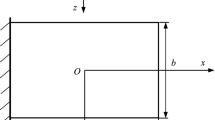
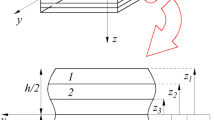
Using an improved multilayered plate model, the influence of surface and interface energies on the bending behaviour of laminated nanoplates is incorporated into the Kirchhoff plate theory. Governing equations taking into account the geometrical nonlinearity are obtained to study the influences of surface/interface energies. Based on the Navier and Ritz methods, closed-form solutions for both simply supported and clamped nanoplates are obtained. Numerical results for single- and multilayered nanoplates indicate that the interface effect can noticeably change the elastic behaviour of laminated plates on the nanometer scale. In addition, the flakiness ratio, external load, and number of layers also affect the surface/interface effects at large deformations. This study will be useful for the design and examination of nanoplates and nanoscale devices, especially multilayered plates at large deformations.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. E.Gurtin and A. I. Murdoch, “Continuum theory of elastic-material surfaces,” Arch. Ration. Mech.and Analysis., 57, No. 4, 291-323 (1975).
R. C.Cammarata and K. Sieradzki, “Surface and interface stresses,” Annual Review of Materials Sci., 24, 215-234 (1994).
M. Godin, V. Tabard-Cossa, Y. Miyahara, et al., “Cantilever-based sensing: the origin of surface stress and optimization strategies,” Nanotechnology, 21, 075501(2010).
D. W. Huang, “Size-dependent response of ultra-thin films with surface effects,” Int. J. of Solids and Struct., 45, No. 2, 568-579 (2008).
P. Lu, L. H. He, H. P. Lee, et al., “Thin plate theory including surface effects,” Int. J. of Solids and Struct., 43, No. 16, 4631-4647 (2006).
H. X. Zhu, J. X. Wang, and B. L. Karihaloo, “Effects of surface and initial stresses on the bending stiffness of trilayer plates and nanofilms,” J. of Mech. Mater. and Struct., 4, No. 3, 589-604 (2009).
V. A. Eremeyev, H. Altenbach, and N. F. Morozov, “The influence of surface tension on the effective stiffness of nanosize plates,” Doklady Fiziki, 54, No. 2, 98-100 (2009).
H. Altenbach, V. A. Eremeyev, and N. F. Morozov, “Linear theory of shells taking into account surface stresses,” Doklady Fiziki, 54, No. 12, 531-535 (2009).
R. E. Miller and V. B. Shenoy, “Size-dependent elastic properties of nanosized structural elements,” Nanotechnology, 11(3), 139-147 (2000).
10. L. H. He, C. W. Lim, and B. S. Wu, “A continuum model for size-dependent deformation of elastic films of nano-scale thickness,” Int. J. of Solids and Struct., 41, Nos.. 3-4, 847-857 (2004).
Z. P. Huang and J. Wang, “A theory of hyperelasticity of multi-phase media with surface/interface energy effect,” Acta Mechanica, 182, Nos. 3-4, 195-210 (2006).
C. W. Lim and L. H. He, “Size-dependent nonlinear response of thin elastic films with nano-scale thickness,” Int. J. of Mech. Sci., 46, No. 11, 1715-1726 (2004).
K. F. Wang and B. L. Wang, “Effects of residual surface stress and surface elasticity on the nonlinear free vibration of nanoscale plates,” J. of Appl. Phys., 112, No. 1 (2012).
R. Dingreville and J. M. Qu, “Interfacial excess energy, excess stress and excess strain in elastic solids: Planar interfaces,” J. of the Mech. and Phys. of Solids, 56, No. 5, 1944-1954 (2008).
G. F.Wang, “Effects of surface energy on the mechanical performance of nanosized beams,” J. of Computational and Theoretical Nanosci., 8, No. 7, 1173-1177 (2011).
G. F. Wang and X. Q. Feng, “Effects of surface elasticity and residual surface tension on the natural frequency of microbeams,” Appl. Phys. Let., 90, No. 23 (2007).
G. F. Wang and X. Q. Feng, “Timoshenko beam model for buckling and vibration of nanowires with surface effects,” J. of Physics D-Applied Physics, 42, No. 15 (2009).
J. W. Gibbs, H. A. Bumstead, and R. G. Van Name, The Scientific Papers of J. Willard Gibbs 1906, London,: New York and Bombay, Longmans, Green and co.
R. C. Cammarata, “Surface and interface stress effects on interfacial and nanostructured materials,” Materials Science and Engineering a-Structural Materials Properties Microstructure and Processing, 237, No. 2, 180-184 (1997).
J. He and C. M. Lilley, “Surface effect on the elastic behavior of static bending nanowires,” Nano Letters, 8, No. 7, 1798-1802 (2008).
T. Y. Chen, M. S. Chiu, and C. N. Weng, “Derivation of the generalized Young-Laplace equation of curved interfaces in nanoscaled solids,” J. of Appl. Phys., 100, No. 7 (2006).
M. E. Gurtin, J. Weissmuller, and F. Larche, “A general theory of curved deformable interfaces in solids at equilibrium,”. Philosophical Magazine a-Physics of Condensed Matter Structure Defects and Mechanical Properties, 78, No. 5, 1093-1109 (1998).
M. E. Gurtin, X. Markenscoff, and R. N. Thurston, “Effect of surface stress on natural frequency of thin crystals,” Appl. Phys. Let., 29, No. 9, 529-530 (1976).
P. Muller and A. Saul, “Elastic effects on surface physics,”. Surface Science Reports, 54, Nos. 5-8, 157-258 (2004).
W. D. Nix and H. J. Gao, “An atomistic interpretation of interface stress,”. Scripta Materialia, 39, No. 12, 1653-1661 (1998).
C. Q. Ru, “Simple geometrical explanation of Gurtin-Murdoch model of surface elasticity with clarification of its related versions,”. Science China-Physics Mechanics & Astronomy, 53, No. 3, 536-544 (2010).
J. N. Reddy and J. N. Reddy, Theory and Analysis of Elastic Plates and Shells, Ed. by J. N. Reddy 2007, Boca Raton, Fla. : London: Boca Raton, Fla. : CRC London : Taylor & Francis distributor.
S. Timoshenko and S. Woinowsky-Krieger, Theory of Plates and Shells. 2d ed. Engineering societies monographs 1959, New York,: McGraw-Hill. 580 p.
A. H. Nayfeh and P. F. Pai, Linear and Nonlinear Structural Mechanics. Wiley series in nonlinear science 2004, Hoboken, N.J.: Wiley-Interscience. xvii, 746 p.
C. Mi, S. Jun, D. A. Kouris, and S. Y. Kim, “Atomistic calculations of interface elastic properties in noncoherent metallic bilayers,” Physical Review B, 77, 075425(2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Russian translation published in Mekhanika Kompozitnykh Materialov, Vol. 52, No. 5, pp. 955-972, September-October, 2016.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, M., Wang, B.L. & Yu, A. Effect of surface and interface energies on the nonlinear bending behaviour of nanoscale laminated thin plates. Mech Compos Mater 52, 673–686 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-016-9616-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-016-9616-x