Abstract
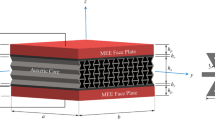
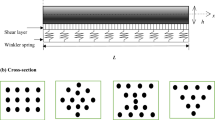
The current work investigates axisymmetric vibration of saturated porous circular micro-plates subjected to uniform in-plane force and coupled with piezoelectric sensor and actuator layers. Including the material length scale parameter, the modified coupled stress theory is chosen to capture the size-dependent behavior of the model. The micro-structure is embedded on an elastic substrate medium modeled by Winkler–Pasternak foundation. In addition, the fluid pressure in the pores is partitioned in the formulation via the linear poroelasticity theory of Biot. Based on first-order shear deformation theory, governing equations of motion and corresponding boundary conditions are obtained by employing Hamilton’s principle and solved by a semi-analytical approach called the differential transform method. To ensure the accuracy and reliability of the developed model, natural frequencies of the presented micro-plate are compared with available data in the literature. Finally, numerical examples are presented for studying the effect of some parameters including material length scale parameter, in-plane force, porosity, fluid pressure, electro-mechanical interaction, and the ratio of the elastic core thickness to piezoelectric layers thickness on vibrational responses of the proposed model for two cases of clamped and simply supported edges. The obtained results show that the proposed method is a reliable way of studying the free vibration response of the micro-structures. On the other hand, it is observed that porosity, fluid pressure, tensile in-plane force, size-effect, and open-circuit electrical condition increase the natural frequency of the system.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data, models, and code generated or used during the study appear in the submitted article.
References
Eringen, A.C.: Nonlocal polar elastic continua. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 10(1), 1–16 (1972)
Gurtin, M.E., Murdoch, A.I.: Addenda to our paper A continuum theory of elastic material surfaces. ArRMA 59(4), 389–390 (1975)
Yang, F., Chong, A.C.M., Lam, D.C.C., Tong, P.: Couple stress based strain gradient theory for elasticity. Int. J. Solids Struct. 39(10), 2731–2743 (2002)
Lam, D.C.C., Yang, F., Chong, A.C.M., Wang, J., Tong, P.: Experiments and theory in strain gradient elasticity. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 51(8), 1477–1508 (2003)
Banhart, J.: Manufacture, characterisation and application of cellular metals and metal foams. Prog. Mater. Sci. 46(6), 559–632 (2001)
Lefebvre, L., Banhart, J., Dunand, D.C.: Porous metals and metallic foams: current status and recent developments. Adv. Eng. Mater. 10(9), 775–787 (2008)
Tampieri, A., Celotti, G., Sprio, S., Delcogliano, A., Franzese, S.: Porosity-graded hydroxyapatite ceramics to replace natural bone. Biomaterials 22(11), 1365–1370 (2001)
Biot, M.A.: Theory of buckling of a porous slab and its thermoelastic analogy. J. Appl. Mech. 31(2), 194 (1964)
Detournay, E., Cheng, A.H.-D.: Fundamentals of poroelasticity. In: Fairhurst, C. (ed.) Analysis and Design Methods, pp. 113–171. Elsevier, Amsterdam (1993)
Crawley, E.F., De Luis, J.: Use of piezoelectric actuators as elements of intelligent structures. AIAA J. 25(10), 1373–1385 (1987)
Spencer, W.J., Corbett, W.T., Dominguez, L.R., Shafer, B.D.: An electronically controlled piezoelectric insulin pump and valves. IEEE Trans. Sonics Ultrason. 25(3), 153–156 (1978)
Chen, X., Fox, C.H.J., Mcwilliam, S.: Optimization of a cantilever microswitch with piezoelectric actuation. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 15(11), 823–834 (2004)
Chee, C.Y.K., Tong, L., Steven, G.P.: A review on the modelling of piezoelectric sensors and actuators incorporated in intelligent structures. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 9(1), 3–19 (1998)
Cao, L., Mantell, S., Polla, D.: Design and simulation of an implantable medical drug delivery system using microelectromechanical systems technology. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 94(1–2), 117–125 (2001)
Winkler, E.: Die Lehre von der Elasticitaet und Festigkeit: mit besonderer Rücksicht auf ihre Anwendung in der Technik für polytechnische Schulen. Bauakademien, Ingenieue, Maschinenbauer, Architecten, etc. H. Dominicus (1867)
Pasternak, P.L.: On a New Method of Analysis of an Elastic Foundation by Means of Two Foundation Constants. Gos. Izd. Lip. po Strait i Arkh, Moscow (1954)
Nazemizadeh, M., Bakhtiari-Nejad, F., Assadi, A., Shahriari, B.: Nonlinear vibration of piezoelectric laminated nanobeams at higher modes based on nonlocal piezoelectric theory. Acta Mech. 231(10), 4259–4274 (2020)
Jalaei, M.H., Thai, H.-T., Civalek, Ӧ: On viscoelastic transient response of magnetically imperfect functionally graded nanobeams. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 172, 103629 (2022)
Civalek, Ӧ, Akbaş, ŞD., Akgöz, B., Dastjerdi, S.: Forced vibration analysis of composite beams reinforced by carbon nanotubes. Nanomaterials 11(3), 571 (2021)
Sobhani, E., Arbabian, A., Civalek, Ӧ: The free vibration analysis of hybrid porous nanocomposite joined hemispherical–cylindrical–conical shells. Eng. Comput. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-021-01453-0
Civalek, Ӧ, Baltacıoglu, A.K.: Free vibration analysis of laminated and FGM composite annular sector plates. Compos. B. Eng. 157, 182–194 (2019)
Akgöz, B., Civalek, Ӧ: A microstructure-dependent sinusoidal plate model based on the strain gradient elasticity theory. Acta Mech. 226(7), 2277–2294 (2015)
Kamali, F., Shahabian, F.: Free vibration of axially functionally graded tapered micro-beams considering uncertain properties. AUT J. Civ. Eng. 5(4), 543–556 (2021). https://doi.org/10.22060/AJCE.2022.18056.5657
Zhou, S., Zhang, R., Zhou, S., Li, A.: Free vibration analysis of bilayered circular micro-plate including surface effects. Appl. Math. Model. 70, 54–66 (2019)
Eshraghi, I., Serkan, D., Soltani, N.: Bending and free vibrations of functionally graded annular and circular micro-plates under thermal loading. Compos. Struct 137, 196–207 (2016)
Korayem, M.H., Homayooni, A.: The size-dependent analysis of multilayer micro-cantilever plate with piezoelectric layer incorporated voltage effect based on a modified couple stress theory. Eur. J. Mech. A Solids 61, 59–72 (2017)
Kamali, F., Shahabian, F.: Analytical solutions for surface stress effects on buckling and post-buckling behavior of thin symmetric porous nano-plates resting on elastic foundation. Arch. Appl. Mech. 91(6), 2853–2880 (2021)
Shahdadi, A., Rahnama, H.: Free vibration of a functionally graded annular sector plate integrated with piezoelectric layers. Appl. Math. Model. 79, 341–361 (2020)
Eftekhari, S., Hashemian, A.M., Toghraie, D.: Optimal vibration control of multi-layer micro-beams actuated by piezoelectric layer based on modified couple stress and surface stress elasticity theories. Phys. A: Stat. Mech. Appl. 546, 123998 (2020)
Arshid, E., Khorshidvand, A.R.: Free vibration analysis of saturated porous FG circular plates integrated with piezoelectric actuators via differential quadrature method. Thin Walled Struct. 125, 220–233 (2018)
Kazemi, A., Vatankhah, R., Farid, M.: Vibration analysis of size-dependent functionally graded micro-plates subjected to electrostatic and piezoelectric excitations. Eur. J. Mech. A Solids 76, 46–56 (2019)
Shen, J., Wang, H., Zheng, S.: Size-dependent pull-in analysis of a composite laminated micro-beam actuated by electrostatic and piezoelectric forces: generalized differential quadrature method. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 135, 353–361 (2018)
Rezaiee-Pajand, M., Kamali, F.: Exact solution for thermal-mechanical post-buckling of functionally graded micro-beams. CEAS Aeronaut. J. 12, 85–100 (2021)
Ghadiri Rad, A., Shahabian, F.: Nonlocal geometrically nonlinear dynamic analysis of nano-beam using a meshless method. Steel Compos. Struct. 32(3), 293–304 (2019)
Arshid, E., Amir, S., Loghman, A.: Thermal buckling analysis of FG graphene nanoplatelets reinforced porous nanocomposite MCST-based annular/circular microplates. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 111, 106561 (2021)
Arshid, E., Amir, S., Loghman, A.: Static and dynamic analyses of FG-GNPs reinforced porous nanocomposite annular micro-plates based on MSGT. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 180, 105656 (2020)
Arshid, E., Khorasani, M., Soleimani-Javid, Z., Amir, S., Tounsi, A.: Porosity-dependent vibration analysis of FG microplates embedded by polymeric nanocomposite patches considering hygrothermal effect via an innovative plate theory. Eng. Comput. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-021-01382-y
Amir, S., Soleimani-Javid, Z., Arshid, E.: Size-dependent free vibration of sandwich micro beam with porous core subjected to thermal load based on SSDBT. Z. Angew. Math. Mech. 99(9), e201800334 (2019)
Arshid, E., Khorshidvand, A.R., Khorsandijou, S.M.: The effect of porosity on free vibration of SPFG circular plates resting on visco-Pasternak elastic foundation based on CPT, FSDT and TSDT. Struct. Eng. Mech. 70(1), 97–112 (2019)
Lal, R., Ahlawat, N.: Axisymmetric vibrations and buckling analysis of functionally graded circular plates via differential transform method. Eur. J. Mech. A Solids 52, 85–94 (2015)
Arvin, H.: Free vibration analysis of micro rotating beams based on the strain gradient theory using the differential transform method: Timoshenko versus Euler–Bernoulli beam models. Eur. J. Mech. A Solids 65, 336–348 (2017)
Arikoglu, A., Ozkol, I.: Vibration analysis of composite sandwich beams with viscoelastic core by using differential transform method. Compos. Struct. 92(12), 3031–3039 (2010)
Nourifar, M., Keyhani, A., Aftabi Sani, A.: Free vibration analysis of rotating Euler–Bernoulli beam with exponentially varying cross-section by differential transform method. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. 18(2), 1850024 (2018)
Hozhabrossadati, S.M., Aftabi Sani, A.: Free vibration of MDOF systems with non-periodically time-varying mass. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. 18(6), 1850077 (2018)
Rezaiee-Pajand, M., Aftabi Sani, A., Hozhabrossadati, S.M.: Application of differential transform method to free vibration of gabled frames with rotational springs. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. 17(1), 1750012 (2017)
Amir, S., Arshid, E., Ghorbanpour Aran, M.R.: Size-dependent magneto-electro-elastic vibration analysis of FG saturated porous annular/circular micro sandwich plates embedded with nano-composite face sheets subjected to multi-physical pre loads. Smart Struct. Syst. 23(5), 429–447 (2020)
Mousavi, S.B., Amir, S., Jafari, A., Arshid, E.: Analytical solution for analyzing initial curvature effect on vibrational behavior of PM beams integrated with FGP layers based on trigonometric theories. Adv. Nano Res. 10(3), 235–251 (2021)
Amir, S., Arshid, E., Khoddami Maraghi, Z.: Vibration analysis of magnetorheological fluid circular sandwich plates with magnetostrictive facesheets exposed to monotonic magnetic field located on visco-Pasternak substrate. J. Vib. Control 26(17–18), 1523–1537 (2020)
Arshid, E., Kiani, A., Amir, S., Zarghami Dehghani, M.: Asymmetric free vibration analysis of first-order shear deformable functionally graded magneto-electro-thermo-elastic circular plates. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 233(16), 5659–5675 (2019)
Amir, S., Arshid, E., Khoddami Maraghi, Z.: Free vibration analysis of magneto-rheological smart annular three-layered plates subjected to magnetic field in viscoelastic medium. Smart Struct. Syst. 25(5), 581–592 (2020)
Liew, K.M., Hand, J.B., Xiao, Z.M.: Vibration analysis of circular Mindlin plates using the differential quadrature method. J. Sound Vib. 205(5), 617–630 (1997)
Liu, X., Wang, Q., Queck, S.T.: Analytical solution for free vibration of piezoelectric coupled moderately thick circular plates. Int. J. Solids Struct. 39, 2129–2151 (2002)
Soleimani-Javid, Z., Arshid, E., Khorasani, M., Amir, S., Tounsi, A.: Size-dependent flexoelectricity-based vibration characteristics of honeycomb sandwich plates with various boundary conditions. Adv. Nano Res. 10(5), 449–460 (2021)
Arshid, E., Arshid, H., Amir, S., Mousavi, S.B.: Free vibration and buckling analyses of FG porous sandwich curved microbeams in thermal environment under magnetic field based on modified couple stress theory. Arch. Civ. Mech. 21(1), 1–23 (2021)
Arshid, E., Amir, S.: Size-dependent vibration analysis of fluid-infiltrated porous curved microbeams integrated with reinforced functionally graded graphene platelets face sheets considering thickness stretching effect. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. L. 235(5), 1077–1099 (2021)
Nourifar, M., Aftabi Sani, A., Keyhani, A.: Efficient multi-step differential transform method: Theory and its application to nonlinear oscillators. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 53, 154–183 (2017)
Detournay, E., Cheng, A.: Fundamentals of Poroelasticity. Pergamon Press, Oxford (1993)
Yang, J.: An Introduction to the Theory of Piezoelectricity, vol. 9, pp. 31–58. Springer, New York (2005)
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kamali, F., Shahabian, F. & Aftabi-Sani, A. Free vibration analysis of saturated porous circular micro-plates integrated with piezoelectric layers; differential transform method. Acta Mech 234, 649–669 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-022-03407-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-022-03407-z