Abstract
Purpose
This study evaluates the application of a microdialysis technique for interstitial chemotherapy using cisplatin in high-grade glioma.
Method
An in vitro study demonstrated that cisplatin can be administered through retrograde microdialysis and defined the recovery for cisplatin. In a subsequent phase I study, 1–4 microdialysis catheters were implanted in tumor tissue, brain adjacent to tumor (BAT) tissue, and subcutaneous tissue in 10 patients with recurrent high-grade glioma. Cisplatin was administered continuously in daily doses between 0.3 and 3.9 mg for 4 to12 days. Microdialysis samples were continuously collected and analyzed for glucose metabolites, glutamate, glycerol, and cisplatin concentrations. Treatment tolerability was evaluated through clinical monitoring. Quality of life was assessed using the EORTC-QLQ-C30 questionnaire for up to 3 months after treatment.
Results
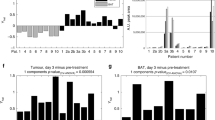
This in vitro study showed that cisplatin could be administrated with a recovery of 41–97%, depending on flowrate, type of catheter, and cisplatin concentration. During the treatment, patients were exposed to a total dose of 1.2–36.8 mg cisplatin. The concentration of cisplatin in BAT, serum, and subcutaneous tissue was close to detection level in all but two patients. A transient neurologic deterioration due to edema was commonly observed, but no systemic side effects were recorded. After onset of treatment, concentrations of glutamate and glycerol were significantly increased in tumor tissue but not in BAT, with a peak after 3 days, and consistent for the rest of the treatment. Five of the patients survived between 153 and 492 days after treatment.
Conclusion
This phase I study demonstrates that retrograde microdialysis can be used to administer cisplatin interstitially into high-grade glioma tissue. A high cytotoxicity was detected in tumor tissue, but not in the surrounding brain. Retrograde microdialysis appears to be a clinically useful method for intratumoral drug administration in high-grade glioma.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaronson NK, Ahmedzai S, Bergman B, Bullinger M, Cull A, Duez NJ, Filiberti A, Flechtner H, Fleishman SB, de Haes JC et al (1993) The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer QLQ-C30: a quality-of-life instrument for use in international clinical trials in oncology. J Natl Cancer Inst 85:365–376. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/85.5.365
Bergenheim AT, Roslin M, Ungerstedt U, Waldenstrom A, Henriksson R, Ronquist G (2006) Metabolic manipulation of glioblastoma in vivo by retrograde microdialysis of L-2, 4 diaminobutyric acid (DAB). J Neuro-Oncol 80:285–293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-006-9186-1
Bergstrom P, Johnsson A, Bergenheim T, Henriksson R (1999) Effects of amifostine on cisplatin induced DNA adduct formation and toxicity in malignant glioma and normal tissues in rat. J Neuro-Oncol 42:13–21. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1006152103476
Bergstrom P, Johnsson A, Cavallin-Stahl E, Bergenheim T, Henriksson R (1997) Effects of cisplatin and amphotericin B on DNA adduct formation and toxicity in malignant glioma and normal tissues in rat. Eur J Cancer 33:153–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0959-8049(96)00339-5
Bjorkblom B, Jonsson P, Tabatabaei P, Bergstrom P, Johansson M, Asklund T, Bergenheim AT, Antti H (2020) Metabolic response patterns in brain microdialysis fluids and serum during interstitial cisplatin treatment of high-grade glioma. Br J Cancer 122:221–232. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-019-0652-x
Bouvier G, Penn RD, Kroin JS, Beique R, Guerard MJ (1987) Direct delivery of medication into a brain tumor through multiple chronically implanted catheters. Neurosurgery 20:286–291. https://doi.org/10.1227/00006123-198702000-00015
Hemstrom P, Nygren Y, Bjorn E, Irgum K (2008) Alternative organic solvents for HILIC separation of cisplatin species with on-line ICP-MS detection. J Sep Sci 31:599–603. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.200700480
Hillered L, Valtysson J, Enblad P, Persson L (1998) Interstitial glycerol as a marker for membrane phospholipid degradation in the acutely injured human brain. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 64:486–491. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.64.4.486
Hillman J, Aneman O, Anderson C, Sjogren F, Saberg C, Mellergard P (2005) A microdialysis technique for routine measurement of macromolecules in the injured human brain. Neurosurgery 56:1264–1268; discussion 1268-1270. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000159711.93592.8d
Joshi S, Ergin A, Wang M, Reif R, Zhang J, Bruce JN, Bigio IJ (2011) Inconsistent blood brain barrier disruption by intraarterial mannitol in rabbits: implications for chemotherapy. J Neuro-Oncol 104:11–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0466-4
Klug F, Prakash H, Huber PE, Seibel T, Bender N, Halama N, Pfirschke C, Voss RH, Timke C, Umansky L, Klapproth K, Schakel K, Garbi N, Jager D, Weitz J, Schmitz-Winnenthal H, Hammerling GJ, Beckhove P (2013) Low-dose irradiation programs macrophage differentiation to an iNOS(+)/M1 phenotype that orchestrates effective T cell immunotherapy. Cancer Cell 24:589–602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2013.09.014
Kroin JS, Penn RD (1982) Intracerebral chemotherapy: chronic microinfusion of cisplatin. Neurosurgery 10:349–354. https://doi.org/10.1227/00006123-198203000-00009
Lesniak MS, Brem H (2004) Targeted therapy for brain tumours. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3:499–508. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd1414
Massimino M, Spreafico F, Cefalo G, Riccardi R, Tesoro-Tess JD, Gandola L, Riva D, Ruggiero A, Valentini L, Mazza E, Genitori L, Di Rocco C, Navarria P, Casanova M, Ferrari A, Luksch R, Terenziani M, Balestrini MR, Colosimo C, Fossati-Bellani F (2002) High response rate to cisplatin/etoposide regimen in childhood low-grade glioma. J Clin Oncol 20:4209–4216. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2002.08.087
Nakashima M, Shibata S, Tokunaga Y, Fujita H, Anda T, Arizono K, Tomiyama N, Sasaki H, Ichikawa M (1997) In-vivo microdialysis study of the distribution of cisplatin into brain tumour tissue after intracarotid infusion in rats with 9L malignant glioma. J Pharm Pharmacol 49:777–780. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2042-7158.1997.tb06111.x
Roslin M, Henriksson R, Bergstrom P, Ungerstedt U, Bergenheim AT (2003) Baseline levels of glucose metabolites, glutamate and glycerol in malignant glioma assessed by stereotactic microdialysis. J Neuro-Oncol 61:151–160. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1022106910017
Sandstrom M, Laudius M, Lindqvist T, Asklund T, Johansson M (2017) A retrospective evaluation of Bevacizumab treatment in patients with progressive malignant Glioma in northern Sweden. Anticancer Res 37:1869–1874. https://doi.org/10.21873/anticanres.11524
Sheleg SV, Korotkevich EA, Zhavrid EA, Muravskaya GV, Smeyanovich AF, Shanko YG, Yurkshtovich TL, Bychkovsky PB, Belyaev SA (2002) Local chemotherapy with cisplatin-depot for glioblastoma multiforme. J Neuro-Oncol 60:53–59. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1020288015457
Stewart DJ (1994) A critique of the role of the blood-brain-barrier in the chemotherapy of human brain-tumors. J Neuro-Oncol 20:121–139. https://doi.org/10.1007/Bf01052723
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, Curschmann J, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Gorlia T, Allgeier A, Lacombe D, Cairncross JG, Eisenhauer E, Mirimanoff RO, European Organisation for R, Treatment of Cancer Brain T, Radiotherapy G, National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials G (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352:987–996. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa043330
Tabatabaei P, Bergstrom P, Henriksson R, Bergenheim AT (2008) Glucose metabolites, glutamate and glycerol in malignant glioma tumours during radiotherapy. J Neuro-Oncol 90:35–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-008-9625-2
Tabatabaei P, Visse E, Bergstrom P, Brannstrom T, Siesjo P, Bergenheim AT (2017) Radiotherapy induces an immediate inflammatory reaction in malignant glioma: a clinical microdialysis study. J Neuro-Oncol 131:83–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-016-2271-1
Taphoorn MJ, Claassens L, Aaronson NK, Coens C, Mauer M, Osoba D, Stupp R, Mirimanoff RO, van den Bent MJ, Bottomley A (2010) An international validation study of the EORTC brain cancer module (EORTC QLQ-BN20) for assessing health-related quality of life and symptoms in brain cancer patients. Eur J Cancer 46:1033–1040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2010.01.012
Tokunaga Y, Nakashima M, Sasaki H, Tomiyama N, Nakashima MN, Ichikawa M, Kaminogo M, Shibata S (2000) Local distribution into brain tumor and pharmacokinetics of 4-pyridoxate diammine hydroxy platinum, a novel cisplatin derivative, after intracarotid administration in rats with 9L malignant glioma: simultaneous brain microdialysis study. Biol Pharm Bull 23:1491–1496. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.23.1491
Von Hoff DD, Schilsky R, Reichert CM, Reddick RL, Rozencweig M, Young RC, Muggia FM (1979) Toxic effects of cis-dichlorodiammineplatinum(II) in man. Cancer Treat Rep 63:1527–1531
Wibom C, Surowiec I, Moren L, Bergstrom P, Johansson M, Antti H, Bergenheim AT (2010) Metabolomic patterns in glioblastoma and changes during radiotherapy: a clinical microdialysis study. J Proteome Res 9:2909–2919. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr901088r
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge Kristin Nyman at the Department of Neurosurgery for her technical skills in managing the microdialysis bedside and Professor Thomas Brännström at the Department of Pathology for verification of IDH mutation status.
Funding
This study was supported by the Swedish Cancer Society, Umeå University Hospital, the Swedish Research Council, the Cancer Research Foundation in Northern Sweden, the Research Foundation of Clinical Neuroscience, Umeå University, and by the regional agreement between Umeå University and Västerbotten County Council on the cooperation in the field of Medicine, Odontology, and Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
The study was approved by the Swedish Medical Products Agency (EU no. 2010-018281-23) and the Ethics Committee of Umeå University Medical Faculty (Ethical permission: 09-199M).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Brain Tumors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tabatabaei, P., Asklund, T., Bergström, P. et al. Intratumoral retrograde microdialysis treatment of high-grade glioma with cisplatin. Acta Neurochir 162, 3043–3053 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-020-04488-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-020-04488-2