Abstract
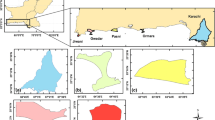
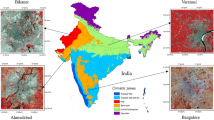
The present study attempts to evaluate the urban energy balance components concerning increasing urbanization and artificial surfaces over Indian metropolitan cities during the 2000–2018 winter seasons by using Landsat 7 and 8 satellite imageries. The results indicate that the estimated ranges of the energy fluxes are in the typical values reported in the earlier literature over global cities. The sensible heat flux (SHF) increased considerably, and the latent heat flux (LHF) slightly decreased during the study period. The mean SHF over the built-up areas (BA) and the dry lands (DL) of Delhi record a maximum increase of 28.2 Wm−2and 39.7 Wm−2 during the study period. The inland cities have high values of SHF over DL than the coastal cities, and the LHF is high over all the land use classes for the west coast cities. The SHF (LHF) shows a positive (negative) correlation with the land surface temperature. The SHF (LHF) is about 19–33% (1.9–15%) of the net radiation flux, and the residual heat flux is about 60 to 80% of the net radiation flux. The present study advocates that the substantial changes of the surface energy balance parameters have a profound influence on the energy exchange mechanism and could affect regional climatic change.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data utilized for the study are available freely for users in the corresponding websites as mentioned in the “Study area and data” section of the manuscript.
Code availability
Software: ArcGIS 10.3, ERDAS Imagine, MATLAB.
References
Allen RG, Tasumi M, Trezza R (2007) Satellite-based energy balance for mapping evapotranspiration with internalized calibration (METRIC) - Model. J Irrig Drain Eng 133:380–394. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9437133:4(380)
Allen R, Waters R, Tasumi M, Trezza R, Bas-tiaanssen W (2002) SEBAL, Surface energy balance algorithms for land, Idaho Implementation. Advanced Training and User’s manual, version 1.0
An N, Hemmati S, Cui Y (2017) Assessment of the methods for determining net radiation at different time-scales of meteorological variables. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 9(2):239–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2016.10.004
Bastiaanssen WGM (2000) SEBAL-based sensible and latent heat fluxes in the irrigated Gediz Basin, Turkey. J Hydrol 229:87–100
Bastiaanssen WGM (1995) Regionalization of surface flux densities and moisture indicators in composite terrain: a remote sensing approach under clear skies in Mediterranean climates. Ph.D. Dissertation, CIP Data KoninklijkeBibliotheek, Den Haag, The Netherlands
Bhatla R, Raju PVS, Mohanty UC, Madanand OP, Mall RK (2011) Study of energy fluxes over the Indian Ocean prior and during the Summer Monsoon. Mar Geodesy 34(2):119–137
Bhatla R, Raju PVS, Mall RK, Bist S (2016) Study of surface fluxes during onset of summer monsoon over India. Int J Climatol 36(4):1821–1832. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.4462
Brenner C, Thiem CE, Wizemann H, Bernhardt M, Schulz K (2017) Estimating spatially distributed turbulent heat fluxes from high-resolution thermal imagery acquired with a UAV system. Int J Remote Sens 38(8–10):3003–3026. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2017.1280202
Brutsaert W (1982) In Evaporation into the atmosphere –Theory, History and Applications. Springer, Dordrecht
Carlson TN, Ripley DA (1997) On the relation between NDVI, fractional vegetation cover, and leaf area index. Remote Sens Environ 62(3):241–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-4257(97)00104-1
Census 2011 of India.Accessed 29 June 2020. http://www.censusindia.gov.in
Chen S, Hu D (2017) Parameterizing anthropogenic heat flux with an energy-consumption inventory and multi-source remote sensing data. Remote Sens 9:1165
Christen A, Vogt R (2004) Energy and radiation balance of a central European city. Int J Climatol 24:1395–1421
Chrysoulakis N et al (2018) Urban energy exchanges monitoring from space. Sci Rep 8:11498. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-29873-x
Crawford TM, Bluestein HB (2000) An operational, diagnostic surface energy budget model. J Appl Meteorol 39:1196–1217
Duijm NJ (1999) Estimation of roughness parameters for arrays of obstacles. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 91:1–22
Eswar R, Sekhar M, Bhattacharya BK (2017) Comparison of three remote sensing-based models for the estimation of latent heat flux over India. Hydrol Sci J 62(16):2705–2719. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2017.1404067
Goldreich Y (1992) Urban climate studies in Johannesburg, a subtropical city located on a ridge – a review. Atmos Environ 26B:407–420
Grimmond CSB (1992) The suburban energy balance: methodological considerations and results for a mid-latitude west coast city under winter and spring conditions. Int J Climatol 12:481–497
Grimmond S (2007) Urbanization and global environmental change: local effects of urban warming. Geogr J 173(1):83–88. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-4959.2007.232_3.x
Grimmond CSB, Oke TR (1999) Aerodynamic properties of urban areas derived from analysis of surface form. J Appl Meteorol 38:1262–1292
Grimmond CSB, Salmond JA, Oke TR, Offerle B, Lemonsu A (2004) Flux and turbulence measurements at a densely build-up site in Marseille: Heat, mass (water and carbon dioxide), and momentum. J Geophys Res 109:4936. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004JD004936
Grimmond CSB, Ward HC, Kotthaus S (2016) How is urbanization altering local and regional climate? In: Seto KC, Solecki WD, Griffith CA (eds) The Routledge Handbook of Urbanization and Global Environmental Change. Routledge, London
Hanna S, Marciotto E, Britter R (2011) Urban energy fluxes in build-up downtown areas and variations across the urban area, for use in dispersion models. J Appl Meteor Climatol 50(6):1341–1353. https://doi.org/10.1175/2011JAMC2555.1
Hrisko J, Ramamurthy P, Gonzalez JE (2021) Estimating heat storage in urban areas using multispectral satellite data and machine learning. Remote Sens Environ 252:112125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2020.112125
Kato S, Yamaguchi Y (2005) Analysis of urban heat-island effect using ASTER and ETM+data: separation of anthropogenic heat discharge and natural heat radiation from sensible heat flux. Remote Sens Environ 99:44–54
Kato S, Yamaguchi Y (2007) Estimation of storage heat flux in an urban area using ASTER data. Remote Sens Environ 110:1–17
Kato S, Yamaguchi Y, Liu CC, Sun CY (2008) Surface heat balance analysis of Tainan City on March 6, 2001, using ASTER and Formosat-2 data. Sensors 8:6026–6044
Kotthaus S, Grimmond CSB (2014) Energy exchange in a dense urban environment – part I: temporal variability of long-term observations in central London. Urban Climate 10:261–280
Kuang W, Dou Y, Zhang C, Chi W, Liu A, Liu Y, Zhang R, Liu J (2015) Quantifying the heat flux regulation of metropolitan land use/land cover components by coupling remote sensing modeling with in-situ measurement. J Geophys Res Atmos 120:113–130. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014JD022249
Landsat 7 (L7) Data Users Handbook, version 2.0, November 2019. Document owner: Ihlen, V., LSRD Project Manager, U.S. Geological Survey. Approved by: Zanter, K., LSDS CCB Chair, U.S. Geological Survey. https://www.usgs.gov/media/files/landsat-7-data-users-handbook
Landsat 8 (L8) Data Users Handbook, version 5.0, November 2019, Document owner: Ihlen, V., LSRD Project Manager, U.S. Geological Survey. Approved by: Zanter, K., LSDS CCB Chair, U.S. Geological Survey. https://www.usgs.gov/land-resources/nli/landsat/landsat-8-data-users-handbook
Liang S, Wang D, He T, Yu Y (2019) Remote sensing of earth’s energy budget: synthesis and review. Int J of Digital Earth 12(7):737–780. https://doi.org/10.1080/17538947.2019.1597189
Macdonald RW, Griffiths RF, Hall DJ (1998) An improved method for the estimation of surface roughness of obstacle arrays. Atmos Environ 32:1857–1864
Masson V, Grimmond CSB, Oke TR (2002) Evaluation of the town energy balance (TEB) scheme with direct measurements from dry districts in two cities. J Appl Meteorol 41:1011–1026
Mauder M, Foken T, Cuxart J (2020) Surface-energy-balance closure over land: a review. Bound-Layer Meteorol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-020-00529-6
Mohanty UC, Rao PLS, Raju PVS, Bhatla R (2003) A study on diagnostic aspects of south Asian summer monsoon. Proc Indian Natl Sci Acad 69A(5):505–521
Mohanty UC, Raju PVS, Bhatla R (2005) A study on climatological features of the Asian summer monsoon: dynamics, energetics and variability. Pure Appl Geophys (PAGEOPH) 162(8):1511–1541
Moriwaki R, Kanda M (2004) Seasonal and diurnal fluxes of radiation, heat, water vapor, and carbon dioxide over a suburban area. J Appl Meteorol 43:1700–1710
Munn RE (1966) Descriptive micrometeorology. Academic Press, New York
Myrup LO (1969) A numerical model of the urban heat island. J Appl Meteorol 8:896–907
Nelli NR, Temimi M, Fonseca RM et al (2019) Micrometeorological measurements in an arid environment: diurnal characteristics and surface energy balance closure. Atmos Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2019.104745
Nishida K, Nemani RR, Running SW, Glassy JM (2003) An operational remote sensing algorithm of land surface evaporation. J Geophys Res 108:4720
Offerle B, Jonsson P, Eliasson I, Grimmond CSB (2005) Urban modification of the surface energy balance in the West African Sahel: Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso. J Clim 18:3983–3995
Oke TR (1982) The energetic basis of the urban heat island. Q J R Meteorol Soc 108:1–24
Oke TR (1988) The urban energy balance. Prog Phys Geogr 12:471–508
Oke TR, Yap D, Fuggle RF (1972) Determination of urban sensible heat fluxes. In: Adams WP, Helleiner FM (eds) International geography. Toronto Press, Toronto, pp 176–178
Oke TR, Zeuner G, Jauregui E (1992) The surface energy balance in Mexico City. Atmos Environ 26B:433–444
Oke TR, Spronken-Smith RA, Jáuregui E, Grimmond CSB (1999) The energy balance of central Mexico City during the dry season. Atmos Environ 33:3919–3930
Paulson CA (1970) The mathematical representation of wind speed and temperature profiles in the unstable atmospheric surface layer. J Appl Meteorol 9:857–861
Pearlmutter D, Bitan A, Berliner P (1999) Microclimatic analysis of “compact” urban canyons in an arid zone. Atmos Environ 33:4143–4150
Pearlmutter D, Berliner P, Shaviv E (2005) Evaluation of urban surface energy fluxes using an open-air scale model. J Appl Meteorol 44:532–545
Pearlmutter D, Berliner P, Shaviv E (2006) Physical modeling of the pedestrian energy exchange within the urban canopy. Build Environ 41:783–795
Probald F (1971) The energy balance as the basis of the urban climate of Budapest. Annal U Sc Budapestinensis Sectio Geographica 7:51–68
Prueger JH, Kustas WP (2005) Aerodynamic methods for estimating turbulent fluxes. Publications from USDA-ARS / UNL Faculty, Madison, p 1394
Rahman MM, Zhang W (2019) Review on estimation methods of the Earth’s surface energy balance components from ground and satellite measurements. J Earth Syst Sci 128:84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-019-1098-5
Roth M (2007) Review of urban climate research in (sub)tropical regions. Int J Climatol 27:1859–1873. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.1591
Roth M (2013) Handbook of Environmental Fluid Dynamics, vol 2. pp 143–159
Roupioz L, Jia L, Nerry F, Menenti M (2016) Estimation of daily solar radiation budget at kilometer resolution over the Tibetan Plateau by integrating MODIS data products and a DEM. Remote Sens 8:504. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8060504
Salmond J (1999) Bibliography of urban climate 1996–1999. Available at: http://www.urban-climate.org (last accessed: 20 April 2020).
Salmond J (2005) Bibliography of urban climate 2000–2004. Available at: http://www.urban-climate.org (last accessed: 20 April 2020).
Seto KC, Güneralp B, Hutyra LR (2012) Global forecasts of urban expansion to 2030 and direct impacts on biodiversity and carbon pools. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(40):16083–16088. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1211658109
Silva BBD, Braga AC, Braga CC, Oliveira LMMD, Montenegro SMGL, Barbosa Junior B (2016) Procedures for calculation of the albedo with OLI-Landsat 8 images: application to the Brazilian semi-arid. Rev Bras Engenharia Agrícola e Ambiental 20:3
Sobrino JA, Oltra-Carrió R, Sòria G, Bianchi R, Paganini M (2012) Impact of spatial resolution and satellite overpass time on evaluation of the surface urban heat island effects. Remote Sens Environ 117:50–56
Spronken-Smith RA (2002) Comparison of summer- and winter-time suburban energy fluxes in Christchurch, New Zealand. Int J Climatol 22:979–992
Sultana S, Satyanarayana ANV (2018) Urban heat island intensity during winter over metropolitan cities of India using remote-sensing techniques: impact of urbanization. Int J Rem Sens 39:6692–6730. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2018.1466072
Sultana S, Satyanarayana ANV (2019) Impact of urbanisation on urban heat island intensity during summer and winter over Indian metropolitan cities. Environ Monit Assess 191(Suppl 3):789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7692-9
Sultana S, Satyanarayana ANV (2020) Assessment of urbanisation and urban heat island intensities using Landsat imageries during 2000–2018 over a sub-tropical Indian City. Sustain Cities Soc 52:101846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2019.101846
Sundborg A (1951) Climatological studies in Uppsala with special regard to the temperature conditions in the urban area. Geographical Institute, Uppsala
Tag PM (1968) Surface temperatures in an urban environment. Pennsylvania State University, Pennsylvania
Templeton NP, Vivoni ER, Wang ZH, Schreiner-McGraw AP (2018) Quantifying water and energy fluxes over different urban land covers in Phoenix, Arizona. J Geophys Res Atmosph 123:2111–2128. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JD027845
Voogt JA, Oke TR (2003) Thermal remote sensing of urban climates. Remote Sens Environ 86:370–384
Webb EK (1970) Profile relationships: the log-linear range, and extension to strong stability. Q J R Meteorol Soc 96:67–90
Weng Q, Hu X, Quattrochi D, Liu H (2014) Assessing intra-urban surface energy fluxes using remotely sensed aster imagery and routine meteorological data: a case study in Indianapolis, USA. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens 7:4046–4057
Wetherley EB, Roberts DA, Tague CL, Jones C, Quattrochi DA, McFadden JP (2021) Remote sensing and energy balance modeling of urban climate variability across a semi-arid megacity. Urban Clim 35:100757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.uclim.2020.100757
World Bank (2017) The World Bank Annual Report. Washington, DC: World Bank. https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/27986License:CC BY-NC-ND3.0IGO. http://hdl.handle.net/10986/27986.
Yang J, Wong MS, Menenti M (2016) Effects of urban geometry on turbulent fluxes: a remote sensing perspective. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 13(12):1767–1771. https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2016.2607759
Yang J, Menenti M, Krayenhoff ES, Wu Z, Shi Q, Ouyang X (2019) Parameterization of urban sensible heat flux from remotely sensed surface temperature: effects of surface structure. Remote Sens 11:1347. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11111347
Acknowledgements
The first author of the manuscript would gratefully acknowledge the Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur, for providing the fellowship and the necessary facilities to conduct the PhD work. The authors are thankful to USGS Earth Resources Observation Systems (EROS) Data Centre for freely providing Landsat imageries used in the study. The authors are thankful to the Wyoming Weather Web–Atmospheric sounding (University of Wyoming) and Weather Underground for freely availing atmospheric soundings. Authors are also thankful to the NOAA data archive for freely availing the NCEP-DOE Reanalysis 2 data sets.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SS and ANVS designed and framed the study. SS analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. ANVS provided intellectual advice and work directions along with review and editing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The authors confirm that this article is original research and is not been published in any journal earlier.
Consent to publication
The authors agree to submit the manuscript in the current form for publication in the journal.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sultana, S., Satyanarayana, A. Impact of urbanization on surface energy balance components over metropolitan cities of India during 2000–2018 winter seasons. Theor Appl Climatol 148, 693–725 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-022-03937-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-022-03937-5