Abstract
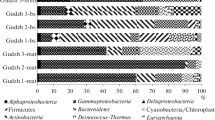
The microbial diversity in maritime meltwater pond sediments from Bratina Island, Ross Sea, Antarctica was investigated by 16S rDNA-dependent molecular phylogeny. Investigations of the vertical distribution, phylogenetic composition, and spatial variability of Bacteria and Archaea in the sediment were carried out. Results revealed the presence of a highly diverse bacterial population and a significantly depth-related composition. Assessment of 173 partial 16S rDNA clones analyzed by amplified rDNA restriction analysis (ARDRA) using tetrameric restriction enzymes (HinP1I 5′G∇CGC3′and Msp I. 5′C∇CGG3′, BioLabs) revealed 153 different bacterial OTUs (operational taxonomic units). However, only seven archaeal OTUs were detected, indicating low archaeal diversity. Based on ARDRA results, 30 bacterial clones were selected for sequencing and the sequenced clones fell into seven major lineages of the domain Bacteria; the α, γ, and δ subdivisions of Proteobacteria, the Cytophaga–Flavobacterium–Bacteroides, the Spirochaetaceae, and the Actinobacteria. All of the archaeal clones sequenced belonged to the group Crenarchaeota and phylogenetic analysis revealed close relationships with members of the deep-branching Group 1 Marine Archaea.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abyzov SS (1993) Microorganisms in the Antarctic ice. In: Friedmann EI (ed) Antarctic microbiology. Wiley-Liss, New York, pp 265–295
Amann G, Stetter OK, Llobet-Brossa E, Amann R, Antón J (2000) Direct proof for the presence and expression of two 5% different 16Sr RNA genes in individual cells of Haloarcula marismortui. Extremophiles 4:373–376
Amann R, Ludwig W, Schleifer KH (1995) Phylogenetic identification and in situ detection of individual microbial cells without cultivation. Microbiol Rev 59:143–169
Bintrim SB, Donohue TJ, Handelsman J, Roberts GP, Goodman RM (1997) Molecular phylogeny of Archaea from soil. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:277–282
Bowman JP, McCammon SA, Brown MV, Nichols DS, McMeekin TA (1997) Diversity and association of pschychrophilic bacteria in Antarctic sea ice. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3068–3078
Bowman JP, Rea SM, McCammon SA, McMeekin TA (2000) Diversity and community structure within anoxic sediment from marine salinity meromitic lakes and a coastal meromitic marine basin, Vestfold Hills, Eastern Antarctica. Environ Microbiol 2:227–237
Brambilla E, Hippe H, Hagelstein A, Tindall BJ, Stackebrandt E (2001) 16S rDNA diversity of cultured and uncultured prokaryotes of mat sample from Lake Fryxell, McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica. Extremophiles 5:23–33
Brune A, Frenzel P, Cypionka H (2000) Life at the oxic–anoxic interface: microbial activities and adaptations. FEMS Microbiol Rev 24:691–710
Buckley DH, Graber JR, Schmidt TM (1998) Phylogenetic analysis of nonthermophilic members of the kingdom Crenarchaeota and their diversity and abundance in soils Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4333–4339
Chandler DP, Fredrickson JK, Brockman FJ (1997) Effect of PCR template concentration on the composition and distribution of total community 16S rDNA clone libraries. Mol Ecol 6:475–482
Christner BC, Mosley-Thompson E, Thompson LG, Reeve JN (2001) Isolation of bacteria and 16S rDNAs from Lake Vostok accretion ice. Environ Microbiol 3:570–577
Cole JR, Chai B, Marsh TL, Farris RJ, Wang Q, Kulam SA, Chandra S, McGarrell DM, Schmidt TM, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM (2003) The Ribosomal Database Project (RDP-II): previewing a new autoaligner that allows regular updates and the new prokaryotic taxonomy. Nucleic Acids Res 31:442–443
DeLong EF (1992) Archaea in coastal marine environments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:5685–5689
DeLong EF, Wu KY, Prézelin BB, Jovine RM (1994) High abundance of Archaea in Antarctic marine picoplankton. Nature 37:695–697
DeMora SJ, Whitehead RF, Gregory M (1994) The chemical composition of glacial melt water ponds and streams on the McMurdo Ice Shelf, Antarctica. Antarct Sci 6:17–27
DeMora SJ, Lee PA, Grout A, Schall C, Heumann KG (1996) Aspects of the biogeochemistry of sulphur in glacial melt water ponds on the McMurdo Ice Shelf, Antarctica. Antarct Sci 8:15–22
Dojka MA, Hugenholtz P, Haack SK, Pace NR (1998) Microbial diversity in a hydrocarbon- and chlorinated-solvent-contaminated aquifer undergoing intrinsic bioremediation. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:3869–3877
Felsenstein J (1993) PHYLIP (phylogenetic inference package) version 3.57c. University of Washington, Seattle, USA
Gordon DA, Priscu J, Giovannoni S (2000) Origin and phylogeny of microbes living in permanent Antarctic lake ice. Microb Ecol 39:197–202
Hart CP (1990) Holocene megafauna in the McMurdo Ice Shelf sediments: fossilization and implications for glacial processes. Antarct J 25:11–14
Knoblauch C, Jørgensen BB, Harder J (1999) Community size and metabolic rates of psychrophilic sulphate-reducing bacteria in Arctic sediments. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 180:2–21
Liu WT, Marsh TL, Cheng H, Forney LJ (1997) Characterization of microbial diversity by determining terminal restriction fragment length polymorphisms of genes encoding 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4516–4522
MacGregor BJ, Moser DP, Alm EW, Nealson KH, Stahl DA (1997) Crenarchaeota in Lake Michigan sediment. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:1178–1181
Mountfort DO, Kaspar HF, Downes M, Asher RA (1999) Partitioning effects during terminal carbon and electron flow in sediments of a low-salinity meltwater pond near Bratina Island, McMurdo Ice Shelf, Antarctica. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:5493–5499
Murray AE, Preston DA, Massana L, Taylor T, Blakis A, Wu K, De Long EF (1998) Seasonal and spatial variability of bacterial and archaeal assemblages in the coastal waters near Anvers Island, Antarctica. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:2582–2595
Muyzer G, Smalla K (1998) Application of denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) and temperature gradient gel electrophoresis (TGGE) in microbial ecology. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek Int J Gen Mol Microbiol 73:127–141
Page RD (1996) TREEVIEW: an application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comput Appl Biosci 12:357–358
Phelps CD, Kerkhof LJ, Young LY (1998) Molecular characterization of a sulfate-reducing consortium which mineralizes benzene. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 27:269–279
Preston CM, Wu KY, Molinski TF, De Long EF (1996) A psychrophilic crenarchaeon in habits a marine sponge: Crenarchaeum symbiosum gen. nov., sp. nov. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:6241–626
Priscu JC, Fritsen CH, Adams EE, Giovannoni SJ, Paerl HW, McKay CP, Doran PT, Gordon DA, Lanoil BD, Pickney JL (1998) Perennial Antarctic Lake Ice: an oasis for life in a polar desert. Science 280:2095–2098
Ravenschlag K, Sahm K, Pernthaler J, Amann R (1999) High bacterial diversity in permanently cold marine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:3982–3989
Rudi KO, Skulber M, Laarsen F, Jakobsen KS (1997) Strain characterization and classification of oxyphotobacteria in clone cultures on the basis of 16S rRNA sequences from the variable regions V6, V7 and V8. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:2593–2599
Stackebrandt E, Goebel BM (1994) A place for DNA–DNA reassociation and 16S ribosomal-RNA sequence analysis in the present species definition in bacteriology. Int J Syst Bacteriol 44:846–849
Stackebrandt E, Liesack W, Goebel BM (1993) Bacterial diversity in a soil sample from a subtropical Australian environment as determined by 16S rRNA analysis. FASEB J 7:232–236
Torsvik V, Goksoyr J, Daae FL (1990) High diversity in DNA of soil bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:782–787
Urakawa H, Yoshida T, Nishimura M, Ohwada K (2000) Characterization of depth-related population variation in microbial communities of a coastal marine sediment using 16S rDNA-based approaches and quinone profiling. Environ Microbiol 2:542–554
Vincent WF (1988) Microbial ecosystems of Antarctica. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
Watanabe K, Teramoto M, Harayama S (1999) An outbreak of nonflocculating catabolic populations caused the breakdown of a phenol-digesting activated-sludge process. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:2813–2819
Acknowledgments
This research was carried out under the auspices of the University of Waikato Antarctic Terrestrial Biology Research program. We gratefully acknowledge financial support from the University of Waikato and Antarctica New Zealand (D.A.C.), the Carl Tryggers Foundation (S.S.) and the Wenner-Gren foundations (S.S.). We thank Dr. M. Thomas for providing useful information on phylogenetic analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by K. Horikoshi
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sjöling, S., Cowan, D.A. High 16S rDNA bacterial diversity in glacial meltwater lake sediment, Bratina Island, Antarctica. Extremophiles 7, 275–282 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-003-0321-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-003-0321-z