Abstract
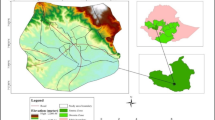
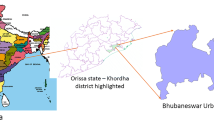
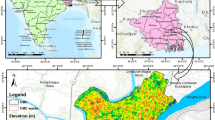
Much of the urbanization that occurs in Africa creates the potential for technological development and economic growth but is also a breeding ground for environmental and health problems. This study was undertaken to evaluate the urban-induced land use/land cover (LULC) change and its contribution to the land surface temperature (LST) and urban heat fluxes from 2001 to 2021. More specifically, the study analyzed different scenarios of LULC change and retrieved the LST to evaluate the trends of the urban heat flux (UHI) in response to the urban-induced LULC change. The analysis of LULC change from 2001 to 2021 indicated that built-up and bare land showed the highest rate of increase at the expense of declining open spaces, agricultural land, and vegetation areas. The built-up areas in Nekemte and Jimma City increased by 929.25 ha (172.75%) and 2285.64 ha (226.93%) over the investigated period, respectively. The highest changes in LULC are seen in built-up areas followed by agricultural land, while the smallest changes are shown by water body followed by bare land. Built-up areas showed the highest net gain, while agricultural land experienced the greatest loss. In areas where the vegetation cover is low, low LST was depicted, and high LST was shown in areas where built-up areas were concentrated in both cities. Due to the LULC changes, the average LST increased by 1.9 °C and 2.2 °C in Nekemte and Jimma City, respectively, over the last 21 years. The urbanization-induced LULC change does not only cause changes in the hydrological process but also changes in the thermal variations and urban heat stress of the two urban centers. The result indicates that the increases in vegetation and green areas are significant in improving the heat stress and thermal characteristics of urban areas. Overall, to achieve sustainable urban development, the integration of land use with urban planning policies could be critical to the resilience of local environment and urban ecosystem.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The land use/land cover data sets generated during this study are available on the reasonable request from the author.
References
Abebe, M. S., Derebew, K. T., & Gemeda, D. O. (2019). Exploiting temporal-spatial patterns of informal settlements using GIS and remote sensing technique: A case study of Jimma city, Southwestern Ethiopia. Environmental Systems Research, 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40068-019-0133-5
Arsiso, B. K., Tsidu, G. M., Stoffberg, G. H., & Tadesse, T. (2017). Climate change and population growth impacts on surface water supply and demand of Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Climate Risk Management, 18, 21–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crm.2017.08.004
Arsiso, B. K., Tsidu, G. M., Stoffberg, G. H., & Tadesse, T. (2018). Influence of urbanization-driven land use/cover change on climate: The case of Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 105, 212–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2018.02.009
Assen, M. (2011). Land use/ cover dynamics and its implications in the dried Lake Alemaya Watershed, Eastern Ethiopia. Journal of Sustainable Development in Africa, 13(4), 267–284.
Ayanlade, A., & Howard, M. T. (2019). Land surface temperature and heat fluxes over three cities in Niger Delta. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 151, 54–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2018.11.027
Baram, H. O., Mohammed, O. A., Hamaamin, H. K., Hamid, A. A., & Mustafa, R. L. (2021). Urbanization and its effect on land surface temperatures in Halabja City. Technium, 3(7), 87–98.
Barbieri, T., Despini, F., & Teggi, S. (2018). A multi-temporal analyses of land surface temperature using Landsat-8 data and open source software: The case study of Modena, Italy. Sustainability, 10(5), 1–23. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10051678
Betru, T., Tolera, M., Sahle, K., & Kassa, H. (2019). Trends and drivers of land use / land cover change in Western Ethiopia. Applied Geography, 104(August 2018), 83–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2019.02.007
CSA. (2007). Summary and statistical report of the 2007 population and housing census. Central Statistical Agency, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
CSA. (2013). Central Statistical Agency: Population projection of Ethiopia for all regions at Wereda level from 2014–2017. Central Statistical Agency, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
Das, N., Mondal, P., Sutradhar, S., & Ghosh, R. (2020). Assessment of variation of land use/land cover and its impact on land surface temperature of Asansol subdivision. The Egyptian Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Sciences, 24(1), 131–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrs.2020.05.001
Debie, E., Anteneh, M., & Asmare, T. (2022). Land use/cover changes and surface temperature dynamics over Abaminus Watershed, Northwest Ethiopia. Air, Soil and Water Research, 15, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1177/11786221221097917
Degefu, M. A., Argaw, M., Feyisa, G. L., & Degefa, S. (2021a). Dynamics of urban landscape nexus spatial dependence of ecosystem services in rapid agglomerate cities of Ethiopia. Science of the Total Environment, 798, 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149192
Degefu, M. A., Argaw, M., Feyisa, G. L., & Degefa, S. (2021b). Effects of urbanization on the relationship between greenspace patterns and evolution of regional heat island in cities of Ethiopia. Chinese Journal of Population, Resources and Environment, 19, 330–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjpre.2022.01.006
Degefu, M. A., Argaw, M., Feyisa, G. L., & Degefa, S. (2023). Dynamics of green spaces- Land surface temperature intensity nexus in cities of Ethiopia. Heliyon. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13274
Degife, A., Worku, H., Gizaw, S., & Legesse, A. (2019). Land use land cover dynamics, its drivers and environmental implications in Lake Hawassa Watershed of Ethiopia. Society and Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsase.2019.03.005
Dessu, T., Korecha, D., Hunde, D., & Worku, A. (2020). Long-term land use land cover change in urban centers of Southwest Ethiopia from a climate change perspective. Frontiers in Climate, 2, 1–23. https://doi.org/10.3389/fclim.2020.577169
Dibaba, W. T. (2018). A review of sustainability of urban drainage system: Traits and consequences. Journal of Sedimentary Environments, 3(3), 131–137. https://doi.org/10.12957/jse.2018.37825
Dibaba, W. T., Demissie, T. A., & Miegel, K. (2020a). Drivers and implications of land use/land cover dynamics in Finchaa catchment, Northwestern Ethiopia. Land, 9(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/land9040113
Dibaba, W. T., Demissie, T. A., & Miegel, K. (2020b). Watershed hydrological response to combined Land use/land cover and climate change in highland Ethiopia: Finchaa catchment. Water, 12(6), 1801. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061801
Dibaba, W. T., & Ebsa, D. G. (2022). Identifying erosion hot spot areas and evaluation of best management practices in the Toba Watershed, Ethiopia. Water Conservation and Management, 6(1), 30–38. https://doi.org/10.26480/wcm.01.2022.30.38
Dibaba, W. T., & Leta, M. K. (2019). Assessment the potential impacts of urbanization: Case of Jimma City. Iranian (Iranica) Journal of Energy & Environment Journal, 10(3), 200–203. https://doi.org/10.5829/ijee.2019.10.03.06
Gemeda, D. O., Feyssa, D. H., & Garedew, W. (2021). Meteorological data trend analysis and local community perception towards climate change: A case study of Jimma City, Southwestern Ethiopia. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 23(4), 5885–5903. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-00851-6
Gobena, N. F. (2020). Nature-based drainage solution for minimizing the risk of flooding in Nekemte city [MSc Thesis, Addis Ababa University, Ethiopia].
Guechi, I., Gherraz, H., & Alkama, D. (2021). Relationship between LULC characteristic and LST using remote sensing and GIS, case study Guelma (Algeria). Romanian Journal of Geography, 65(2), 203–222.
Halder, B., Haghbin, M., & Farooque, A. A. (2021). An assessment of urban expansion impacts on land transformation of Rajpur-Sonarpur municipality. KBES, 2(3), 34–53. https://doi.org/10.51526/kbes.2021.2.3.34-53
Halder, B., Karimi, A., Mohammad, P., Bandyopadhyay, J., Brown, R. D., & Yaseen, Z. M. (2022). Investigating the relationship between land alteration and the urban heat island of Seville city using multi-temporal Landsat data. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 150, 613–635. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-022-04180-8
Haylemariyam, M. B. (2018). Detection of land surface temperature in relation to land use land cover change: Dire Dawa City, Ethiopia. Journal of Remote Sensing & GIS, 7(3), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.4172/2469-4134.1000245
IPCC. (2014). Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. In Core Writing Team, R. K. Pachauri, & L. A. Meyer (Eds.). IPCC, Geneva, Switzerland.
IPCC. (2019). Climate change and land: An IPCC special report on climate change, desertification, land degradation, sustainable land management, food security, and greenhouse gas fluxes in terrestrial ecosystems. [P.R. Shukla, J. Skea, E. Calvo Buendia, V. Masson-Delmotte, H.-O. Pörtner, D. C. Roberts, P. Zhai, R. Slade, S. Connors, R. van Diemen, M. Ferrat, E. Haughey, S. Luz, S. Neogi, M. Pathak, J. Petzold, J. Portugal Pereira, P. Vyas, E. Huntley, K. Kissick, M. Belkacemi, J. Malley, (eds.)]. In press.
Khan, R., Li, H., Basir, M., Chen, Y. L., Sajjad, M. M., Haq, I. U., Ullah, B., Arif, M., & Hassan, W. (2022). Monitoring land use land cover changes and its impacts on land surface temperature over Mardan and Charsadda Districts, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (KP), Pakistan. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 194(6). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10072-1
Kuddus, A., Tynan, E., & Mcbryde, E. (2020). Urbanization: A problem for the rich and the poor? Public Health Reviews, 41(1), 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40985-019-0116-0
Mezgebo, T. G. (2021). Urbanization and development in Ethiopia: Policy issues, trends and prospects. In Mengistu K. & Getachew D. (Ed.), State of the Ethiopian Economy 2020/2021: Economic Development, Population Dynamics and Welfare:Addis Ababa: Ethiopian Economic Association.
Miheretu, B. A., & Yimer, A. A. (2017). Land use / land cover changes and their environmental implications in the Gelana sub _ watershed of Northern highlands of Ethiopia. Environmental Systems Research, 6(7). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40068-017-0084-7
O’Driscoll, M., Clinton, S., Jefferson, A., Manda, A., & Mcmillan, S. (2010). Urbanization effects on watershed hydrology and in-stream processes in the Southern United States. Water, 2, 605–648. https://doi.org/10.3390/w2030605
Oloke, O. C., Fayomi, O. S. I., Oluwatayo, A., Adagunodo, T. A., Akinwumi, I. I., & Amusan, L. (2021). The nexus of climate change, urban infrastructure and sustainable development in developing countries. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 012051. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/665/1/012051
Pal, S., & Ziaul, S. (2017). Detection of land use and land cover change and land surface temperature in English Bazar urban centre. Egyptian Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Science, 20, 125–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrs.2016.11.003
Perry, G., Gebresenbet, F., Dapra, M., Branco, P., Whibesilassie, W., Jelacic, M., & Eyob, A. E. (2022). Why urban ecology matters in Ethiopia. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 10, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fevo.2022.843698
Pulighe, G., Baiocchi, V., & Lupia, F. (2015). Horizontal accuracy assessment of very high-resolution Google Earth images in the city of Rome, Italy. International Journal of Digital Earth, 9, 342–362. https://doi.org/10.1080/17538947.2015.1031716
Stemn, E., & Kumi-Boateng, B. (2020). Modelling of land surface temperature changes as determinant of urban heat island and risk of heat-related conditions in the Wassa West Mining Area of Ghana. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 6, 1727–1740. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-020-00786-x
Tadele, H., Mekuriaw, A., Selassie, Y. G., & Tsegaye, L. (2017). Land use / land cover factor values and accuracy assessment using a GIS and remote sensing in the case of the Quashay watershed in northwestern. Journal of Natural Resources and Development, 07, 38–44. https://doi.org/10.5027/jnrd.v7i0.05
Temesgen, H., Wu, W., Legesse, A., Yirsaw, E., & Bekele, B. (2018). Landscape-based upstream-downstream prevalence of land-use/cover change drivers in southeastern rift escarpment of Ethiopia. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 190(3). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6479-8
Viera, A. J., & Garrett, J. M. (2005). Anthony J. Viera, MD; Joanne M. Garrett, PhD (2005). Understanding interobserver agreement: The kappa statistic. Family Medicine, 37(5), 360–363.
Wang, Y., Yi, G., Zhou, X., Zhang, T., Bie, X., Li, J., & Ji, B. (2021). Spatial distribution and influencing factors on urban land surface temperature of twelve megacities in China from 2000 to 2017. Ecological Indicators, 125, 1–16.
World Bank Group. (2015). Ethiopia Urbanization Review: Urban Institutions for a Middle-Income Ethiopia. https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/22979. License: CC BY 3.0 IGO.
Yesuph, A. Y., & Dagnew, A. B. (2019). Land use/cover spatiotemporal dynamics, driving forces and implications at the Beshillo catchment of the Blue Nile Basin, North Eastern Highlands of Ethiopia. Environmental Systems Research, 8(21). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40068-019-0148-y
Zhao, A. Z., He, B., Li, L., Wang, H.-B., & Darko, A. (2017). Profile and concentric zonal analysis of relationships between land use/land cover and land surface temperature: Case study of Shenyang, China. Energy & Buildings. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2017.09.046
Acknowledgements
I am very grateful to the ExiST KfW project in Jimma Institute of Technology for supporting the study by providing the required resources. I would also thank the Nekemte City municipality and Jimma City municipality offices in providing necessary data and facilitating for data collections.
Funding
This research has received a financial support for data collections and analysis from the Higher Education and TVET Program Ethiopia Phase 3 KfW Project No. 51235, BMZ o2011 66 305.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the survey data, Landsat processing, image classification and analysis, and manuscript write up was done by Wakjira Takala Dibaba.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The author has read, understood, and have compiled as applicable with the statement on “Ethical responsibilities of authors” as found in the instructions for authors.
Competing interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dibaba, W.T. Urbanization-induced land use/land cover change and its impact on surface temperature and heat fluxes over two major cities in Western Ethiopia. Environ Monit Assess 195, 1083 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11698-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11698-5