Abstract
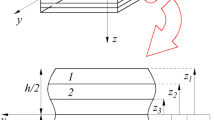
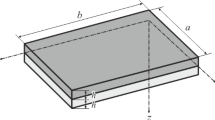
Based on Gurtin–Murdoch’s theory, a new mechanistic laminated nanoplate model composed of nanocomposites under various boundary conditions is proposed, where the top and bottom surfaces of the laminated nanoplate are regarded as two-dimensional films which have independent surface elastic parameters. The influence of surface Lamé constants and residual stress on static bending and vibration properties for the laminated nanoplate is studied. In order to get approximate solutions of bending deflections and first-order frequencies for the laminated nanoplate with complex boundary conditions, the variational method is employed in this paper. The effectiveness of the presented variational method is verified by comparison with available results. Numerical results indicate that the effective bending stiffness of the laminated nanoplate considering surface effects is obviously different from the classical result. Moreover, the influences of surface effects on bending deflections and first-order frequencies are related to the surface elastic parameters and boundary conditions. The presented method and results provide a theoretical benchmark for other numerical and experimental methods to study nano laminates.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adab, N., Arefi, M., Amabili, M.: A comprehensive vibration analysis of rotating truncated sandwich conical microshells including porous core and GPL-reinforced face-sheets. Compos. Struct. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.114761
Guo, J., Gao, J., Xiao, C., Chen, L., Qian, L.: Mechanochemical reactions of GaN-Al2O3 interface at the nanoasperity contact: Roles of crystallographic polarity and ambient humidity. Friction. 10(7), 1005–1018 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40544-021-0501-9
Shen, F., Zhang, D., Zhang, Q., Li, Z.J., Guo, H.Y., Gong, Y., Peng, Y.: Influence of temperature difference on performance of solid-liquid triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2022.107431
Xin, C.F., Li, Z.J., Zhang, Q., Peng, Y., Guo, H.Y., Xie, S.R.: Investigating the output performance of triboelectric nanogenerators with single/double-sided interlayer. Nano Energy (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2022.107448
Craighead, H.G.: Nanoelectromechanical systems. Science 290(5496), 1532–1535 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.290.5496.1532
Lavrik, N.V., Sepaniak, M.J., Datskos, P.G.: Cantilever transducers as a platform for chemical and biological sensors. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 75(7), 2229–2253 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1763252
Cao, D.Y., Malakooti, S., Kulkarni, V.N., Ren, Y., Liu, Y.J., Nie, X., Qian, D., Griffith, D.T., Lu, H.B.: The effect of resin uptake on the flexural properties of compression molded sandwich composites. Wind Energy 25(1), 71–93 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/we.2661
Wang, X., Xu, T., de Andrade, M.J., Rampalli, I., Cao, D., Haque, M., Roy, S., Baughman, R.H., Lu, H.: The interfacial shear strength of carbon nanotube sheet modified carbon fiber composites. Chall. Mech. Time Depend. Mater. 2, 25–32 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59542-5_4
Shaat, M., Mahmoud, F.F., Alshorbagy, A.E., Alieldin, S.S.: Bending analysis of ultra-thin functionally graded Mindlin plates incorporating surface energy effects. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 75, 223–232 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2013.07.001
Liew, K.M., Wong, C.H., Tan, M.J.: Tensile and compressive properties of carbon nanotube bundles. Acta Mater. 54(1), 225–231 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2005.09.002
Hao, R.-B., Lu, Z.-Q., Ding, H., Chen, L.-Q.: A nonlinear vibration isolator supported on a flexible plate: analysis and experiment. Nonlinear Dyn. 108(2), 941–958 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07243-7
Cao, D., Malakooti, S., Kulkarni, V.N., Ren, Y., Lu, H.: Nanoindentation measurement of core–skin interphase viscoelastic properties in a sandwich glass composite. Mech. Time-Depend. Mater. 25(3), 353–363 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11043-020-09448-y
Gurtin, M.E., Ian Murdoch, A.: A continuum theory of elastic material surfaces. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal. 57(4), 291–323 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00261375
Gurtin, M.E., Murdoch, A.I.: Addenda to our paper A continuum theory of elastic material surfaces. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal. 59(4), 389–390 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00250426
Gurtin, M.E., Ian Murdoch, A.: Surface stress in solids. Int. J. Solids Struct. 14(6), 431–440 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1016/0020-7683(78)90008-2
Murdoch, A.I.: Some fundamental aspects of surface modelling. J. Elast. 80(1), 33 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10659-005-9024-2
Sun, C.T., Zhang, H.: Size-dependent elastic moduli of platelike nanomaterials. J. Appl. Phys. 93(2), 1212–1218 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1530365
Duan, H.L., Wang, J., Huang, Z.P., Karihaloo, B.L.: Size-dependent effective elastic constants of solids containing nano-inhomogeneities with interface stress. J. Mech. Phys. Solids. 53(7), 1574–1596 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmps.2005.02.009
Feng, X.-Q., Xia, R., Li, X., Li, B.: Surface effects on the elastic modulus of nanoporous materials. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94(1), 011916 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3067999
Yang, Y., Zou, J., Lee, K.Y., Li, X.-F.: Bending of circular nanoplates with consideration of surface effects. Meccanica 53(4), 985–999 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-017-0760-8
Yang, Y., Lee, K.Y., Li, X.F.: Surface effects on delamination of a thin film bonded to an elastic substrate. Int. J. Fract. 210(1), 81–94 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-018-0262-2
Wang, W., Li, P., Jin, F.: An analytical model of a broadband magnetic energy nanoharvester array with consideration of flexoelectricity and surface effect. J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463%2Faab292
Liu, S., Yu, T., Lich, L.V., Yin, S., Bui, T.Q.: Size and surface effects on mechanical behavior of thin nanoplates incorporating microstructures using isogeometric analysis. Comput. Struct. 212, 173–187 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2018.10.009
Arefi, M., Amabili, M.: A comprehensive electro-magneto-elastic buckling and bending analyses of three-layered doubly curved nanoshell, based on nonlocal three-dimensional theory. Compos. Struct. 257, 113100 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.113100
Lu, L., Guo, X., Zhao, J.: A unified size-dependent plate model based on nonlocal strain gradient theory including surface effects. Appl. Math. Model. 68, 583–602 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2018.11.023
Fan, F., Lei, B., Sahmani, S., Safaei, B.: On the surface elastic-based shear buckling characteristics of functionally graded composite skew nanoplates. Thin-Walled Struct. 154, 106841 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2020.106841
Tong, L.H., Lin, F., Xiang, Y., Shen, H.S., Lim, C.W.: Buckling analysis of nanoplates based on a generic third-order plate theory with shear-dependent non-isotropic surface stresses. Compos. Struct. 265, 113708 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.113708
Abdollahi, F., Ghassemi, A.: Surface and nonlocal effects on coupled in-plane shear buckling and vibration of single-layered graphene sheets resting on elastic media and thermal environments using DQM. J. Mech. 34(6), 847–862 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1017/jmech.2018.14
Gholami, R., Ansari, R.: Imperfection sensitivity of post-buckling behavior and vibration response in pre- and post-buckled regions of nanoscale plates considering surface effects. Int. J. Appl. Mech. 10(03), 1850027 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1142/s1758825118500278
Lu, L., Guo, X., Zhao, J.: On the mechanics of Kirchhoff and Mindlin plates incorporating surface energy. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 124, 24–40 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijengsci.2017.11.020
Wang, K.F., Wang, B.L., Xu, M.H., Yu, A.B.: Influences of surface and interface energies on the nonlinear vibration of laminated nanoscale plates. Compos. Struct. 183, 423–433 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.04.054
Arpanahi, R.A., Hosseini-Hashemi, S., Rahmanian, S., Hashemi, S.H., Ahmadi-Savadkoohi, A.: Nonlocal surface energy effect on free vibration behavior of nanoplates submerged in incompressible fluid. Thin-Walled Struct. 143, 106212 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2019.106212
Karimi, M., Rafieian, S.: A comprehensive investigation into the impact of nonlocal strain gradient and modified couple stress models on the rates of surface energy layers of BiTiO3–CoFe2O4 nanoplates: a vibration analysis. Mater. Res. Express. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab151b
Wang, J., Xiao, J.: Analytical solutions of bending analysis and vibration of rectangular nano laminates with surface effects. Appl. Math. Model. 110, 663–673 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2022.06.012
Xu, M., Wang, B.L., Yu, A.: Effect of surface and interface energies on the nonlinear bending behaviour of nanoscale laminated thin plates. Mech. Compos. Mater. 52(5), 673–686 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-016-9616-x
Fallah, A., Khorshidi, K.: The effect of nonlinear temperature distribution on the vibrational behavior of a size-dependent FG laminated rectangular plates undergoing prescribed overall motion. Polym. Compos. 40(2), 766–778 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.24735
Lu, P., He, L.H., Lee, H.P., Lu, C.: Thin plate theory including surface effects. Int. J. Solids Struct. 43(16), 4631–4647 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2005.07.036
Arefi, M., Najafitabar, F.: Buckling and free vibration analyses of a sandwich beam made of a soft core with FG-GNPs reinforced composite face-sheets using Ritz Method. Thin-Walled Struct. 158, 107200 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2020.107200
Behera, L., Chakraverty, S.: Effect of scaling effect parameters on the vibration characteristics of nanoplates. J. Vib. Control. 22(10), 2389–2399 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1177/1077546314547376
Miller, R.E., Shenoy, V.B.: Size-dependent elastic properties of nanosized structural elements. Nanotechnology 11(3), 139–147 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/11/3/301
Shenoy, V.B.: Atomistic calculations of elastic properties of metallic FCC crystal surfaces. PhRvB. 71(9), 094104 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.71.094104
Sapsathiarn, Y., Rajapakse, R.K.N.D.: Static and dynamic analyses of nanoscale rectangular plates incorporating surface energy. Acta Mech. 228(8), 2849–2863 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-015-1521-1
Zhang, X., Chen, K.S., Ghodssi, R., Ayón, A.A., Spearing, S.M.: Residual stress and fracture in thick tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) and silane-based PECVD oxide films. Sens. Actuator A-Phys. 91(3), 373–380 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-4247(01)00610-0
Pauleau, Y.: Generation and evolution of residual stresses in physical vapour-deposited thin films. Vacuum 61(2), 175–181 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0042-207X(00)00475-9
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (A2022203025) and the Science and Technology Project of Hebei Education Department (ZD2021104).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, J., Wang, J. Variational analysis of laminated nanoplates for various boundary conditions. Acta Mech 233, 4711–4728 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-022-03352-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-022-03352-x