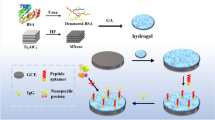
Abstract
An antifouling electrochemical biosensor was constructed based on chondroitin sulfate (CS)-functionalized polyaniline (CS/PANI) and DNA-peptide conjugates that is capable of assaying cortisol directly in human fluids. First, a CS-doped PANI nanocomposite (sensing substrate) was electrodeposited onto a bare glassy carbon electrode to promote electron transport, providing the sensing signal from high peak currents of PANI to improve the sensitivity of the biosensor. Dendritic DNA-peptide conjugates were assembled onto the CS/PANI by exploiting the highly specific and strong interactions between biotin and streptavidin, which amplified the sensing signals toward cortisol. The integration of the DNA-peptide conjugates into the CS/PANI nanocomposite ensured that the biosensor had a synergistic antifouling effect and was capable of detecting cortisol directly in body fluids (sweat, saliva, and tears). When assaying cortisol levels, the biosensor exhibited a linear range over the cortisol concentrations of 1 × 10–12–1 × 10–7 M and a low limit of detection (0.333 × 10–12 M). In the detection of cortisol in real samples, the relative standard deviation (RSD) of the biological samples ranged from 2.94 to 4.23%, and the recovery were calculated to be in the range 95.2–103.2%.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zea M, Bellagambi FG, Ben Halima H, Zine N, Jaffrezic-Renault N, Villa R, Gabriel G, Errachid A (2020) Electrochemical sensors for cortisol detections: Almost there. Trends Anal Chem 132:116058
Russell E, Koren G, Rieder M, Uum SHMV (2014) The detection of cortisol in human sweat: Implications for measurement of cortisol in hair. Ther Drug Monit 36:30–34
Raff H, Findling JW (2003) A physiologic approach to diagnosis of the cushing syndrome. Ann Intern Med 138:980–991
Lenfant C, Chobbanian AV, Jones DW, Roccella EJ (2003) Seventh report of the joint national committee on the prevention, detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure. Hypertension 107:2993–2994
Kaushik A, Vasudev A, Arya SK, Pasha SK, Bhansali S (2014) Recent advances in cortisol sensing technologies for point-of-care application. Biosens Bioelectron 53:499–512
Dalirirad S, Steckl AJ (2019) Aptamer-based lateral flow assay for point of care cortisol detection in sweat. Sens Actuators B 283:79–86
Singh NK, Chung S, Sveiven M, Hall DA (2021) Detection in undiluted human serum using a sensitive electrochemical structure-switching aptamer over an antifouling nanocomposite layer. ACS Omega 42:27888–27897
Khumngern S, Jeerapan I (2023) Advances in wearable electrochemical antibody-based sensors for cortisol sensing. Anal Bioanal Chem 415:3863–3877
Karuppaiah G, Velayutham J, Sethy NK, Manickam P (2023) DNA aptamer and gold-nanofiller integrated hybrid hydrogel network for electrochemical detection of salivary cortisol. Mater Lett 342:134310
Karuppaiah G, Velayutham J, Hansda S, Narayana N, Bhansali S, Manickam P (2022) Towards the development of reagent-free and reusable electrochemical aptamer-based cortisol sensor. Bioelectrochemistry 145:108098
Mugo SM, Alberkant J (2020) Flexible molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor for cortisol monitoring in sweat. Anal Bioanal Chem 412:1825–1833
Sun K, Ramgir N, Bhansali S (2008) An immunoelectrochemical sensor for salivary cortisol measurement. Sens Actuators B 133:533–537
Lee I, Loew N, Tsugawa W, Ikebukuro K, Sode K (2019) Development of a third-generation glucose sensor based on the open circuit potential for continuous glucose monitoring. Biosens Bioelectron 124–125:216–223
Dai YF, Xu W, Liu CC (2020) Immunoglobulin g-based steric hindrance assay for protein detection. ACS Sens 5:140–146
Hui N, Wang JS, Wang DW, Wang PP, Luo XL, Lv SP (2022) An ultrasensitive biosensor for prostate specific antigen detection in complex serum based on functional signal amplifier and designed peptides with both antifouling and recognizing capabilities. Biosens Bioelectron 200:113921
Zheng LC, Sundaram HS, Wei ZY, Li CC, Yuan ZF (2017) Applications of zwitterionic polymers. React Funct Polym 118:51–61
Xia YQ, Adibnia V, Huang RL, Murschel F, Faivre J, Xie GJ, Olszewski M, De CG, Qi W, He ZM, Su RX, Matyjaszewski K, Banquy X (2019) Biomimetic bottlebrush polymer coatings for fabrication of ultralow fouling surfaces. Angew Chem Int Ed 58:1308–1314
Chen Q, Yu S, Zhang DH, Zhang WJ, Zhang HD, Zou JC, Mao ZW, Yuan Y, Gao CY, Liu RH (2019) Impact of antifouling PEG layer on the performance of functional peptides in regulating cell behaviors. J Am Chem Soc 141:16772–16780
Zhou Y, Petrova SP, Edgar KJ (2021) Chemical synthesis of polysaccharide-protein and polysaccharide-peptide conjugates: A review. Carbohydr Polym 274:118662
Wang H, Lü HT, Yang LL, Song Z, Hui N (2020) Glycyrrhiza polysaccharide doped the conducting polymer PEDOT hybrid-modified biosensors for the ultrasensitive detection of microRNA. Anal Chim Acta 1139:155–163
Wang JS, Wang DW, Hui N (2020) A low fouling electrochemical biosensor based on the zwitterionic polypeptide doped conducting polymer PEDOT for breast cancer marker BRCA1 detection. Bioelectrochemistry 136:107595
Yuan ZF, Li BW, Niu LQ, Tang CJ, McMullen P, Jain P, He YW, Jiang SY (2020) Zwitterionic peptide cloak mimics protein surfaces for protein protection. Angew Chem Int Ed 59:22378–22381
Jiang C, Wang GX, Hein R, Liu NZ, Luo XL, Davis JJ (2020) Antifouling strategies for selective In vitro and In vivo sensing. Chem Rev 120:3852–3889
Cui M, Ma YH, Wang L, Wang Y, Wang S, Luo XL (2020) Antifouling sensors based on peptides for biomarker detection. Trends Anal Chem 127:115903
Nowinski AK, Sun F, White AD, Keefe AJ, Jiang SY (2012) Sequence, structure, and function of peptide self-assembled monolayers. J Am Chem Soc 134:6000–6005
Liu NZ, Hui N, Davis JJ, Luo XL (2018) Low fouling protein detection in complex biological media supported by a designed multifunctional peptide. ACS Sens 3:1210–1216
Liu NZ, Song JY, Lu YW, Davis JJ, Gao FX, Luo XL (2019) Electrochemical aptasensor for ultralow fouling cancer cell quantification in complex biological media based on designed branched peptides. Anal Chem 91:8334–8340
Han R, Wang GX, Xu ZY, Zhang LY, Li Q, Han YF, Luo XL (2020) Designed antifouling peptides planted in conducting polymers through controlled partial doping for electrochemical detection of biomarkers in human serum. Biosens Bioelectron 164:112317
Lu BY, Yuk H, Lin ST, Jian NN, Qu K, Xu JK, Zhao XH (2019) Pure PEDOT: PSS hydrogels. Nat Commun 10:1043
Zhu JQ, Yuan HH, Zhang SQ, Hao X, Lan MB (2022) Construction of antifouling and antibacterial polyhexamethylguanidine/chondroitin sulfate coating on polyurethane surface based on polydopamine rapid deposition. J Appl Polym Sci 139:e53009
Liao GF, Li Q, Xu ZS (2019) The chemical modification of polyaniline with enhanced properties: A review. Prog Org Coat 126:35–43
Wei Q, Becherer T, Angioletti-Uberti S, Dzubiella J, Wischke C, Neffe AT, Lendlein A, Ballauff M, Haag R (2014) Protein interactions with polymer coatings and b iomaterials. Angew Chem Int Ed 53:8004–8031
Lü HT, Yang LL, Zhou Y, Qu RH, Xu Y, Shang SQ, Hui N (2021) Non-enzymatic electrochemical sensors based on conducting polymer hydrogels for ultrasensitive carbaryl pesticide detection. J Electrochem Soc 168:047506
Funding
This work was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province of China (ZR2022MB069), Shandong Provincial Key R & D Plan (Major Scientific and Technological Innovation Project) (2022CXGC010611, 2022CXGC010401), and Shandong Peanut Industry Technology System Project (SDAIT-04–09).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, K., Yang, J., Shen, L. et al. An antifouling electrochemical biosensor based on chondroitin sulfate-functionalized polyaniline and DNA-peptide conjugates for cortisol determination in body fluids. Microchim Acta 190, 494 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-06083-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-06083-5