34˚C. The molecular docking illustrated that His59 and Asp322 act as catalytic residues in the PhySc. MD simulation showed that PhySc at 40 ˚C has higher structural stability over those of the temperatures 60 and 80 ˚C that support the thermodynamic in vitro investigations. Secondary structure content results obtained from MD simulation indicated that PhySc consists of 34.03, 33.09, 17.5, 12.31, and 3.05% of coil, helix, turn, sheet, and helix310, respectively, which is almost consistent with the experimental results.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that all relevant data are included in this article.
References
Allouche A (2012) Software news and updates Gabedit — a graphical user interface for computational chemistry softwares. J Comput Chem 32:174–182. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc
Alnoch RC, Stefanello AA, Paula Martini V et al (2018) Co-expression, purification and characterization of the lipase and foldase of Burkholderia contaminans LTEB11. Int J Biol Macromol 116:1222–1231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.05.086
Andlid TA, Veide J, Sandberg A (2004) Metabolism of extracellular inositol hexaphosphate (phytate) by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Int J Food Microbiol 97:157–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2004.04.016
Andreeva N, Ledova L, Ryasanova L et al (2019) The acid phosphatase Pho5 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is not involved in polyphosphate breakdown. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 64:867–873. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-019-00702-6
Ashraf NM, Krishnagopal A, Hussain A et al (2019) Engineering of serine protease for improved thermostability and catalytic activity using rational design. Int J Biol Macromol 126:229–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.12.218
Bae HD, Yanke LJ, Cheng KJ, Selinger LB (1999) A novel staining method for detecting phytase activity. J Microbiol Methods 39:17–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-7012(99)00096-2
Balchin D, Hayer-Hartl M, Hartl FU (2020) Recent advances in understanding catalysis of protein folding by molecular chaperones. FEBS Lett 594:2770–2781. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.13844
Bhatwa A, Wang W, Hassan YI et al (2021) Challenges associated with the formation of recombinant protein inclusion bodies in Escherichia coli and strategies to address them for industrial applications. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2021.630551
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Chen M, Song F, Qin Y et al (2022) Improving thermostability and catalytic activity of glycosyltransferase from Panax ginseng by semi-rational design for rebaudioside D synthesis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 10:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2022.884898
Craig DB, Dombkowski AA (2013) Disulfide by Design 2.0: a web-based tool for disulfide engineering in proteins. BMC Bioinformatics 14:346. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-346
Dash R, Ali MC, Dash N et al (2019) Structural and dynamic characterizations highlight the deleterious role of SULT1A1 R213H polymorphism in substrate binding. Int J Mol Sci 20:6256. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20246256
De Marco A, Ferrer-Miralles N, Garcia-Fruitós E et al (2019) Bacterial inclusion bodies are industrially exploitable amyloids. FEMS Microbiol Rev 43:53–72. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsre/fuy038
Dersjant-Li Y, Awati A, Schulze H, Partridge G (2015) Phytase in non-ruminant animal nutrition: a critical review on phytase activities in the gastrointestinal tract and influencing factors. J Sci Food Agric 95:878–896. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.6998
Dvořáková J, Volfová O, Kopecký J (1997) Characterization of Phytase produced by Aspergillus Niger. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 42:349–352. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02816948
Eddehech A, Rahier R, Smichi N et al (2021) Heterologous expression, kinetic characterization and molecular modeling of a new sn-1,3-regioselective triacylglycerol lipase from Serratia sp. W3. Process Biochem 103:87–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2021.02.009
Fonseca-Maldonado R, Maller A, Bonneil E et al (2014) Biochemical properties of glycosylation and characterization of a histidine acid phosphatase (phytase) expressed in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr Purif 99:43–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2014.03.006
Goodell V, McNeel D, Disis ML (2008) His-tag ELISA for the detection of humoral tumor-specific immunity. BMC Immunol 9:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2172-9-23
Gotresmant MAXE, Nikiforov V (1992) GroEL/GroES 89:10341–10344. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.89.21.10341
Greiner R (2006) Phytate-degrading enzymes: regulation of synthesis in microorganisms and plants. In: Inositol Phosphates: Linking Agriculture and the Environment. pp 78–96
Gribenko AV, Patel MM, Liu J et al (2009) Rational stabilization of enzymes by computational redesign of surface charge-charge interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:2601–2606. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0808220106
Gupta RK, Gangoliya SS (2015) Reduction of phytic acid and enhancement of bioavailable micronutrients in food grains. 52:676–684. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-013-0978-y
Hamdan SH, Maiangwa J, Nezhad NG et al (2023) Knotting terminal ends of mutant T1 lipase with disulfide bond improved structure rigidity and stability. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12396-5
Han W, Christen P (2003) Mechanism of the targeting action of DnaJ in the DnaK molecular chaperone system. J Biol Chem 278:19038–19043. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M300756200
Heinonen JK, Lahti RJ (1981) A new and convenient colorimetric determination of inorganic orthophosphate and its application to the assay of inorganic pyrophosphatase. Anal Biochem 113:313–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(81)90082-8
Hesampour A, Ehsan S, Siadat R (2014) Enhancement of thermostability and kinetic efficiency of Aspergillus Niger PhyA phytase by site-directed mutagenesis. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1440-y
Ji W, Yuan C, Chakraborty P et al (2019) Stoichiometry-controlled secondary structure transition of amyloid-derived supramolecular dipeptide co-assemblies. Commun Chem. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42004-019-0170-z. 2:
Kaur J, Kumar A, Kaur J (2018) Strategies for optimization of heterologous protein expression in E. Coli: roadblocks and reinforcements. Int J Biol Macromol 106:803–822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.08.080
Kollman PA, Massova I, Reyes C et al (2000) Calculating structures and free energies of complex molecules: combining molecular mechanics and continuum models. Acc Chem Res 33:889–897. https://doi.org/10.1021/ar000033j
Krieger E, Vriend G (2015) New ways to boost molecular dynamics simulations. J Comput Chem 36:996–1007. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.23899
Kumar V, Nath A, Verma P, Sangwan P (2017) β-propeller phytases: diversity, catalytic attributes, current developments and potential biotechnological applications. Int J Biol Macromol 98:595–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.01.134
Laskowski RA, MacArthur MW, Moss DS, Thornton JM (1993) PROCHECK: a program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J Appl Crystallogr 26:283–291. https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889892009944
Li G, Chen Y, Fang X et al (2018) Identification of a hot-spot to enhance Candida rugosa lipase thermostability by rational design methods. RSC Adv 8:1948–1957. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra11679a
Li W, Li S, Hu Y et al (2019) Impact of hot alkali modification conditions on secondary structure of peanut protein and embedding rate of curcumin. Food Sci Hum Wellness 8:283–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fshw.2019.05.004
Lim D, Golovan S, Forsberg CW, Jia Z (2000) Crystal structures of Escherichia coli phytase and its complex with phytate. Nat Struct Biol 7:108–113. https://doi.org/10.1038/72371
Liu Q, Huang Q, Lei XG, Hao Q (2004) Crystallographic snapshots of aspergillus fumigatus phytase, revealing its enzymatic dynamics. Structure 12:1575–1583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2004.06.015
Lovell SC, Davis IW, Arendall WB et al (2003) Structure validation by Cα geometry: φ,ψ and Cβ deviation. Proteins Struct Funct Genet 50:437–450. https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.10286
Makolomakwa M, Puri AK, Permaul K, Singh S (2017) Thermo-acid-stable phytase-mediated enhancement of bioethanol production using Colocasia esculenta. Bioresour Technol 235:396–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.03.157
Marchenkov VV, Semisotnov GV (2009) GroEL-assisted protein folding: does it occur within the chaperonin inner cavity? Int J Mol Sci 10:2066–2083. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms10052066
Mital S, Christie G, Dikicioglu D (2021) Recombinant expression of insoluble enzymes in Escherichia coli: a systematic review of experimental design and its manufacturing implications. Microb Cell Fact 20:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-021-01698-w
Nagi AD, Regan L (1997) An inverse correlation between loop length and stability in a four-helix-bundle protein. Fold Des 2:67–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-0278(97)00007-2
Nezhad NG, Abd Rahman RNZ, Normi YM et al (2020) Integrative structural and computational biology of Phytases for the animal feed industry. Catalysts 10:1–24. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10080844
Nezhad NG, Abd Rahman RNZ, Normi YM et al (2023a) Recent advances in simultaneous thermostability-activity improvement of industrial enzymes through structure modification. Int J Biol Macromol 232:123440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.123440
Nezhad NG, Rahman RNZRA, Normi YM et al (2023b) Isolation, screening and molecular characterization of phytase-producing microorganisms to discover the novel phytase. Biol (Bratisl). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-023-01391-w
Niu C, Luo H, Shi P et al (2016) N-glycosylation improves the pepsin resistance of histidine acid phosphatase phytases by enhancing their stability at acidic pHs and reducing Pepsin’s accessibility to its cleavage sites. Appl Environ Microbiol 82:1004–1014. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02881-15
Pal Roy M, Mazumdar D, Dutta S et al (2016) Cloning and expression of phytase appA gene from Shigella sp. CD2 in Pichia pastoris and comparison of properties with recombinant enzyme expressed in E. Coli. PLoS ONE 11:e0145745. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0145745
Peprah Addai F, Wang T, Kosiba AA et al (2020) Integration of elastin-like polypeptide fusion system into the expression and purification of Lactobacillus sp. B164 β-galactosidase for lactose hydrolysis. Bioresour Technol 311:123513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123513
Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC et al (2004) UCSF Chimera - A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem 25:1605–1612. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.20084
Pulido IY, Prieto E, Pieffet GP et al (2020) Functional heterologous expression of mature lipase lipa from Pseudomonas aeruginosa psa01 in Escherichia coli shuffle and bl21 (De3): effect of the expression host on thermal stability and solvent tolerance of the enzyme produced. Int J Mol Sci 21:1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21113925
Ragon M, Hoh F (2009) Structure of Debaryomyces castellii CBS 2923 phytase. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 321–326. https://doi.org/10.1107/S1744309109008653
Rivera I, Robles M, Mateos-Díaz JC et al (2017) Functional expression, extracellular production, purification, structure modeling and biochemical characterization of Carica papaya lipase 1. Process Biochem 56:109–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2017.02.009
Rosano GL, Ceccarelli EA (2014) Recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli: advances and challenges. Front Microbiol 5:1–17. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00172
Saab-Rincón G, Alwaseem H, Guzmán-Luna V et al (2018) Stabilization of the reductase domain in the catalytically self-sufficient cytochrome P450BM3 by consensus-guided mutagenesis. ChemBioChem 19:622–632. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201700546
Sambrook J, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, second edi. New York, USA
Sanikommu S, Pasupuleti M, Vadalkonda L (2014) Comparison of phosphate estimating methods in the presence of phytic acid for the determination of phytase activity. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 44:231–241. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826068.2013.797434
Shin S, Ha NC, Oh BC et al (2001) Enzyme mechanism and catalytic property of β propeller phytase. Structure 9:851–858. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0969-2126(01)00637-2
Sievers F, Wilm A, Dineen D et al (2011) Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using clustal omega. Mol Syst Biol 7:539. https://doi.org/10.1038/msb.2011.75
Singh B, Satyanarayana T (2015) Fungal phytases: characteristics and amelioration of nutritional quality and growth of non-ruminants. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl) 99:646–660. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpn.12236
Singh H, Felts RL, Schuermann JP et al (2009) Crystal structures of the histidine acid phosphatase from Francisella tularensis provide insight into substrate recognition. J Mol Biol 394:893–904. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2009.10.009
Singh B, Sharma KK, Kumari A et al (2018) Molecular modeling and docking of recombinant HAP-phytase of a thermophilic mould Sporotrichum thermophile reveals insights into molecular catalysis and biochemical properties. Int J Biol Macromol 115:501–508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.04.086
Sparvoli F, Cominelli E (2015) Seed biofortification and phytic acid reduction: a conflict of interest for the plant? Plants 4:728–755. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants4040728
Teufel F, Almagro Armenteros JJ, Johansen AR et al (2022) SignalP 6.0 predicts all five types of signal peptides using protein language models. Nat Biotechnol 40:1023–1025. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-021-01156-3
Tsao GT, Zheng Y, Lu J, Gong CS (1997) Adsorption of heavy metal ions by immobilized phytic acid. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 63–65:731–741. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02920471
Tyagi NK, Fenton WA, Horwich AL (2009) GroEL/GroES cycling: ATP binds to an open ring before substrate protein favoring protein binding and production of the native state. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:20264–20269. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0911556106
Ushasree MV, Vidya J, Pandey A (2014) Gene cloning and soluble expression of Aspergillus Niger phytase in E. Coli cytosol via chaperone co-expression. Biotechnol Lett 36:85–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-013-1322-3
Vicente AI, Viña-Gonzalez J, Mateljak I et al (2020) Enhancing thermostability by modifying flexible surface loops in an evolved high-redox potential laccase. AIChE J 66:e16747. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.16747
Wallace AC, Laskowski RA, Thornton JM (1995) Ligplot: a program to generate schematic diagrams of protein-ligand interactions. Protein Eng Des Sel 8:127–134. https://doi.org/10.1093/protein/8.2.127
Xia Y, Li X, Yang L et al (2021) Development of thermostable sucrose phosphorylase by semi-rational design for efficient biosynthesis of alpha-D-glucosylglycerol. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105:7309–7319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11551-0
Yao MZ, Wang X, Wang W et al (2013) Improving the thermostability of Escherichia coli phytase, appA, by enhancement of glycosylation. Biotechnol Lett 35:1669–1676. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-013-1255-x
Yao D, Fan J, Han R et al (2020) Enhancing soluble expression of sucrose phosphorylase in Escherichia coli by molecular chaperones. Protein Expr Purif 169:105571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2020.105571
Yokoyama H, Mizutani R, Noguchi S, Hayashida N (2019) Structural and biochemical basis of the formation of isoaspartate in the complementarity-determining region of antibody 64 M-5 Fab. Sci Rep 9:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-54918-0
Yu H, Yan Y, Zhang C, Dalby PA (2017) Two strategies to engineer flexible loops for improved enzyme thermostability. Sci Rep 7:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep41212
Zhou CY, Guo X, Wang ST et al (2011) Effects of temperature and additives on stability and spectrum of a therapeutic fibroblast growth factor. DARU. J Pharm Sci 19:138–144
Funding
This work has received funding from Ministry of Higher Education (MOHE) under Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FRGS/1/2019/STG05/UPM/02/15).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NGN and TCL conceived, designed and wrote the manuscript. NGN performed the research, tabulated, and analyzed the data. SZBJ, RNZRA, NMY, SNO, FMS, and NMI contributed for providing the materials and chemicals.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nezhad, N.G., Jamaludin, S.Z.B., Rahman, R.N.Z.R.A. et al. Functional expression, purification, biochemical and biophysical characterizations, and molecular dynamics simulation of a histidine acid phosphatase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 40, 171 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-024-03970-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-024-03970-8