Abstract
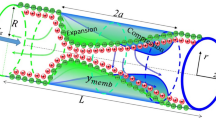
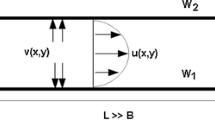
We present a three-dimensional model for flow pumping in a channel induced by two moving contractions from the upper wall. This pumping model is inspired by insect respiration processes, specifically, the rhythmic collapses that take place within their tracheal tube networks. The present work is a natural extension of our previous theoretical and numerical investigations of a two-dimensional insect-inspired micropumping model, which accounts for three-dimensional effects and further validates our insect-inspired pumping paradigm (Aboelkassem and Staples in Acta Mech 223(3):463–480, 2012a; Theor Comput Fluid Dyn, 2012b. doi:10.1007/s00162-012-0269-7). The formal goal of this article is to compare three-dimensional Stokeslets-meshfree numerical results with results from our previous two-dimensional analytical pumping model. We use regularized Stokeslets-meshfree computations in three dimensions to reconstruct the flow motions induced by wall contractions and to calculate the time-averaged net flow pumping rate. The results show that, although the net flow rate distribution as a function of the wall motion time (phase) lag parameter for the three-dimensional Stokeslets-meshfree computations and the two-dimensional analytical model displays some differences, the same basic features appear in both cases, leading to the same general conclusions about the proposed pumping paradigm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aboelkassem, Y.: Novel Bioinspired Pumping Models for Microscale Flow Transport. PhD. Dissertation, Virginia Tech (2012)
Aboelkassem Y., Staples A.E.: Flow transport in a microchannel induced by moving wall contractions: a novel micropumping mechanism. Acta Mech. 223(3), 463–480 (2012a)
Aboelkassem Y., Staples A.E.: Stokeslets-meshfree computations and theory for flow in a collapsible microchannel. Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 27(5), 681–700 (2012b) doi:10.1007/s00162-012-0269-7
Aboelkassem, Y., Staples, A.E.: A bioinspired pumping model for flow in a microtube with rhythmic wall contractions. J. Fluids Struct. (in press), (2013a). doi:10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2013.06.003
Aboelkassem Y., Staples A.E.: Selective pumping in a network: insect-style microscale flow transport. Bioinspir. Biomim. 8, 026004 (2013)
Aboelkassem Y., Staples A.E., Socha J.: Microscale flow pumping inspired by rhythmic tracheal compressions in insects. Proc. ASME Press. Vessel. Piping PVP2011, 57061 (2011)
Ainley J., Durkin S., Embid R., Boindala P., Cortez R.: The method of images for regularized stokeslets. J. Comput. Phys. 227, 4600–4616 (2008)
Alves C., Silvestre A.: Density results using stokeslets and a method of fundamental solutions for the stokes equations. Eng. Anal. Boundary Elem. 28, 1245–1252 (2004)
Aranda V., Cortez R., Fauci L.: Stokesian peristaltic pumping in a three-dimensional tube with a phase-shift asymmetry. Phys. Fluids 23, 081901 (2011)
Cortez R.: The method of regularized stokeslets. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 23, 1204–1225 (2001)
Cortez R., Fauci L., Medovikov A.: The method of regularized stokeslets in three dimensions: analysis, validation, and applications to helical swimming. Phys. Fluids 17, 031504 (2005)
Macagno E., Christensen J.: Fluid mechanics of the duodenum. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 12, 139–158 (1980)
Macagno E., Christensen J., Lee L.: Modeling the effect of wall movement on absorption in the intestine. Am. J. Physiol. 243, G541–G550 (1982)
Mahmood T., Merkin J.: The flow in a narrow duct with an indentation or hump on one wall. Wärme- und Stoffübertragung 22, 69–76 (1990)
Neumaier A.: Solving ill-conditioned and singular linear systems: a tutorial on regularization. SIAM Rev. 40, 636–666 (1998)
Pedley T., Stephanoff K.D.: Flow along channel with a time-dependent indentation in one wall: the generation of vorticity waves. J. Fluid Mech. 160, 337–367 (1985)
Ralph M., Pedley T.J.: Flow in a channel with moving indentation. J. Fluid Mech. 190, 87–112 (1988)
Secomb T.: Flow in a channel with pulsating walls. J. Fluid Mech. 88, 273–288 (1978)
Singh P., Radhakrishnan V., Narayan K.A.: Squeezing flow between parallel plates. Ingenieur-Archiv 60, 274–281 (1990)
Skalak F., Wang C.Y.: On the unsteady squeezing of a viscous fluid from a tube. J. Aust. Math. Soc. 21(Series B), 65–74 (1978)
Socha J.J., Förster T., Greenlee K.: Issues of convection in insects respiration: insights from synchrotron X-ray imaging and beyond. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 173, S65–S73 (2010)
Socha J.J., Lee W.-K., Harrison J.F., Waters J.S., Fezzaa K., Westneat M.W.: Correlated patterns of tracheal compression and convective gas exchange in a carabid beetle. J. Exp. Biol. 211, 3409–3420 (2008)
Tsuda A., Rogers R.A., H P.E., Butler J.P.: Chaotic mixing deep in the lung. PNAS 99(15), 10173–10178 (2002)
Uchida S., Aoki H.: Unsteady flows in a semi-infinite contracting or expanding pipe. J. Fluid Mech. 82, 371–387 (1977)
Wang C.Y.: Arbitrary squeezing of fluid from a tube at low squeeze numbers. J. Appl. Math. Phys. (ZAMP) 31, 620–627 (1980)
Westneat M.W., Socha J., Lee W.-K.: Advances in biological structure, function and physiology using synchrotron X-ray imaging. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 70, 119–142 (2008)
Westneat M.W., Betz O., Blob R.W., Fezzaa K., Cooper W.J., Lee W.-K.: Tracheal respiration in insects visualized with synchrotron X-ray imaging. Science 299, 558–560 (2003)
Young D.L., Chen C., Fan C.M., Murugesan K., Tsai C.C.: The method of fundamental solutions for stokes flow in a rectangular cavity with cylinders. J. Mech. B-Fluids 24, 703–716 (2005)
Young D.L., Jane S.J., Fan C.M., Murugesan K., Tsai C.C.: The method of fundamental solutions for 2d and 3d stokes problems. J. Comput. Phys. 211, 1–8 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aboelkassem, Y., Staples, A.E. A three-dimensional model for flow pumping in a microchannel inspired by insect respiration. Acta Mech 225, 493–507 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-013-0964-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-013-0964-5