Abstract
Objective
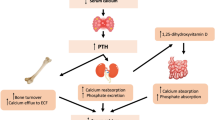
To assess the serum and salivary levels of biomarkers related to bone metabolism in cirrhotic patients as well as the evidence of osteoporotic changes on panoramic radiographs.
Materials and methods
Thirty-eight cirrhotic patients underwent anamnesis and physical examination. Specimens of blood and saliva were collected for evaluation by using Luminex™ xMAP technology to quantify RANKL, OPG, IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α. Panoramic radiographs were evaluated based on the mandibular cortical index (MCI) and the resulting data were compared to the expression of biomarkers in serum and saliva. Descriptive data analysis was performed and the Mann–Whitney’s test and Spearman’s correlation were used.
Results
Most of the sample consisted of males (68.4%) who had cirrhosis mostly resulting from alcoholism (28.9%). Median concentration values of RANKL (74.44 pg/mL), IL-1 β (45.91 pg/mL), IL-6 (67.69 pg/mL) and TNF-α (5.97 pg/mL) in saliva were higher than those observed in serum. In 72.7% of the panoramic radiographs, MCI was found to be suggestive of osteoporotic changes. No statistically significant correlation was observed between salivary and serum expressions of biomarkers or between biomarkers and MCI.
Conclusion
RANKL, OPG, IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α are expressed differently in serum and saliva and the concentration of these biomarkers is not related to MCI.
Clinical relevance
This study contributes to the study of the mechanisms of osteoporosis in cirrhotic individuals.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pinzani M (2015) Pathophysiology of liver fibrosis. Dig Dis 33(4):492–497. https://doi.org/10.1159/000374096
Luxon BA (2011) Bone disorders in chronic liver diseases. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 13(1):40–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-010-0166-4
Guañabens N, Parés A (2012) Osteoporosis en la cirrosis hepática [Osteoporosis in liver cirrhosis]. Gastroenterol Hepatol 35(6):411–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gastrohep.2012.01.017
Moschen AR, Kaser A, Stadlmann S et al (2005) The RANKL/OPG system and bone mineral density in patients with chronic liver disease. J Hepatol 43(6):973–983. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2005.05.0345
Calciolari E, Donos N, Park JC et al (2015) Panoramic measures for oral bone mass in detecting osteoporosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Dent Res 94(3 Suppl):17S-27S. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034514554949
Taguchi A, Sanada M, Krall E et al (2003) Relationship between dental panoramic radiographic findings and biochemical markers of bone turnover. J Bone Miner Res 18(9):1689–1694. https://doi.org/10.1359/jbmr.2003.18.9.16897
Vlasiadis KZ, Damilakis J, Velegrakis GA et al (2008) Relationship between BMD, dental panoramic radiographic findings and biochemical markers of bone turnover in diagnosis of osteoporosis. Maturitas 59(3):226–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.maturitas.2008.01.006
Nagi R, Devi BKY, Rakesh N et al (2014) Relationship between femur bone mineral density, body mass index and dental panoramic mandibular cortical width in diagnosis of elderly postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. J Clin Diagn Res 8(8):ZC36–ZC40. https://doi.org/10.7860/JCDR/2014/9210.4748
Balto KA, Gomaa MM, Feteih RM et al (2018) Dental panoramic radiographic indices as a predictor of osteoporosis in postmenopausal Saudi Women. J Bone Metab 25(3):165–173. https://doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2018.25.3.165
Woitge HW, Pecherstorfer M, Li Y et al (1999) Novel serum markers of bone resorption: clinical assessment and comparison with established urinary indices. J Bone Miner Res Off J Am Soc Bone Miner Res 14(5):792–801. https://doi.org/10.1359/jbmr.1999.14.5.792
Tyrovola JB (2017) The “Mechanostat” principle and the Osteoprotegerin-OPG/RANKL/RANK System PART II. The role of the hypothalamic-pituitary axis. J Cell Biochem 118(5):962–966. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.25793
Walsh MC, Choi Y (2014) Biology of the RANKL-RANK-OPG System in immunity, bone, and beyond. Front Immunol 5:511. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2014.00511
Tan W, Zhang W, Strasner A et al (2011) Tumour-infiltrating regulatory T cells stimulate mammary cancer metastasis through RANKL-RANK signalling. Nature 470(7335):548–553. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09707
Remuzgo-Martínez S, Genre F, López-Mejías R et al (2016) Expression of osteoprotegerin and its ligands, RANKL and TRAIL, in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci Rep 6:29713. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep29713
Yasuda H (2013) RANKL, a necessary chance for clinical application to osteoporosis and cancer-related bone diseases. World J Orthopedics 4(4):207–217. https://doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v4.i4.207
Santos LA, Romeiro FG (2016) Diagnosis and management of cirrhosis-related osteoporosis. Biomed Res Int 2016:1423462. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/1423462
Del Campo JA, Gallego P, Grande L (2018) Role of inflammatory response in liver diseases: therapeutic strategies. World J Hepatol 10(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v10.i1.1
Bonnel AR, Bunchorntavakul C, Reddy KR (2011) Immune dysfunction and infections in patients with cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 9(9):727–738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2011.02.031
Cozma S, Dima-Cozma LC, Ghiciuc CM et al (2017) Salivary cortisol and α-amylase: subclinical indicators of stress as cardiometabolic risk. Braz J Med Biol Res 50(2):e5577. https://doi.org/10.1590/1414-431X20165577
Stanescu II, Calenic B, Dima A et al (2018) Salivary biomarkers of inflammation in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Anat 219:89–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aanat.2018.02.012
Bezinelli LM, Eduardo FP, de Carvalho D et al (2017) Therapeutic salivary monitoring of IV busulfan in patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a pilot study. Bone Marrow Transplant 52(10):1384–1389. https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2017.142
Figueiredo MA, Domingues Fink MC, Castro T et al (2017) Detection of human polyomaviruses JC and BK in liver pretransplant patients. Oral Dis 23(8):1127–1133. https://doi.org/10.1111/odi.12707
Wright NC, Looker AC, Saag KG et al (2014) The recent prevalence of osteoporosis and low bone mass in the United States based on bone mineral density at the femoral neck or lumbar spine. J Bone Miner Res 29(11):2520–2526. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.2269
Klemetti E, Kolmakov S, Kröger H (1994) Pantomography in assessment of the osteoporosis risk group. Scand J Dent Res 102(1):68–72. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0722.1994.tb01156.x
Wariaghli G, Mounach A, Achemlal L et al (2010) Osteoporosis in chronic liver disease: a case-control study. Rheumatol Int 30(7):893–899. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-009-1071-8
Liang J, Meng WD, Yang JM et al (2018) The association between liver cirrhosis and fracture risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Endocrinol 89(4):408–413. https://doi.org/10.1111/cen.13762
Arita ES, Pippa MG, Marcucci M et al (2013) Assessment of osteoporotic alterations in achondroplastic patients: a case series. Clin Rheumatol 32(3):399–402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-012-2126-x
Munhoz L, Aoki EM, Cortes A et al (2018) Osteoporotic alterations in a group of different ethnicity Brazilian postmenopausal women: an observational study. Gerodontology 35(2):101–109. https://doi.org/10.1111/ger.12322
Liu W, Zhang X (2015) Receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand (RANKL)/RANK/osteoprotegerin system in bone and other tissues (review). Mol Med Rep 11(5):3212–3218. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2015.3152
Azizieh FY, Shehab D, Jarallah KA et al (2019) Circulatory levels of RANKL, OPG, and oxidative stress markers in postmenopausal women with normal or low bone mineral density. Biomark Insights 14:1177271919843825. https://doi.org/10.1177/1177271919843825
Albillos A, Lario M, Álvarez-Mon M (2014) Cirrhosis-associated immune dysfunction: distinctive features and clinical relevance. J Hepatol 61(6):1385–1396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2014.08.010
Di Profio B, Inoue G, Marui VC et al (2018) Periodontal status of liver transplant candidates and healthy controls. J Periodontol 89(12):1383–1389. https://doi.org/10.1002/JPER.17-0710
Ng PY, Donley M, Hausmann E et al (2007) Candidate salivary biomarkers associated with alveolar bone loss: cross-sectional and in vitro studies. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 49(2):252–260. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-695X.2006.00187.x
Scannapieco FA, Ng P, Hovey K et al (2007) Salivary biomarkers associated with alveolar bone loss. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1098:496–497. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1384.034
Kc S, Wang XZ, Gallagher JE (2020) Diagnostic sensitivity and specificity of host-derived salivary biomarkers in periodontal disease amongst adults: Systematic review. J Clin Periodontol 47(3):289–308. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.13218
García-Valdecasas-Campelo E, González-Reimers E, Santolaria-Fernández F et al (2006) Serum osteoprotegerin and RANKL levels in chronic alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol Alcohol 41(3):261–266. https://doi.org/10.1093/alcalc/agl004
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq grant no. 44004/2014–5), São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP grant no. 2015/07727) and the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES Finance Code 001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualisation—Jefferson Rocha Tenório, Karem López Ortega. Methodology—Jefferson Rocha Tenório, Nathália Tuany Duarte, Mariana Lobo Bergamini. Formal analysis and investigation—Jefferson Rocha Tenório, Natália Andrade, Ana Carolina Mamana Fernandes de Souza. Writing (original draft preparation)—Jefferson Rocha Tenório, Natália Andrade, Karem López Ortega. Writing (review and editing)—Jefferson Rocha Tenório, Paulo Henrique Braz-Silva, Karem López Ortega. Funding acquisition—Paulo Henrique Braz-Silva; Supervision: Karem López Ortega.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tenório, J.R., Duarte, N.T., Andrade, N.S. et al. Assessment of bone metabolism biomarkers in serum and saliva of cirrhotic patients. Clin Oral Invest 26, 1861–1868 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-021-04161-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-021-04161-7