Abstract
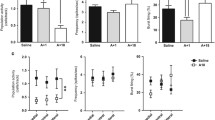
We evaluated Na+,K+-ATPase activity in hippocampus of rats submitted to an animal model of mania which included the use of lithium and valproate. In the acute treatment, amphetamine or saline was administered to rats for 14 days, between day 8 and 14, rats were treated with lithium, valproate or saline. In the maintenance treatment, rats were treated with lithium, valproate or saline, between day 8 and 14, amphetamine or saline were administered. Locomotor activity was assessed by open field test and Na+,K+-ATPase activity was measured. Our results showed that mood stabilizers reversed and prevented amphetamine-induced behavioral effects. Moreover, amphetamine (acute treatment) increased Na+,K+-ATPase activity, and administration of lithium or valproate reversed this effect. In the maintenance treatment, amphetamine increased Na+,K+-ATPase activity in saline-pretreated rats. Amphetamine administration in lithium- or valproate-pretreated animals did not alter Na+,K+-ATPase activity. The findings suggest that amphetamine-induced hyperactivity may be associated with an increase in Na+,K+-ATPase.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anand A, Verhoeff P, Seneca N et al (2000) Brain SPECT imaging of amphetamine-induced dopamine release in euthymic bipolar disorder patients. Am J Psychiatry 157:1108–1114
Beaulieu JM, Sotnikova TD, Yao WD et al (2004) Lithium antagonizes dopamine-dependent behaviors mediated by an AKT/glycogen synthase kinase 3 signaling cascade. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:5099–5104
Bell EC, Willson MC, Wilman AH (2005) Lithium and valproate attenuate dextroamphetamine-induced changes in brain activation. Hum Psychopharmacol 20:87–96
Belmaker RH (2004) Bipolar disorder. N Engl J Med 351:476–486
Bezchlibnyk Y, Young LT (2002) The neurobiology of bipolar disorder: focus on signal transduction pathways and the regulation of gene expression. Can J Psychiatry 47:135–148
Bhattacharjee AK, Chang L, Chen M et al (2008) Chronic d-amphetamine depresses an imaging marker of arachidonic acid metabolism in rat brain. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 11:957–969
Chan KM, Delfer D, Junger KD (1986) A direct colorimetric assay for Ca2+-stimulated ATPase activity. Anal Biochem 157:375–380
Chang MC, Contreras MA, Rosenberger TA et al (2001) Chronic valproate treatment decreases the in vivo turnover of arachidonic acid in brain phospholipids: a possible common effect of mood stabilizers. J Neurochem 77:796–803
Chen C, Lokhandwala MF (1993) Inhibition of Na+,K+-ATPase activity in rat renal proximal tubules by dopamine involved DA-1 receptor activation. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 347:286–295
Corrêa C, Amboni G, Assis LC et al (2007) Effects of lithium and valproate on hippocampus citrate synthase activity in an animal model of mania. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 31:887–891
Coyle JT, Duman RS (2003) Finding the intracellular signaling pathways affected by mood disorder treatments. Neuron 38:157–160
Einat H, Yuan P, Gould TD (2003) The role of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway in mood regulation. J Neurosci 23:7311–7316
Erecinska M, Silver IA (1994) Ions and energy in mammalian brain. Prog Neurobiol 43:37–71
Fienberg AA, Hiroi N, Mermelstein P et al (1998) DARPP-32: regulator of the efficacy of dopaminergic neurotransmission. Science 281:838–842
Frey BN, Andreazza AC, Cereser KM et al (2006) Effects of mood stabilizers on hippocampus BDNF levels in an animal model of mania. Life Sci 79:281–286
Gamaro GD, Streck EL, Matté C et al (2003) Reduction of hippocampal Na+,K+-ATPase activity in rats subjected to an experimental model of depression. Neurochem Res 28:1339–1344
Goldstein I, Levy T, Galili D et al (2006) Involvement of Na+,K+-ATPase and endogenous digitalis-like compounds in depressive disorders. Biol Psychiatry 60:491–499
Gould TD, Manji HK (2002) The Wnt signaling pathway in bipolar disorder. Neuroscientist 8:497–511
Grisar T (1984) Glial and neuronal Na+K+ pump in epilepsy. Ann Neurol 16:128–134
Jacobsen FM (1993) Low-dose valproate: a new treatment for cyclothymia, mild rapid cycling disorders, and premenstrual syndrome. J Clin Psychiatry 54:229–234
Jones DH, Matus AI (1974) Isolation of plasma synaptic membrane from brain by combination flotation-sedimentation density gradient centrifugation. Biochim Biophys Acta 356:276–287
Kato T, Kato N (2000) Mitochondrial dysfunction in bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord 2:180–190
Kim SH, Yu HS, Park HG et al (2008) Dose-dependent effect of intracerebroventricular injection of ouabain on the phosphorylation of the MEK1/2-ERK1/2-p90RSK pathway in the rat brain related to locomotor activity. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 32:1637–1642
Konradi C, Eaton M, MacDonald ML et al (2004) Molecular evidence for mitochondrial dysfunction in bipolar disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 61:300–308
Kupfer DJ (2005) The increasing medical burden in bipolar disorder. JAMA 293:2528–2530
Kurup AR, Kurup PA (2002) Membrane Na+-K+-ATPase mediated cascade in bipolar mood disorder, major depressive disorder, and schizophrenia-relationship to hemispheric dominance. Int J Neurosci 112:965–982
Lees GJ (1993) Contributory mechanisms in the causation of neurodegenerative disorders. Neuroscience 54:287–322
Machado-Vieira R, Kapczinski F, Soares JC (2004) Perspectives for the development of animal models of bipolar disorder. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 28:209–224
Mai L, Jope RS, Li X (2002) BDNF-mediated signal transduction is modulated by GSK3beta and mood stabilizing agents. J Neurochem 82:75–83
Manji HK, Chen G (2002) PKC, MAP kinases and the bcl-2 family of proteins as long-term targets for mood stabilizers. Mol Psychiatry 7:S46–S56
Manji HK, Lenox RH (2000) Signaling: cellular insights into the pathophysiology of bipolar disorder. Biol Psychiatry 48:518–530
Manji HK, Drevets WC, Charney DS (2001) The cellular neurobiology of depression. Nat Med 7:541–547
Montezinho LP, Mork A, Duarte CB et al (2007) Effects of mood stabilizers on the inhibition of adenylate cyclase via dopamine D(2)-like receptors. Bipolar Disord 9:290–297
Müller-Oerlinghausen B, Berghöfer A, Bauer M (2002) Bipolar disorder. Lancet 359:241–247
Strakowski SM, Sax KW (1998) Progressive behavioral response to repeated D-amphetamine challenge: further evidence for sensitization in humans. Biol Psychiatry 44:1171–1177
Streck EL, Matte C, Vieira PS et al (2002) Reduction of Na+,K+-ATPase activity in hippocampus of rats subjected to chemically induced hyperhomocysteinemia. Neurochem Res 27:1593–1598
Streck EL, Amboni G, Scaini G et al (2008) Brain creatine kinase activity in an animal model of mania. Life Sci 82:424–429
Vaillend C, Mason SE, Cuttle MF et al (2002) Mechanisms of neuronal hyperexcitability caused by partial inhibition of Na+,K+-ATPases in the rat CA1 hippocampal region. J Neurophysiol 88:2963–2978
Vatta M, Peña C, Fernández BE et al (2004) Endobain E, a brain Na+,K+-ATPase inhibitor, decreases norepinephrine uptake in rat hypothalamus. Life Sci 76:359–365
Wyse ATS, Wajner M, Brusque A et al (1995) Alanine reverses the inhibitory effect of phenylalanine and its metabolites on Na+,K+-ATPase in synaptic plasma membranes from cerebral cortex of rats. Biochem Soc Trans 23:227S
Wyse ATS, Streck EL, Barros SVT et al (2000) Methylmalonate administration decreases Na+,K+-ATPase activity in cerebral cortex of rats. Neuroreport 11:2311–2315
Wyse AT, Zugno AI, Streck EL et al (2002) Inhibition of Na+,K+-ATPase activity in hippocampus of rats subjected to acute administration of homocysteine is prevented by vitamins E and C treatment. Neurochem Res 27:1685–1689
Yamaguchi I, Walk SF, Jose PA et al (1996) Dopamine D2L receptors stimulate Na+,K+-ATPase activity in murine LTK-cells. Mol Pharmacol 49:373–378
Yanagita T, Maruta T, Uezono Y et al (2007) Lithium inhibits function of voltage-dependent sodium channels and catecholamine secretion independent of glycogen synthase kinase-3 in adrenal chromaffin cells. Neuropharmacology 53:881–889
Yang ZJ, Torbey M, Li X et al (2007) Dopamine receptor modulation of hypoxic-ischemic neuronal injury in striatum of newborn piglets. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27:1339–1351
Zugno AI, Stefanello FM, Streck EL et al (2003) Inhibition of Na+,K+-ATPase activity in rat striatum by guanidinoacetate. Int J Dev Neurosci 21:183–189
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), Fundação de Apoio à Pesquisa Científica e Tecnológica do Estado de Santa Catarina (FAPESC) and Universidade do Extremo Sul Catarinense (UNESC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zugno, A.I., Valvassori, S.S., Scherer, E.B.S. et al. Na+,K+-ATPase activity in an animal model of mania. J Neural Transm 116, 431–436 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-009-0198-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-009-0198-9