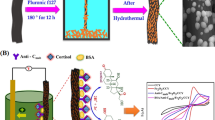
Abstract
A selective cortisol sensor based on molecularly imprinted poly(glycidylmethacrylate-co ethylene glycol dimethacrylate) (poly(GMA-co-EGDMA)) has been demonstrated for detection of cortisol in human sweat. The non-enzymatic biomimetric flexible sweat sensor was fabricated inexpensively by layer by layer (LbL) assembly. The sensor layers comprised a stretchable polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) base with carbon nanotubes-cellulose nanocrystals (CNC/CNT) conductive nanoporous nanofilms. The imprinted (MIP) poly(GMA-co-EGDMA) deposited on the CNC/CNT was the cortisol biomimetric receptor. Rapid in analyte response (3 min), the cortisol MIP sensor demonstrated excellent performance. The sensor has a limit of detection (LOD) of 2.0 ng/mL ± 0.4 ng/mL, dynamic range of 10–66 ng/mL, and a sensor reproducibility of 2.6% relative standard deviation (RSD). The MIP sensor also had high cortisol specificity and was inherently blind to selected interfering species including glucose, epinephrine, β-estradiol, and methoxyprogestrone. The MIP was four orders of magnitude more sensitive than its non-imprinted (NIP) counterpart. The MIP sensor remains stable over time, responding proportionately to doses of cortisol in human sweat.

Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kassal P, Steinberg MD, Steinberg IM. Wireless chemical sensors and biosensors. A review. Sens. Actuat B: Chemical. 2018;266:228–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.03.074.
Bandodkar AJ, Wang J. Wearable chemical sensors: present challenges and future prospects. ACS. Sens. 2017;1:464–82. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.6b00250.
Roy S, Moshe DP, Hanaein Y. Carbon nanotube-based ion selective sensors for wearable applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9:35169–77. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b07346.
Choi J, Ghaffari R, Baker LB, Rogers JA. Skin-interfaced systems for sweat collection and analytics. Sci Adv. 2018;4:eaar3921. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aar3921.
Jalal AH, Alam F, Roychoudhury S, Umasankar Y, Pala N. Prospects and challenges of volatile organic compound sensors in human healthcare. ACS Sens. 2018;3:1246–63. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.8b00400.
Kim SJ, Choi SJ, Cho HJ, Kim ID. Innovative nanosensor for disease diagnosis. Acc Chem Res. 2017;50:1587–96. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00047.
Bandodkar AJ, Wang J. Non-invasive wearable electrochemical sensors: a review. Trends Biotechnol. 2014;32:363–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2014.04.005.
Nyein HYY, Tai LC, Ngo TQP, Chao M, Zhang GB. A wearable microfluidic sensing patch for dynamic sweat secretion analysis. ACS Sens. 2018;3:944–52. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.7b00961.
Oh SY, Hong SY, Jeong YR, Yun J, Park H. Skin-attachable, stretchable electrochemical sweat sensor for glucose and pH detection. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10:13729–40. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b03342.
Padmanathan N, Shao H, Razeeb KM. Multifunctional nickel phosphate nano/microflakes 3D electrode for electrochemical energy storage, nonenzymatic glucose, and sweat pH sensors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10:8599–610. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b17187.
Mitsubayashi K, Suzuki M, Tamiya E, Karube I. Analysis of metabolites in sweat as a measure of physical condition. Anal Chem Actica. 1994;289:27–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2670(94)80004-9.
Anastasova S, Crewther B, Bembnowicz P, Curto V, Ip H. A wearable multisensing patch for continuous sweat monitoring. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;93:139–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.09.038.
Tuteja SK, Ormsby C, Neethiraja S. Noninvasive label-free detection of cortisol and lactate using graphene embedded screen-printed electrode. Nano Micro Lett. 2018;10:41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-018-0193-5.
Jia M, Chew WM, Feinstein Y, Sheath P, Sternberg EM. Quantification of cortisol in human eccrine sweat by liquid chromatography – tandem mass spectrometry. Analyst. 2016;141:2053–60. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5AN02387D.
Martin JA, Chavez JL, Chushak Y, Chapleau RR, Hagen J. Tunable stringency aptamer selection and gold nanoparticle assay for detection of cortisol. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2014;406:4637–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-014-7883-8.
Kessler RC, Berglund P, Demler O, Jin R, Merikangas KR, Walters EE. Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the national comorbidity survey replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62:593–602. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.62.6.593.
Ramstrom O, Ye L, Mosback K. Artificial antibodies to corticosteroids prepared by molecular imprinting. Chem Biodivers. 1996;3:471–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1074-5521(96)90095-2.
Zhang Q, Mugo SM. Nano-sized structured platforms for facile solid-phase nanoextraction for molecular capture and (Bio) chemical analysis. Nanomat Design Sens Appl Elsevier. 2019:111–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-814505-0.00005-9.
Parlak O, Keene ST, Marais A, Curto VF, Salleo A. Molecularly selective nanoporous membrane-based wearable organic electrochemical device for noninvasive cortisol sensing. Sci. Adv. 2018;4:eaar2904. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aar2904.
Cooke J, Hebret D, Kelly JA. Sweet nanochemistry: a fast, reliable alternative synthesis of yellow colloidal silver nanoparticles using benign reagents. J Chem Educ. 2015;92:345–9. https://doi.org/10.1021/ed5004756.
Dhanjai, Yu N, Mugo SM. A flexible-imprinted capacitive sensor for rapid detection of adrenaline. Talanta. 2019;204:602–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.06.016.
Wu W, Mitra N, Yan ECY, Zhou S. Multifunctional hybrid nanogel for integration of optical glucose sensing and self-regulated insulin release at physiological pH. ACS Nano. 2010;4:4831–9. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn1008319.
Alzaid M, Roth J, Wang Y, Almutairi E, Brown SL. Enhancing the elasticity of ultrathin single-wall carbon nanotube films with colloidal nanocrystal. Langmuir. 2017;33:7889–95. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b01988.
Plawsky JL, Kim JK, Schubert EF. Engineered nanoporous and nanostructured films. Mater Today. 2009;12:36–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1369-7021(09)70179-8.
Nemoto J, Saito T, Isogai A. Simple freeze-drying procedure for producing nanocellulose aerogel-containing, high-performance air filters. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7:19809–15. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b05841.
Zaryanov NV, Nikitina VN, Karpova EV, Karyakina EE, Karyakin AA. Nonenzymatic sensor for lactate detection in human sweat. Anal Chem. 2017;89:11198–202. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b03662.
Sekar M, Pandiaraj M, Bhansali S, Ponpandian N, Viswanathan C. Carbon fiber based electrochemical sensor for sweat cortisol measurement. Sci Rep. 2019;9:403. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-37243-w.
Sun B, Gou Y, Ma Y, Zheng X, Bai R. Investigate electrochemical immunosensor of cortisol based on gold nanoparticles/magnetic functionalized reduced graphene oxide. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;88:55–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.07.047.
Kim KS, Lim SR, Kim SE, Lee JY, Chung CH. Highly sensitive and selective electrochemical cortisol sensor using bifunctional protein interlayer-modified graphene electrodes. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2017;242:1121–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.09.135.
Acknowledgments
Mugo research group acknowledges funding from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC), Canada Summer Jobs Program and MacEwan University. We also acknowledge the assistance of Lisa Mugo (St. Mary’s Elementary, Edmonton) in designing the graphical abstract.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Informed consent was obtained from the student volunteer participant included in the study. The study was approved by the MacEwan Research Ethics Board (REB) to ascertain the study was performed in accordance with acceptable ethical standards.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mugo, S.M., Alberkant, J. Flexible molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor for cortisol monitoring in sweat. Anal Bioanal Chem 412, 1825–1833 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-02430-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-02430-0