Abstract
Background
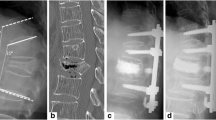
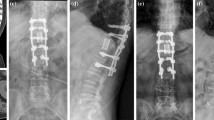
Advanced states of vertebral osteomyelitis accompanied by spinal instability, epidural abscess formation, and neurological deficits require surgical decompression, stabilization, and often reconstruction of the anterior and posterior columns. The efficacy of a posterolateral approach with resection of inflammatory tissue, and interbody (titanium cages) and dorsal fusion was investigated and the clinical and radiological parameters (correction of kyphosis and fusion rates) were evaluated.
Method
From 2011 to 2014, ten consecutive patients were treated at our institution using the modified technique of a transversecomy without costal resection to decompress neural structures and resect inflammatory tissue in destructive thoracic vertebral osteomyelitis. Flattening of the endplates without complete corpectomy, 360-degree stabilization, and correction of kyphosis by posterior shortening instead of anterior distraction were performed to avoid an additional ventral approach. Clinical and radiological data were retrospectively analyzed.
Results
All ten patients (six male and four female, mean age, 66 years) suffered from severe and destructive osteomyelitis. Surgery was performed successfully in all ten patients. Mean surgical time was 308 min. Mean follow-up was 19 months (range, 2–32 months). Neither approach-related or pulmonary complications nor recurrence of osteomyelitis were observed. All patients experienced pain relief after the procedure (mean back pain VAS was 8.8 pre-treatment and 3.2 at the final follow-up). Fusion was observed in all patients on the basis of computerized tomography scans. The mean radiological segmental kyphosis was corrected from 20° preoperatively to 7° after surgery and 9° at the final follow-up.
Conclusions
The modified posterior transversectomy with 360-degree decompression and anterior wall reconstruction with titanium cages in combination with posterior instrumentation for sagittal alignment correction is a reliable, effective, and safe treatment option.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbar M, Lehner B, Doustdar S, Fürstenberg CH, Hemmer S, Bruckner T, Carstens C, Wiedenhöfer B (2011) Pyogenic spondylodiscitis of the thoracic and lumbar spine: a new classification and guide for surgical decision-making. Orthopade 40:614–623
Bettini N, Girardo M, Dema E, Cervellati S (2009) Evaluation of conservative treatment of non-specific spondylodiscitis. Eur Spine J 18(Suppl 1):143–150
Cobb J (1948) Outline for the study of scoliosis. In: Instructional course letters, vol 5. American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, Ann Arbor
D’Aliberti G, Talamonti G, Villa F, Debernardi A (2012) The anterior stand-alone approach (ASAA) during the acute phase of spondylodiscitis: results in 40 consecutively treated patients. Eur Spine J 21(Suppl 1):75–82
Eicker SO, Cornelius JF, Steiger HJ, Hänggi D (2012) 360-degree osteosynthesis via a posterolateral transpedicular approach in high-risk patients. Eur Spine J 21(6):1207–1213
Eismont FJ, Bohlnaan HH, Soni PL, Goldberg VM, Freehafer AA (1983) Pyogenic and fungal vertebral osteomyelitis with paralysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 65:19–29
Eysel P, Hopf C, Vogel I, Rompe JD (1997) Primary stable anterior instrumentation or dorsoventral spondylodesis in spondylodiscitis? Results of a comparative study. Eur Spine J 6(3):152–157
Fayazi AH, Ludwig SC, Dabbah M, Bryan Butler R, Gelb DE (2004) Preliminary results of staged anterior debridement and reconstruction using titanium mesh cages in the treatment of thoracolumbar vertebral osteomyelitis. Spine J 4:388–395
Frangen TM, Kälicke T, Gottwald M, Andereya S, Andress HJ, Russe O, Müller E, Muhr G, Schinkel C (2006) Die operative Therapie der Spondylodiszitis: Eine Analyse von 78 Patienten. Unfallchirurg 109:743–753
Frankel H, Hancock G, Hyslop G (1969) The value of postural reduction in the initial treatment of closed injuries of the spine with paraplegia and tetraplegia. Paraplegia 7:179–185
Garg N, Vohra R (2014) Minimally invasive surgical approaches in the management of tuberculosis of the thoracic and lumbar spine. Clin Orthop Relat Res 472(6):1855–1867
Guastella V, Mick G, Soriano C, Vallet L, Escande G, Dubray C, Eschalier A (2011) A prospective study of neuropathic pain induced by thoracotomy: incidence, clinical description, and diagnosis. Pain 152(1):74–81
Hee H, Majd M, Holt R, Pienkowski D (2002) Better treatment of vertebral osteomyelitis using posterior stabilisation and titanium mesh cages. J Spinal Disord 15:149–156
Hodgson AR, Stock FE (1960) Anterior spine fusion for the treatment of tuberculosis of the spine. J Bone Joint Surg Am 42:295–310
Hsieh PC, Wienecke RJ, O’Shaughnessy BA, Koski TR, Ondra SL (2004) Surgical strategies for vertebral osteomyelitis and epidural abscess. Neurosurg Focus 17:E4
Kawahara N, Tomita K, Kobayashi T, Abdel-Wanis ME, Murakami H, Akamaru T (2005) Influence of acute shortening on the spinal cord: an experimental study. Spine 30(6):613–620
Kirkaldy-Willis WH, Thomas TG (1965) Anterior approaches in the diagnosis and treatment of infections of the vertebral bodies. J Bone Joint Surg Am 47:87–110
Klockner C (2001) Alignment of the sagittal profile after surgical therapy of nonspecific destructive spondylodiscitis: ventral or ventrodorsal method - A comparison of outcomes. Orthopade 30:965–976
Klockner C, Wiedenhöfer B (2012) Therapy of unspecific destructive spondylodiscitis with special consideration to sagittal alignment. Orthopade 41(9):736–741
Korovessis P, Petsinis G, Koureas G, Iliopoulos P, Zacharatos S (2006) Anterior surgery with insertion of titanium mesh cage and posterior instrumented fusion performed sequentially on the same day under one anesthesia for septic spondylitis of thoracolumbar spine: is the use of titanium mesh cages safe? Spine 31:1014–1019
Korovessis P, Petsinis G, Koureas G, Iliopoulos P, Zacharatos S (2006) One-stage combined surgery with mesh cages for treatment of septic spondylitis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 444:51–59
Krodel A, Kruger A, Lohscheidt K, Pfahler M, Refior H (1999) Anterior debridement, fusion, and extrafocal stabilisation in the treatment of osteomyelitis of the spine. J Spinal Disord 12:17–26
Liljenqvist U, Lerner T, Bullmann V, Hackenberg L, Halm H, Winkelmann W (2003) Titanium cages in the surgical treatment of severe vertebral osteomyelitis. Eur Spine J 12(6):606–612
Lindholm TS (1979) Pyogenic spondylitis. Analysis of three surgically treated cases. Ann Chir Gynaecol 68:90–93
Matsui H, Hirano N, Sakaguchi Y (1998) Vertebral osteomyelitis: an analysis of 38 surgically treated cases. Eur Spine J 7:50–54
McGuire RA, Eismont FJ (1994) The fate of autogenous bone graft in surgically treated pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis. J Spinal Disord 7:206–215
Oga M, Arizono T, Takasita M, Sugioka Y (1993) Evaluation of the risk of instrumentation as a foreign body in spinal tuberculosis. Spine 18:1890–1894
Przybylski G, Sharan A (2001) Single-stage autogenous bone grafting and internal fixation in the surgical management of pyogenic discitis and vertebral osteomyelitis. J Neurosurg 94:1–7
Rajasekaran S, Soundarapandian S (1989) Progression of kyphosis in tuberculosis of the spine treated by anterior arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 71:1314–1323
Rath SA, Neff U, Schneider O, Richter HP (1996) Neurosurgical management of thoracic and lumbar vertebral osteomyelitis and discitis in adults: a review of 43 consecutive surgically treated patients. Neurosurgery 38:926–933
Sapico FL (1996) Microbiology and antimicrobial therapy of spinal infections. Orthop Clin N Am 27(1):9–13
Suk SI, Chung ER, Kim JH, Kim SS, Lee JS, Choi WK (2005) Posterior vertebral column resection for severe rigid scoliosis. Spine 30:1682–1687
Suk SI, Kim JH, Kim WJ, Lee SM, Chung ER, Nah KH (2002) Posterior vertebral column resection for severe spinal deformities. Spine 27:2374–2382
Tomita K, Kawahara N, Murakami H, Demura S (2006) Total en bloc spondylectomy for spinal tumors: improvement of the technique and its associated basic background. J Orthop Sci 11:3–12
Vedantam R, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Haas J, Linville DA (2000) A prospective evaluation of pulmonary function in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis relative to the surgical approach used for spinal arthrodesis. Spine 25(1):82–90
Zarghooni K, Röllinghoff M, Sobottke R, Eysel P (2012) Treatment of spondylodiscitis. Int Orthop 36:405–411
Patient consent
All patients have consented to this paper’s submission to the journal.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Marc Dreimann and Lennart Viezens contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dreimann, M., Viezens, L., Hoffmann, M. et al. Retrospective feasibility analysis of modified posterior partial vertebrectomy with 360-degree decompression in destructive thoracic spondylodiscitis. Acta Neurochir 157, 1611–1618 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-015-2507-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-015-2507-4