Summary
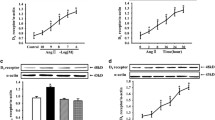
Endogenous kidney dopamine (DA) causes natriuresis and diuresis, at least partly, via inhibition of proximal tubular Na+,K+-ATPase. The present study was done to identify the dopamine receptor subtype(s) involved in dopamine-induced inhibition of Na+,K+-ATPase activity. Suspensions of renal proximal tubules from Sprague-Dawley rats were incubated with dopamine, the DA-1 receptor agonist fenoldopam or the DA-2 receptor agonist SK&F 89124 in the presence or absence of either the DA-1 receptor antagonist SCH 23390 or the DA-2 receptor antagonist domperidone. Dopamine and fenoldopam (10−5 to 10−8 mol/1) produced a concentration-dependent inhibition of Na+,K+-ATPase activity. However, SK&F 89124 failed to produce any significant effect over the same concentration range. Incubation with fenoldopam (10−5 to 10−8 mol/1) in the presence of SK&F 89124 (10−6 mol/l) inhibited Na+,K+-ATPase activity to a degree similar to that with fenoldopam alone. Furthermore, DA-induced inhibition of Na+,K+-ATPase activity was attenuated by SCH 23390, but not by domperidone. Since α-adrenoceptor activation is reported to stimulate Na+,K+-ATPase activity and, at higher concentrations, dopamine also acts as an a-adrenoceptor agonist, the potential opposing effect from α-adrenoceptor activation on DA-induced inhibition of Na+,K+-ATPase activity was investigated by using the α-adrenoceptor blocker phentolamine. We found that, in the lower concentration range (10−5 to 10−7 mol/1), dopamine-induced inhibition of Na+,K+-ATPase activity in the presence of phentolamine was similar in magnitude to that observed with dopamine alone. However, at the highest concentration used (10−4 mol/1), dopamine produced a significantly larger degree of inhibition of Na+,K+-ATPase activity in the presence of phentolamine. These results indicate that the DA-1 dopamine receptor subtype, but not the DA-2 receptor subtype, is involved in dopamine-mediated inhibition of Na+,K+-ATPase. At higher concentrations of dopamine, the DA-1 receptor-mediated inhibitory effect on Na+,K+-ATPase activity may be partly opposed by a simultaneous α-adrenoceptor-mediated stimulation of the activity of this enzyme.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aperia A, Bertorello A, Seri I (1987) Dopamine causes inhibition of Na+,K+-ATPase activity in rat proximal convoluted tubule segments. Am J Physiol 252:F39-F45
Aperia A, Fryckstedt J, Svensson L, Hemmings JC Jr, Nairn AC, Greengard P (1991) Phosphorylated Mr 32000 dopamine- and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein inhibits Na+,K+-ATPase activity in renal tubule cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:2798–2801
Baines AD, Ho P, Drangova R (1992) Proximal tubular dopamine production regulates basolateral Na+,K+-ATPase. Am J Physiol 262:F566-F571
Beach RE, Schwab SJ, Brazy PC, Dennis VW (1987) Norepinephrine increases Na+,K+-ATPase and solute transport in rabbit proximal tubules. Am J Physiol 252:F215-F220
Bertorello A, Aperia A (1989) Na+,K+-ATPase is an effector protein for protein kinase C in renal proximal tubule cells. Am J Physiol 256:F370-F373
Bertorello A, Aperia A (1990) Inhibition of proximal tubule Na+,K+-ATPase activity requires simultaneous activation of DA1 and DA2 receptors. Am J Physiol 259:F924-F928
Bertorello A, Hokfelt T, Goldstein M, Aperia A (1988) Proximal tubule Na+,K+-ATPase activity is inhibited during high salt diet: Evidence for DA-mediated effect. Am J Physiol 252:F32-F45
Bertorello A, Aperia A, Walaas I, Nairn A, Greengard P (1991) Phosphorylation of the catalytic subunit of Na+,K+-ATPase inhibits the activity of the enzyme (abstract). J Amer Soc Nephrol 2:721
Chen CJ, Vyas SJ, Beach RE, Eichberg J, Lokhandwala MIT (1991) Diminished natriuresis to dopamine in spontaneously hypertensive rats is due to a defect in phospholipase C-mediated inhibition of Na+,K+-ATPase (abstract). J Amer See Nephrol 2:472
Chen CJ, Vyas SJ, Eichberg J, Beach RE, Lokhandwala MF (1992) dopamine-1 receptor mediated inhibition of renal tubular Na+,K+-ATPase activity in spontaneously hypertensive rats. In: J Sassard (ed) Genetic hypertension. Colloque INSERM/John Libbey Eurotext, France, 218:463–465
Chen CJ, Beach RE, Lokhandwala MF Dopamine fails to inhibit renal tubular sodium pump in hypertensive rats. Hypertension (in press)
Felder RA, Blecher M, Eisner GM, Jose PA (1984) Cortical tubular and glomerular dopamine receptors in the rat kidney. Am J Physiol 246:F557-F568
Felder CC, Blecher M, Jose PA (1989a) Dopamine-1 mediated stimulation of phospholipase-C activity in rat renal cortical membrane. J Biol Chem 264:8789–8795
Felder CC, McKelvey AM, Gilter MS, Eisner GM, Jose PA (1989b) Dopamine receptor subtypes in renal brush border and basolateral membrane. Kidney Int 36:183–193
Felder CC, Campbell T, Albrecht F, Jose PA (1990) Dopamine inhibits Na+-H+exchanger activity in renal BBMV by stimulation of adenylate cyclase. Am J Physiol 259:F297-F303
Frederickson EO, Bradley T, Goldberg LI (1985) Blockade of the renal effects of dopamine in the dog by the DA-1 antagonist SCH 23390. Am J Physiol 249:F236-F240
Gesek FA, Wolff DW, Strandhoy JW (1987) Improved separation method for rat proximal and distal renal tubules. Am J Physiol 253:F358-F365
Hegde SS, Lokhandwala MF (1989) Activation of DA-1 but not DA-2 receptors by endogenous DA contributes to the natriuretic response to volume expansion in rats (abstract). FASEB J 3:A895
Huffman WIT, Hall RF, Grant JA, Wilson JW, Hieble JP, Hahn RA (1983) Communications to the editor. J Med Chem 26:933–935
Huo T, Healy DP (1989) Autoradiographic localization of dopamine DA-1 receptors in rat kidney with (3H) SCH 23390. Am J Physiol 257:F414-F423
Kinoshita S, Ohlstein EH, Felder RA (1990) Dopamine-1 receptors in rat proximal convoluted tubule: regulation by intrarenal dopamine. Am J Physiol 258:F1068-F1074
Lokhandwala MF, Amenta F (1991) Anatomical distribution and function of dopamine receptors in the kidney. FASEB J 5:3023–3030
Lowry DH, Rosenbrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RLJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Nishi A, Eklof AC, Bertorello A, Aperia A (1991) Dopamine down regulation of proximal tubule Na+,K+-ATPase activity is lacking in Dahl salt-sensitive rats (abstract). J Amer Soc Nephrol 2:481
Quigley JP, Gotterer GS (1969) Distribution of Na+,K+ -stimulated ATPase activity in rat intestinal mucosa. Biochem Biophys Acta 173:456–468
Ricci A, Collier WL, Rossodivita I, Amenta F (1991) Dopamine receptors mediating inhibition of the cyclic adenosine monophosphate generating system in the rat renal cortex. J Auton Pharmacol 11:121–128
Seri I, Kone BC, Gullans SR, Aperia A (1988) Locally formed dopamine inhibits Na+,K+-ATPase activity in rat renal cortical tubule cells. Am J Physiol 255:F666-F673
Seri I, Kone BC, Gullans SR, Brenner BM, Ballermann BJ (1989) Inhibition of Na+,K+-ATPase (Na-K) in rat renal cortical tubule cells (RCTC) by locally formed dopamine (DA) involves DA -1 but not DA-2 receptors (abstract). Kidney Int 35:320
Seri I, Kone BC, Gullans SR, Aperia A, Brenner BM, Ballermann BJ (1990) Influence of Na+ intake on dopamine-induced inhibition of renal cortical Na+,K+-ATPase. Am J Physiol 258:F52-F60
Siragy HM, Felder RA, Howell NL, Chevalier RL, Peach MJ, Carey RM (1989) Evidence that intrarenal dopamine acts as a paracrine substance at the renal tubule. Am J Physiol 257:F469-F477
Swagzdis JE, Wittendorf RW, DeMarinis RM, Mico BA (1986) Pharmacokinetics of dopamine-2 agonists in rats and dogs. J Pharm Sci 75:925–928
Vinay P, Gougoux A, Lemieux G (1981) Isolation of a pure suspension of rat proximal tubules. Am J Physiol 241:F403-F411
Vyas SJ, Eichberg J, Lokhandwala MF (1992) Characterization of receptors involved in dopamine-induced activation of phospholipase-C in rat renal cortex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 260:134–139
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, C., Lokhandwala, M.F. Inhibition of Na+, K+-ATPase in rat renal proximal tubules by dopamine involved DA-1 receptor activation. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 347, 289–295 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00167447
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00167447