Abstract
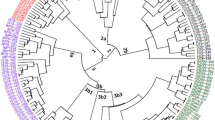
Due to precise evaluation of genetic diversity of Carthamus species, sixty-two genotypes consisting fifty-two from five wild (C. oxyacanthus M. Bieb, C. lanatus L., C. dentatus Vahl, C. boissieri Halácsy, C. glaucus M.B.) and ten from cultivated species (C. tinctorius L.) were selected for evaluation of the genetic diversity in Carthamus species. A total of 238 (81.2 %) polymorphic bands were detected by 12 SRAP primer combinations with an average of 22 bands per combination. Me4-Em1 and Me5-Em2 primer combinations were known as the most informative SRAP markers based on the PIC values (0.34) where they distinguished all studied Carthamus species. Cluster analysis classified all accessions into five main groups among which clusters containing cultivated individuals were distinctly separated from those containing wilds. The most and the least genetic variation based on analysis of molecular variance, were detected within (76.90 %) and among (22.84 %) groups, respectively. The obtained results suggested that C. dentatus, C. glaucus and C. boissieri species may be classified in one section including C. dentatus in one and C. glaucus and C. boissieri in another subsection. The results also revealed high genetic similarity between C. oxyacanthus and C. tinctorius despite their different morphological characteristics.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amini F, Saeidi G, Arzani A (2008) Study of genetic diversity in safflower genotypes using agro-morphological traits and RAPD markers. Euphytica 163:21–30
Anderson JA, Churchill GA, Autrique JE, Sorells ME, Tanksley SD (1993) Optimizing parental selection for genetic-linkage maps. Genome 36:181–186
Ashri A, Knowles PF (1960) Cytogenetics of Safflower (Carthamus L.) species and their hybrids. Agron J 52:11–17
Baghalian K, Maghsodi M, Naghavi MR (2010) Genetic diversity of Iranian madder (Rubia tinctorum) populations based on agro-morphological traits, phytochemical content and RAPD markers. Ind Crops Prod 31:557–562
Bassiri A (1977) Identification and polymorphism of cultivars and wild ecotypes of safflower based on isozyme patterns. Euphytica 26:709–719
Budak H, Shearman RC, Parmaksiz I, Dweikat I (2004) Comparative analysis of seeded and vegetative biotype buffalograsses based o phylogenetic relationship using ISSRs, SSRs, RAPDs, and SRAPs. Theor Appl Genet 109:280–288
Chapman MA, Hvala J, Strever J, Matvienko M, Kozik A, Michelmore RW, Tang S, Knapp SJ, Burke JM (2009) Development, polymorphism, and cross-taxon utility of EST-SSR markers from safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.). Theor Appl Genet 120:85–91
Cravero V, Martin E, Cointry E (2007) Genetic diversity in Cynara cardunculus determined by sequence-related amplified polymorphism markers. J Am Soc Hort Sci 132:208–212
Deshpande RB (1952) Wild safflower (Carthamus oxyacantha Bieb.)—a possible oil crop for the desert and arid regions. Ind J Genet Plant Breed 12:10–14
Esselman EJ, Crawford DJ, Brauner S, Stuessy TF, Anderson GJ, Silvia OM (2000) RAPD marker diversity within and divergence among species of Dendroseris (Asteraceae: Lactuceae). Am J Bot 87:591–596
Ferriol M, Pico B, Nuez F (2003) Genetic diversity of a germplasm collection of Cucurbita pepo using SRAP and AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 107:271–282
Gajera BB, Kumar N, Singh AS, Punvar BS, Ravikiran R, Subhash N, Jadeja GC (2010) Assessment of genetic diversity in castor (Ricinus communis L.) using RAPD and ISSR markers. Ind Crops Prod 32:491–498
Garcı′a-Moreno MJ, Velasco L, Fernández-Martínez JM, Pérez-Vich B (2008) Transferability of sunflower microsatellite markers to safflower. In: Proceedings of the 7th International Safflower Conference,Wagga Wagga, New South Wales, 3–6 November, Australia
Hanelt P (1963) Monographische Übersicht der Gattung Carthamus L. (Compositae). Fedds Repertorium Specierum Novarum Regni Vegetabilis 67:41–180
Han J, Zhang W, Cao H, Chen S, Wang Y (2007) Genetic diversity and biogeography of the traditional Chinese medicine, Gardenia jasminoides, based on AFLP markers. Biochem Syst Ecol 35:138–145
Jaccard P (1908) Nouvelles recherches sur la distribution florale. Bull Soc Vaud Sci Nat 44:223–270
Johnson RC, Bergman JW, Flynn CR (1999) Oil and meal characteristics of core and non-core safflower accessions from the USDA collection. Genet Resour Crop Evol 46:611–618
Khan MA, Witzke-Ehbrecht SV, Maass BL, Becker HC (2009) Relationships among different geographical groups, agro-morphology, fatty acid composition and RAPD marker diversity in safflower (Carthamus tinctorius). Genet Resour Crop Evol 56:19–30
Khidir MO, Knowles PF (1970) Cytogenetic studies of Carthamus species (Compositae) with 32 pairs of chromosomes. II Intersectional hybridization. Can J Genet Cytol 12:90–99
Li G, Quiros CF (2001) Sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP), a new marker system based on a simple PCR reaction: its application to mapping and gene tagging in Brassica. Theor Appl Genet 103:455–461
Li P, Yangdong W, Chen Y, Zhang SH (2009) Genetic diversity and association of ISSR markers with the eleostearic content in tung tree (Vernicia fordii). Afr J Biotechnol 8:4782–4788
Lopez-Gonzalez G (1989) Acerca del la classificacion natural del genero Carthamus L., s.l. An Jard Bot Madr 47:11–34
Mantel NA (1967) The detection of disease clustering and a generalized regression approach. Cancer Res 27:209–220
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4325
Peng S, Feng N, Guo M, Chen Y, Guo Q (2008) Genetic variation of Carthamus tinctorius L. and related species revealed by SRAP analysis. Biochem Syst Ecol 36:531–538
Rahimmalek M, Bahreininejad B, Khorrami M, Sayed Tabatabaei BE (2009) Genetic variability and geographic differentiation in Thymus daenensis subsp. daenensis, an endangered medicinal plant, as revealed by Inter Simple Sequence Repeat (ISSR) markers. Biochem Genet 47:831–842
Rohlf FJ (1998) NTSYS-PC Numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system, Version 2.02. Exter Publications, Setauket, NY, pp 1–31
Sabzalian MR, Mirlohi A, Saeidi G, Rabbani MT (2009) Genetic variation among populations of wild safflower, Carthamus oxyacanthus using agro-morphological traits and ISSR markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 54:415–420
Safavi SA, Pourdad SS, Taeb M, Khosroshahli M (2010) Assessment of genetic variation among safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) accessions using agro-morphological traits and molecular markers. Int J Food Agric Environ 8:616–625
Sehgal D, Raina N (2005) Genotyping safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) cultivars by DNA fingerprints. Euphytica 146:67–76
Sehgal D, Rajpal VR, Raina SN (2008) Chloroplast DNA diversity reveals the contribution of two wild species to the origin and evolution of diploid safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.). Genome 51:638–643
Sehgal D, Raina N, Devarumath RM, Sasanuma T, Sasakuma T (2009) Nuclear DNA assay in solving issues related to ancestry of the domesticated diploid safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) and the polyploid (Carthamus) taxa, and phylogenetic and genomic relationships in the genus Carthamus L. (Asteraceae). Mol Phylogenet Evol 53:631–644
Shao QS, Guo QS, Deng YM, Guo HP (2010) A comparative analysis of genetic diversity in medicinal Chrysanthemum morifolium based on morphology, ISSR and SRAP markers. Biochem Syst Ecol 38:1160–1169
Singh V, Nimbkar N (2006) Safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.). In: Singh RJ (ed) Genetic resources, chromosome engineering, and crop improvement. CRC, New York, pp 167–194
Singh S, Kumar Panda M, Nayak S (2012) Evaluation of genetic diversity in turmeric (Curcuma longa L.) using RAPD and ISSR markers. Ind Crops Prod 37:284–291
Uzun A, Yesiloglu T, Aka-Kacar Y, Tuzcu O, Gulsen O (2009) Genetic diversity and relationships within citrus and related genera based on sequence related amplified polymorphism markers (SRAPs). Sci Hortic 121:306–312
Uzun A, Yesiloglu T, Polat I, Aka-Kacar Y, Gulsen O, Yildirim B, Tuzcu O, Tepe S, Canan I, Anil S (2010) Evaluation of genetic diversity in Lemons and some of their relatives based on SRAP and SSR markers. Plant Mol Biol Rep, pp 1–9
Vilatersana RT, Garnatje T, Susanna A, Garcia-Jacas N (2005) Taxonomic problems in Carthamus (Asteraceae): RAPD markers and sectional classification. Bot J Linn Soc 147:375–383
Vilatersana R, Brysting AK, Brochmann C (2007) Molecular evidence for hybrid origins of the invasive polyploids Carthamus creticus and C. turkestanicus (Cardueae, Asteraceae). Mol Phylogenet Evol 4:610–621
Xie W, Zhang X, Cai H, Liu W, Peng Y (2010) Genetic diversity analysis and transferability of cereal EST-SSR markers to orchardgrass (Dactylis glomerata L.). Biochem Syst Ecol 38:740–749
Yang W, Lover BJW, Rao GY, Yang J (2006) Molecular evidence for multiple polyploidization and lineage recombination in the Chrysanthemum indicum polyploidy complex (Asteraceae). New Phytol 171:875–886
Yang YX, Wu W, Zheng YL, Chen L, Liu RJ, Huang CY (2007) Genetic diversity and relationships among safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) analyzed by inter-simple-sequence repeats (ISSRs). Genet Resour Crop Evol 54:1043–1051
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mokhtari, N., Rahimmalek, M., Talebi, M. et al. Assessment of genetic diversity among and within Carthamus species using sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) markers. Plant Syst Evol 299, 1285–1294 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-013-0796-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-013-0796-8