Abstract
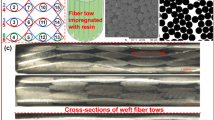
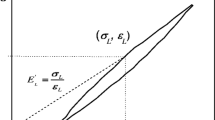
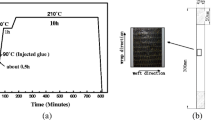
In this paper, the progressive damage of 2.5D layer-to-layer angle-interlock woven composites under quasi-static tension is investigated on a mesoscopic scale. A damage model is developed, considering the fiber damage, matrix crack and interfacial damage. The representative volume cell is established to predict the strength of the 2.5D woven composites. The damage initiation and propagation criteria are based on the Puck criterion for the fiber yarn, the paraboloidal yield criterion for the matrix and the quadratic stress criterion for the fiber yarn–matrix interface. The tensile stress–strain curve and damage evolution law of the woven composites are predicted. Some typical experiments are carried out to verify this numerical model. The damage behavior of the composites, where the variation of the interfacial fracture energy is taken into consideration, is simulated to study the influence of the interface properties on the strength. The results show that the fiber yarn–matrix interface damage characteristics play an important role in tensile strength.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dalmaz, A., Reynaud, P., Rouby, D., Fantozzi, G., Abbe, F.: Mechanical behavior and damage development during cyclic fatigue at high-temperature of a 2.5D carbon/SiC composite. Compos. Sci. Technol. 58, 693–699 (1998)
Boitier, G., Vicens, J., Chermant, J.L.: Understanding the creep behavior of a 2.5D Cf–SiC composite-I. Morphology and microstructure of the as-received material. Mater. Sci. Eng. A(279), 73–80 (2000)
Boitier, G., Vicens, J., Chermant, J.L.: Understanding the creep behavior of a 2.5D Cf–SiC composite. III. From mesoscale to nanoscale microstructural and morphological investigation towards creep mechanism. Mater. Sci. Eng. A(313), 53–63 (2001)
Ma, J., Xu, Y., Zhang, L., Cheng, L., Nie, J., Dong, N.: Microstructure characterization and tensile behavior of 2.5D C/SiC composites fabricated by chemical vapor infiltration. Scr. Mater. 54(11), 1967–1971 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2006.01.047
Dong, W.F., Xiao, J., Li, Y.: Finite element analysis of the tensile properties of 2.5D braided composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 457(1–2), 199–204 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2006.12.032
Kong, C., Sun, Z., Niu, X., Song, Y.: Analytical model of elastic modulus and coefficient of thermal expansion for 2.5D C/SiC composite. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 28(3), 494–499 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-013-0719-0
Lu, Z., Zhou, Y., Yang, Z., Liu, Q.: Multi-scale finite element analysis of 2.5D woven fabric composites under on-axis and off-axis tension. Comput. Mater. Sci. 79, 485–494 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2013.07.003
Sun, B., Gu, B., Ding, X.: Compressive behavior of 3-D angle-interlock woven fabric composites at various strain rates. Polym. Test. 24(4), 447–454 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2005.01.005
Dong, K., Liu, K., Pan, L.J., Gu, B.H., Sun, B.Z.: Experimental and numerical investigation on the thermal conduction properties of 2.5D angle-interlock woven composites. Compos. Struct. 154, 319–333 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2016.07.071
Guo-dong, F., Jun, L., Bao-lai, W.: Progressive damage and nonlinear analysis of 3D four-directional braided composites under unidirectional tension. Compos. Struct. 89(1), 126–133 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2008.07.016
Zhong, S., Guo, L., liu, G., Lu, H., Zeng, T.: A continuum damage model for three-dimensional woven composites and finite element implementation. Compos. Struct. 128, 1–9 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2015.03.030
Zhong, S., Guo, L., Liu, G., Zhang, L., Pan, S.: A random waveness model for the stiffness and strength evaluation of 3D woven composites. Compos. Struct. 152, 1024–1032 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2016.06.051
Sun, Z., Kong, C., Niu, X., Song, Y., Wang, X.: Optimization and reliability analysis of 2.5D C/SiC composites turbine stator vane. Appl. Compos. Mater. 21(5), 789–803 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-013-9374-z
Song, J., Wen, W., Cui, H., Zhang, H., Xu, Y.: Finite element analysis of 2.5D woven composites, part II: damage behavior simulation and strength prediction. Appl. Compos. Mater. 23(1), 45–69 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-015-9449-0
Rahali, Y., Assidi, M., Goda, I., Zghal, A., Ganghoffer, J.F.: Computation of the effective mechanical properties including nonclassical moduli of 2.5D and 3D interlocks by micromechanical approaches. Compos. Part B Eng. 98, 194–212 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2016.04.066
Ismar, H., Schröter, F., Streicher, F.: Influence of the fiber volume fraction and the fiber Weibull modul on the behavior of 2D woven SiC_SiC—a finite element simulation. Acta Mech. 149, 41–54 (2001)
Shindo, Y., Narita, F., Sato, T.: Analysis of mode II interlaminar fracture and damage behavior in end notched flexure testing of GFRP woven laminates at cryogenic temperatures. Acta Mech. 187(1–4), 231–240 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-006-0357-0
Fish, J., Filonova, V., Kuznetsov, S.: Micro-inertia effects in nonlinear heterogeneous media. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 91(13), 1406–1426 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.4322
Hashin, Z.: Fatigue failure criteria for unidirectional fiber composites. J. Appl. Mech. 48, 846–852 (1981)
Puck, A., Schürmann, H.: Failure analysis of FRP laminates by means of physically based phenomenological models. Compos. Sci. Technol. 58, 1045–1067 (1998)
Puck, A., Kopp, J., Knops, M.: Guidelines for the determination of the parameters in Puck’s action plane strength criterion. Compos. Sci. Technol. 62, 371–378 (2002)
Chang, F.-K., Chang, K.-Y.: A progressive damage model for laminated composites containing stress. J. Compos. Mater. 21, 0834–0855 (1987)
Tsai, S.W., Wu, E.M.: A general theory of strength for anisotropic materials. J. Compos. Mater. 5, 58–80 (1971)
Hoffman, O.: The brittle strength of orthotropic materials. Journal of Composite Materials. J. Compos. Mater. 1, 200–206 (1967)
Hill, R.: A theory of the yielding and plastic flow of anisotropic metals. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 193, 281–297 (1948)
Tandon, G.P., Kim, R.Y., Bechel, V.T.: Fiber–matrix interfacial failure characterization using a cruciform-shaped specimen. J. Compos. Mater. 36(23), 2667–2691 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1177/002199802761675575
Zhandarov, S.: Characterization of fiber/matrix interface strength: applicability of different tests, approaches and parameters. Compos. Sci. Technol. 65(1), 149–160 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2004.07.003
Yang, L., Thomason, J.L.: Interface strength in glass fibre-polypropylene measured using the fibre pull-out and microbond methods. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 41(9), 1077–1083 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2009.10.005
Ogihara, S., Koyanagi, J.: Investigation of combined stress state failure criterion for glass fiber/epoxy interface by the cruciform specimen method. Compos. Sci. Technol. 70(1), 143–150 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2009.10.002
Catalanotti, G., Camanho, P.P., Marques, A.T.: Three-dimensional failure criteria for fiber-reinforced laminates. Compos. Struct. 95, 63–79 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2012.07.016
Koyanagi, J., Hatta, H., Kotani, M., Kawada, H.: A comprehensive model for determining tensile strengths of various unidirectional composites. J. Compos. Mater. 43(18), 1901–1914 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1177/0021998309341847
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, H., Guo, L., Liu, G. et al. Progressive damage investigation of 2.5D woven composites under quasi-static tension. Acta Mech 230, 1323–1336 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-017-2024-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-017-2024-z