Summary
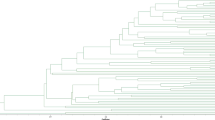
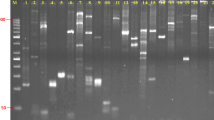
Carthamus tinctorius (2n = 2x = 24) (family Asteraceae), commonly known as safflower, is widely cultivated in agricultural production systems of Asia, Europe, Australia and the Americas as a source of high-quality vegetable and industrial oil. India ranks first in the production of safflower oil. Fourteen cultivars, widely cultivated in various agro-climatic regions of India, have been fingerprinted by RAPD, ISSR, and AFLP markers utilizing 36, 21 primers, and 4 primer combinations, respectively. On an individual assay basis, AFLP has proven to be the best marker system as compared with the other two markers applied as assessed by high discriminating power (0.98), assay efficiency index (33.2), marker index (18.2), resolving power (40.62), and genotype index (0.856). Thirty-six RAPD and 21 SSR primers could differentiate a maximum of eight and four cultivars, respectively, whereas, two AFLP primer combinations could fingerprint all the 14 cultivars. To understand genetic relationships among these cultivars, Jaccard's similarity coefficient and UPGMA clustering algorithm were applied to the three marker data sets. Mean genetic similarities ranged from 0.689 (AFLP) to 0.952 (ISSR). Correlation coefficient comparisons between similarity matrices and co-phenetic matrices obtained with the three markers revealed that AFLP displayed no congruence vis-a-vis RAPD and ISSR data. However, strong correlation was observed between RAPD and ISSR marker systems. This paper reports the start of molecular biology programme targeting nuclear genome of safflower, a major world oilseed crop about whose genetics very little is known.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal, R.K., V.V. Shenoy, J. Ramadevi, R. Rajkumar & L. Singh, 2002. Molecular characterization of some Indian Basmati and other elite genotypes using fluorescent AFLP. Theor Appl Genet 105: 680–690.
Anderson, J.A., G.A. Churchill, J.E. Autroque, S.D. Tanksley & M.E. Swells, 1993. Optimising selection for plant linkage map. Genome 36: 181–186.
Araki, S., Y. Tsuchiya, T. Masachika, T. Tamaki & K. Shinotsuka, 1998. Identification of hop cultivars by DNA marker analysis. J Amer Soc Br Chem 56: 93–98.
Archak, S., A.B. Galkwad, D. Gautam, E.V.V.B. Rao, K.R.M. Swamy & J.L. Karihaloo, 2003. Comparative assessment of DNA fingerprinting techniques (RAPD, ISSR and AFLP) for genetic analysis of cashew (Anacardium occidentale L.) accessions of India. Genome 46: 362–369.
Ashri, A. & P.F. Knowles, 1960. Cytogenetics of safflower Carthamus L. species and their hybrids. Agronomy J 52(1): 11–17.
Ashri, A., 1971a. Evaluation of world collection of safflower C. tinctorius L.1 Reaction to several diseases and association with morphological characters in Israel. Crop Sci 11: 253–257.
Ashri, A., 1971b. Evaluation of world collection of C.tinctorius L 11 resistance to safflower fly A. helianthi R. Euphytica 20: 410-415.
Ashri, A., 1973. Divergence and evolution in the safflower genus Carthamus L. Final Research Report, PL 480, USDA, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Faculty of Agriculture, Rehovot, Israel.
Ashri, A., 1975. Evaluation of the germplasm collection of safflower Carthamus tinctorius L. V Distribution and regional divergence for morphological characters. Euphytica 24: 651–659.
Ashri, A., D.E. Zimmer, A.L. Urie, A. Cahaner & A. Marani, 1974. Evaluation of world collection of safflower Carthamus tinctorius L IV Yield and yield components and their relationships. Crop Sci 14: 799–802.
Aslam, M. & G.R. Hazara, 1993. Evaluation of world collection of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L) for yield and other agronomic characters In: L. Dajue & H. Yuanzhou (Eds.), Third International Safflower Conference, Beijing, China, June 9–13, 1993, p. 238.
Belaj, A., Z. Satovic, G. Cipriani, L. Baldoni, R. Testolin, L. Rallo & I. Trujillo, 2003. Comparative study of the discriminating capacity of RAPD, AFLP and SSR markers and of their effectiveness in establishing genetic relationships in olive. Theor Appl Genet 107: 736–744.
Blair, M.M., O. Panaud & S.R. McCouch, 1999. Inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) amplification for analysis of microsatellite motif frequency and fingerprinting in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 98: 780–792.
Bohn, M., H.F. Utz & A.E. Melchinger, 1999. Genetic similarities among winter wheat cultivars determined on the basis of RFLPs, AFLPs and SSRs and their use for predicting progeny variance. Crop Sci 39: 228–237.
Degani, C., L.J. Rowland, A.J.A. Saunders, S.C. Hokanson, E.L. Ogden, A. Golan-Goldhirsh & G.J. Galletta, 2001. A comparison of genetic relationship measures in strawberry (Frageria × ananassa Duch.) based on AFLPs, RAPDs, and Pedigree data. Euphytica 117: 1–12.
Fang, D.Q. & M.L. Roose, 1997. Identification of closely related citrus cultivars with inter-simple sequence repeat markers. Theor Appl Genet 95: 408–417.
Fernandez-Martinez, J., M. Rio & A. Haro, 1993. Survey of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L) germplasm for variants in fatty acid composition and other seed characters. Euphytica 19(1/2): 115–122.
Fuentes, J.L., F. Escobar, A. Alvarez, G. Gallego, M.C. Duque, M. Ferrer, J.E. Deus & J.M. Tohme, 1999. Analysis of genetic diversity in Cuban rice varieties using isozyme, RAPD and AFLP markers. Euphytica 109: 107–115.
Futehally, S., 1982. Inheritance of very high levels of Linoleic acid in the seed oil of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L). M.S. thesis, University of California, Davis.
Garcia-Mas, J., M. Oliver, H. Gómez-Paniagua & M.C. de Vicente, 2000. Comparing AFLP, RAPD, and RFLP markers for measuring genetic diversity in melon. Theor Appl Genet 101: 860–864.
Guena, F., M. Tochi & D. Bassi, 2003. The use of AFLP markers for cultivar identification in apricot. Plant Breeding 122: 526–531.
Han, Y. & D. Li, 1992. Evaluation of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L) germplasm-analysis in fatty acid composition of seeds of domestic and exotic safflower varieties. Bot Res 6: 28–35.
Knowles, P.F., 1955. Safflower: Production, processing and utilization. Econ Bot 9: 273–299.
Kumar, H., 1991. Cytogenetics of Safflower. In: Y. Tsuchiya & P.K. Gupta (Eds.), Chromosome engineering in plants: Genetics, breeding, evolution. Part B, pp. 251–277. Elsevier Science Publishers, The Netherlands.
Lombard, V., C.P. Baril, P. Dubreuil, F. Blouet & D. Zhang, 2000. Genetic relationships and fingerprinting of rapeseed culivars using AFLP: Conequences for varietal registration. Crop Sci 40: 1417–1425.
Mantel, N., 1967. The detection of disease clustering and a generalized regression approach. Can Res 27: 209–220.
Milbourne, D., R. Meyer, J.E. Bradshaw, E. Baird, N. Bonar, J. Provan, W. Powell & R. Waugh, 1997. Comparison of PCR-based marker systems for the analysis of genetic relationships in cultivated potato. Mol Breed 3: 127–136.
Paczos-Grzęda, E., 2004. Pedigree, RAPD and simplified AFLP-based assessment of genetic relationships among Avena sativa L. cultivars. Euphytica 138: 13–22.
Pejic, I., P. Ajmone-Marsan, M. Morgante, V. Kozumplick, P. Castiglioni, G. Taramino & M. Motto, 1998. Comparative analysis of genetic similarity among maize inbred lines detected by RFLPs, RAPDs, SSRs, and AFLPs. Theor Appl Genet 97: 1248–1255.
Porebski, S., L.G. Bailey & B.R. Baum, 1997. Modification of a CTAB extraction protocol for plants containing high polysaccharide and polyphenol components. Plant Mol Bio Reports 15(1): 8–15.
Powell, W., M. Morgante, C. Andre, M. Hanafey, J. Vogel, S. Tingey & A. Rafalski, 1996. The comparison of RFLP, RAPD, AFLP and SSR (microsatellite) markers for germplasm analysis. Mol Breed 2: 225–238.
Prevost, A. & M.J. Wilkinson, 1999. A new system of comparing PCR primers applied to ISSR fingerprinting of potato cultivars. Theor Appl Genet 98: 107–112.
Rohlf, F.J., 1992. NTSYS-PC: Numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system version 2.02k. State University of New York, Stony Brook N.Y.
Russell, J.R., J.D. Fuller, M. Macaulay, B.G. Hatz, A. Jahoor, W. Powell & R. Waugh, 1997. Direct comparison of levels of genetic variation among barley accessions detected by RFLPs, AFLPs, SSRs, and RAPDs. Theor Appl Genet 95: 714–722.
Tessier, C., J. David, P. This, J.M. Boursiquot & A. Charrier, 1999. Optimization of the choice of molecular markers for varietal identification in Vitis vinifera L. Theor Appl Genet 98: 171–177.
Thein, S.I. & R.R. Wallace, 1986. The use of synthetic oligonucleotides as specific hybridization probes in the diagnosis of genetic disorders. In: K.E. Davis (Ed.), Human genetic diseases: A practical approach, pp. 33–50. IRL, Oxford.
Weiss, E.A., 1971. Castor, Sesame and Safflower. Leonard Hill Books, University Press, Aberdeen, London, pp. 529-774.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sehgal, D., Raina, S.N. Genotyping safflower (Carthamus tinctorius) cultivars by DNA fingerprints. Euphytica 146, 67–76 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-005-8496-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-005-8496-2