Abstract
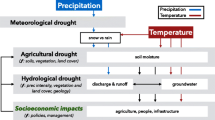
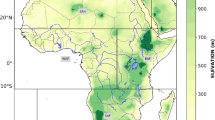
This study focuses on the assessment of successive drought relations by using the standardized precipitation index, standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index, and the streamflow drought index. The main goal is to propose lag times between drought events using factors like longitude and elevation and to construct maps that cover precipitation threshold values, and critical precipitation values corresponding to return periods using meteorological indices. For this purpose, monthly streamflow datasets of 42 stations and monthly meteorological datasets of 25 stations from 1972 to 2011 were used. Results indicate that mean elevations of the sub-catchments showed a decisive role in the amount of drought delay. The sub-catchments located in the low altitudes showed no delay in translation, whereas the sub-catchments located in the highly elevated regions showed 2-month delay in the monthly time scale. Moreover, the success of drought relations is more pronounced with temperature datasets, especially in the highly elevated regions for greater drought periods. In the second part, the spatial variation of the precipitation in defining the threshold values depicts that although there is some variety in the precipitation values for time scales less than 12 months, there is no visual difference between the two indices for yearly time scales. And, the mild and extreme droughts are obtained for yearly precipitation values of less than 628 and 427 mm, respectively. With calculations in return-period precipitation amounts, it is inferred that temperature is a strong dataset in defining precipitation values for return periods greater than 10 years and duration time less than 5 months. Since the findings in this study present physical and practical value, they can be key for stakeholders, policymakers, and end users in water allocation studies. Furthermore, it can be useful in ungauged points with missing data and therefore, if necessary, modification in crop patterns and changes in land use for specific areas can be done. And this study can be more beneficial by adding datasets covering climate change scenarios as future work.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The meteorological and hydrological datasets can be purchased from the Turkish State Meteorological Service (TSMS) and State Hydraulic works (DSİ) respectively.
Code availability
The author used different software such as Matlab, ArcGIS, and Microsoft Excel for preparation or analyzing data and producing maps.
Abbreviations
- D:
-
Drought duration
- ETDI:
-
Evapotranspiration deficit index
- I:
-
Drought intensity
- k :
-
Time scale
- LT:
-
Lag time
- M:
-
Month
- NDVI:
-
Normalized difference vegetation index
- P:
-
Precipitation
- PDF:
-
Probability distribution function
- PDSI:
-
Palmer Drought Severity Index
- PET:
-
Evapotranspiration
- PrecipDF:
-
Precipitation-duration-frequency
- RDI:
-
Reconnaissance drought index
- RP:
-
Return period
- S :
-
Drought severity
- S max :
-
Critical drought severity
- SDI:
-
Streamflow drought index
- SGI:
-
Standardized groundwater index
- SPEI:
-
Standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index
- SPI:
-
Standardized precipitation index
- SRI:
-
Standardized runoff index
- T e :
-
Drought end time
- T i :
-
Drought initiation time
- TH :
-
Threshold
- UTRC:
-
Upper Tigris River catchment
- WS:
-
Water surplus
- VCI :
-
Vegetation condition index
- α :
-
Shape parameter
- β :
-
Scale parameter
- Γ(α) :
-
Gamma function
- K :
-
Correction coefficient
- T :
-
Monthly mean temperature (°C)
- H :
-
Heat index
- h :
-
Coefficient of heat index
- P r :
-
Exceedance probability
References
Abramowitz M, Stegun IA (1964) Handbook of mathematical functions with formulas, graphs, and mathematical tables. Government Printing Office, U.S
Adnan RM, Mostafa RR, Islam ARMT et al (2021) Improving drought modeling using hybrid random vector functional link methods. Water 13:3379. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13233379
Adnan RM, Dai H-L, Kuriqi A et al (2023) Improving drought modeling based on new heuristic machine learning methods. Ain Shams Eng J 14:102168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2023.102168
Alizamir M, Kisi O, Muhammad Adnan R, Kuriqi A (2020) Modelling reference evapotranspiration by combining neuro-fuzzy and evolutionary strategies. Acta Geophys 68:1113–1126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-020-00446-9
Bachmair S, Stahl K, Collins K et al (2016) Drought indicators revisited: the need for a wider consideration of environment and society. Wires Water 3:516–536. https://doi.org/10.1002/wat2.1154
Barker LJ, Hannaford J, Chiverton A, Svensson C (2016) From meteorological to hydrological drought using standardised indicators. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 20:2483–2505. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-20-2483-2016
Bayer Altin T, Altin BN (2021) Response of hydrological drought to meteorological drought in the eastern Mediterranean Basin of Turkey. J Arid Land 13:470–486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40333-021-0064-7
Bloomfield JP, Marchant BP (2013) Analysis of groundwater drought building on the standardised precipitation index approach. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 17:4769–4787. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-17-4769-2013
Cai X, Shafiee-Jood M, Apurv T et al (2017) Key issues in drought preparedness: reflections on experiences and strategies in the United States and selected countries. Water Security 2:32–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasec.2017.11.001
Cancelliere A, Salas JD (2004) Drought length properties for periodic-stochastic hydrologic data. Water Resour Res 40:1-13. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002WR001750
Cavus Y, Aksoy H (2020) Critical drought severity/intensity-duration-frequency curves based on precipitation deficit. J Hydrol 584:124312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124312
Crausbay SD, Ramirez AR, Carter SL et al (2017) Defining ecological drought for the twenty-first century. Bull Am Meteor Soc 98:2543–2550. https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-16-0292.1
Dai A (2011) Characteristics and trends in various forms of the Palmer Drought Severity Index during 1900–2008. J Geophys Res: Atmospheres 116:D12115. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010JD015541
Danandeh Mehr A, Sorman AU, Kahya E, Hesami Afshar M (2020) Climate change impacts on meteorological drought using SPI and SPEI: case study of Ankara, Turkey. Hydrol Sci J 65:254–268. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2019.1691218
Gevaert AI, Veldkamp TIE, Ward PJ (2018) The effect of climate type on timescales of drought propagation in an ensemble of global hydrological models. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 22:4649–4665. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-22-4649-2018
Guttman NB (1994) On the sensitivity of sample L moments to sample size. J Climate 7:1026–1029. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(1994)007%3c1026:OTSOSL%3e2.0.CO;2
Hao Z, Singh VP (2015) Integrating entropy and copula theories for hydrologic modeling and analysis. Entropy 17:2253–2280. https://doi.org/10.3390/e17042253
Haslinger K, Koffler D, Schöner W, Laaha G (2014) Exploring the link between meteorological drought and streamflow: effects of climate-catchment interaction. Water Resour Res 50:2468–2487. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013WR015051
Huang S, Li P, Huang Q et al (2017) The propagation from meteorological to hydrological drought and its potential influence factors. J Hydrol 547:184–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.01.041
Jones C, Sultan M, Yan E et al (2008) Hydrologic impacts of engineering projects on the Tigris-Euphrates system and its marshlands. J Hydrol 353:59–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.01.029
Kibaroglu A (2019) State-of-the-art review of transboundary water governance in the Euphrates-Tigris river basin. Int J Water Resour Dev 35:4–29. https://doi.org/10.1080/07900627.2017.1408458
Kogan FN (1995) Application of vegetation index and brightness temperature for drought detection. Adv Space Res 15:91–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/0273-1177(95)00079-T
Kottek M, Grieser J, Beck C, Rudolf B, Rubel F (2006) World Map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification updated. Meteorol Z 3:259–263
Kubiak-Wójcicka K, Pilarska A, Kamiński D (2021) The analysis of long-term trends in the meteorological and hydrological drought occurrences using non-parametric methods—case study of the catchment of the upper Noteć River (Central Poland). Atmosphere 12:1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091098
Kuriqi A, Pinheiro AN, Sordo-Ward A, Garrote L (2019) Influence of hydrologically based environmental flow methods on flow alteration and energy production in a run-of-river hydropower plant. J Clean Prod 232:1028–1042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.05.358
Kuriqi A, Pinheiro AN, Sordo-Ward A et al (2021) Ecological impacts of run-of-river hydropower plants—current status and future prospects on the brink of energy transition. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 142:110833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2021.110833
Labudová L, Labuda M, Takáč J (2017) Comparison of SPI and SPEI applicability for drought impact assessment on crop production in the Danubian Lowland and the East Slovakian Lowland. Theor Appl Climatol 128:491–506. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-016-1870-2
Li B, Liang Z, Zhang J, Wang G (2017) A revised drought index based on precipitation and pan evaporation. Int J Climatol 37:793–801. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.4740
Liu WT, Kogan FN (1996) Monitoring regional drought using the vegetation condition index. Int J Remote Sens 17:2761–2782. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431169608949106
López-Moreno JI, Vicente-Serrano SM, Zabalza J et al (2013) Hydrological response to climate variability at different time scales: a study in the Ebro basin. J Hydrol 477:175–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.11.028
López-Moreno JI, Vicente-Serrano SM, Beguería S et al (2009) Dam effects on droughts magnitude and duration in a transboundary basin: the lower River Tagus, Spain and Portugal. Water Resour Res 45(2):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008WR007198
McEvoy DJ, Huntington JL, Abatzoglou JT, Edwards LM (2012) An evaluation of multiscalar drought indices in Nevada and Eastern California. Earth Interact 16:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1175/2012EI000447.1
McGuire KJ, McDonnell JJ (2006) A review and evaluation of catchment transit time modeling. J Hydrol 330:543–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2006.04.020
McKee TB, Doesken NJ, Kleist J (1993) The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. In: Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Applied Climatology. p 6
Mishra AK, Singh VP, Desai VR (2009) Drought characterization: a probabilistic approach. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 23:41–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-007-0194-2
Mishra AK (2010) A review of drought concepts. J Hydrol 15
Miyan MA (2015) Droughts in Asian Least developed countries: vulnerability and sustainability. Weather Clim Extremes 7:8–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wace.2014.06.003
Młyński D, Wałęga A, Kuriqi A (2021) Influence of meteorological drought on environmental flows in mountain catchments. Ecol Indic 133:108460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.108460
Mukherjee S, Mishra A, Trenberth KE (2018) Climate change and drought: a perspective on drought indices. Curr Clim Change Rep 4:145–163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40641-018-0098-x
Muratoglu A (2019) Water footprint assessment within a catchment: a case study for Upper Tigris River Basin. Ecol Indic 106:105467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.105467
Nalbantis I, Tsakiris G (2009) Assessment of hydrological drought revisited. Water Resour Manage 23:881–897. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-008-9305-1
Narasimhan B, Srinivasan R (2005) Development and evaluation of soil moisture deficit index (SMDI) and evapotranspiration deficit index (ETDI) for agricultural drought monitoring. Agric for Meteorol 133:69–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2005.07.012
Özdoğan M (2011) Climate change impacts on snow water availability in the Euphrates-Tigris basin. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 15:2789–2803. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-15-2789-2011
Ozkaya A, Zerberg Y (2019) A 40-year analysis of the hydrological drought index for the Tigris Basin. Turkey Water 11:657. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040657
Palmer WC (1965) Meteorological drought. U.S. Department of Commerce, Weather Bureau
Panu US, Sharma TC (2002) Challenges in drought research: some perspectives and future directions. Hydrol Sci J 47:S19–S30. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626660209493019
Pardo-Igúzquiza E (1998) Comparison of geostatistical methods for estimating the areal average climatological rainfall mean using data on precipitation and topography. Int J Climatol 18:1031–1047. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0088(199807)18:9%3c1031::AID-JOC303%3e3.0.CO;2-U
Paulo AA, Rosa RD, Pereira LS (2012) Climate trends and behaviour of drought indices based on precipitation and evapotranspiration in Portugal. Nat Hazard 12:1481–1491. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-12-1481-2012
Pei Z, Fang S, Wang L, Yang W (2020) Comparative analysis of drought indicated by the SPI and SPEI at various timescales in Inner Mongolia. China Water 12:1925. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071925
Quesada-Montano B, Wetterhall F, Westerberg IK et al (2018) Characterising droughts in Central America with uncertain hydro-meteorological data. Theor Appl Climatol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-018-2730-z
Schmandt J, Kibaroglu A, Buono R, Thomas S (2021) Sustainability of engineered rivers in arid lands: challenge and response. Cambridge University Press
Shukla S, Wood AW (2008) Use of a standardized runoff index for characterizing hydrologic drought. Geophysical Research Letters 35:. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007GL032487
Thorn HCS (1966) Some methods of climatological analysis. Secretariat of the World Meteorological Organization, Geneva, Switzerland
Thornthwaite CW (1948) An approach toward a rational classification of climate. Geogr Rev 38:55–94. https://doi.org/10.2307/210739
Tsakiris G, Kordalis N, Tigkas D et al (2016) Analysing drought severity and areal extent by 2D Archimedean copulas. Water Resour Manage 30:5723–5735. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1543-z
Tsakiris G, Vangelis H (2005) Establishing a drought index incorporating evapotranspiration. Eur Water 9(10):3–11.
Uysal G (2022) Product- and hydro-validation of satellite-based precipitation data sets for a poorly gauged snow-fed basin in Turkey. Water 14:2758. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14172758
Van Loon AF, Van Lanen HAJ (2012) A process-based typology of hydrological drought. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 16:1915–1946. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-16-1915-2012
Van Loon AF, Gleeson T, Clark J et al (2016) Drought in the Anthropocene. Nature Geosci 9:89–91. https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo2646
Vasiliades L, Loukas A (2009) Hydrological response to meteorological drought using the Palmer drought indices in Thessaly, Greece. Desalination 237:3–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2007.12.019
Vicente-Serrano SM, Beguería S, López-Moreno JI (2010) A multiscalar drought index sensitive to global warming: the standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index. J Clim 23:1696–1718. https://doi.org/10.1175/2009JCLI2909.1
Wilhite DA, Glantz MH (1985) Understanding: the drought phenomenon: the role of definitions. Water Int 10:111–120. https://doi.org/10.1080/02508068508686328
Wu J, Chen X, Yao H et al (2017) Non-linear relationship of hydrological drought responding to meteorological drought and impact of a large reservoir. J Hydrol 551:495–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.06.029
Xu Y, Zhang X, Wang X et al (2019) Propagation from meteorological drought to hydrological drought under the impact of human activities: a case study in northern China. J Hydrol 579:124147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124147
Yevjevich V (1967) An objective approach to definitions and investigations of continental hydrologic droughts. Colorado State University, Fort Collins
Zuo D, Hou W, Hu J (2017) An entropy-based investigation into bivariate drought analysis in China. Water 9:632. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9090632
Acknowledgements
The author is grateful to the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions to further improve this paper. The meteorological and hydrological datasets were provided by the Turkish State Meteorological Service (TSMS) and State Hydraulic works (DSİ) respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All analyses presented here were performed by the author of this paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
The author consented to participate of the present study.
Consent for publication
The author read the manuscript and agreed for the publication.
Conflict of interest
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ozkaya, A. Evaluating the relation between meteorological drought and hydrological drought, and the precipitation distribution for drought classes and return periods over the upper Tigris River catchment. Theor Appl Climatol 153, 727–753 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-023-04494-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-023-04494-1