Abstract
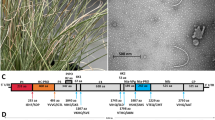
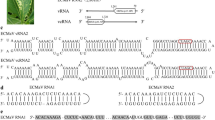
A new sobemovirus, which we have named “mimosa mosaic virus” (MimMV), was found by high-throughput sequencing and isolated from a mimosa (Mimosa sensitiva L.) plant. The genome sequence was confirmed by Sanger sequencing and comprises 4595 nucleotides. Phylogenetic analysis based on the predicted amino acid (aa) sequences of the P2b protein (encoded by ORF2b) and the coat protein showed 52.7% and 31.8% aa sequence identity, respectively, to those of blueberry shoestring virus. The complete genome sequence of MimMV was less than 47% identical to those of other sobemoviruses. These data suggest that MimMV is a member of a new species in the genus Sobemovirus, for which the binomial name “Sobemovirus mimosae” is proposed.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Cali BB, Moyer JW (1981) Purification, serology, and particle morphology of two russet crack strains of sweet potato feathery mottle virus. Phytopathology 71:302–305
Blawid R, Silva JMF, Nagata T (2017) Discovering and sequencing new plant viral genomes by next-generation sequencing: description of a practical pipeline. Ann Appl Biol 170:301–314
Nicolini C, Inoue-Nagata AK, Nagata T (2015) Complete genome sequence of a proposed new tymovirus, tomato blistering mosaic virus. Arch Virol 160:609–612
Sõmera M, Sarmiento C, Truve E (2015) Overview on sobemoviruses and a proposal for the creation of the family Sobemoviridae. Viruses 7:3076–3115
Desbiez C, Verdin E, Lecoq H (2021) Complete sequence of an isolate of snake melon asteroid mosaic virus confirms that it is a member of a distinct sobemovirus species. Arch Virol 166:2311–2313
Siré C, Bangratz-Reyser M, Fargette D et al (2008) Genetic diversity and silencing suppression effects of Rice yellow mottle virus and the P1 protein. Virol J 5:1–12
Ling R, Pate AR, Carr JP et al (2013) An essential fifth coding ORF in the sobemoviruses. Virology 446:397–408
Olspert A, Peil L, Hebrard E et al (2011) Protein–RNA linkage and post-translational modifications of two sobemovirus VPgs. J Gen Virol 92:445–452
Tamm T, Suurväli J, Lucchesi J et al (2009) Stem-loop structure of cocksfoot mottle virus RNA is indispensable for programmed -1 ribosomal frameshifting. Virus Res 146:73–80
Lorenz R, Bernhart SH, HönerzuSiederdissenC, et al (2011) ViennaRNA Package 2.0. Algorithms Mol Biol 6:1–4
Martin DP, Murrell B, Golden M et al (2015) RDP4: detection and analysis of recombination patterns in virus genomes. Virus Evol 1:1–5
Minh BQ, Schmidt HA, Chernomor O (2020) IQ-TREE 2: new models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Mol Biol Evol 37:1530–1534
Kalyaanamoorthy S, Minh BQ, Wong TK et al (2017) ModelFinder: fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat Methods 14:587–589
Sõmera M, Fargette D, Hébrard E et al (2021) ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Solemoviridae 2021. J Gen Virol 102:001707
Acknowledgements
CMK and TN are CNPq fellows, Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Ralf Georg Dietzgen.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kauffmann, C.M., de Jesus Boari, A., Silva, J.M.F. et al. Complete genome sequence of mimosa mosaic virus, a new sobemovirus infecting Mimosa sensitiva L.. Arch Virol 168, 28 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-022-05683-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-022-05683-5