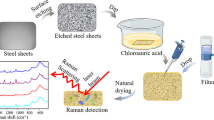
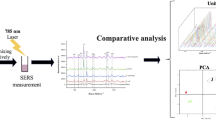
Abstract
A new surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) biosensor of Graphene@Ag-MLF composite structure has been fabricated by loading AgNPs on graphene films. The response of the biosensor is based on plasmonic sensing. The results showed that the enhancement factor of three different spores reached 107 based on the Graphene@Ag-MLF substrate. In addition, the SERS performance was stable, with good reproducibility (RSD<3%). Multivariate statistical analysis and chemometrics were used to distinguish different spores. The accumulated variance contribution rate was up to 96.35% for the top three PCs, while HCA results revealed that the spectra were differentiated completely. Based on optimal principal components, chemometrics of KNN and LS-SVM were applied to construct a model for rapid qualitative identification of different spores, of which the prediction set and training set of LS-SVM achieved 100%. Finally, based on the Graphene@Ag-MLF substrate, the LOD of three different spores was lower than 102 CFU/mL. Hence, this novel Graphene@Ag-MLF SERS substrate sensor was rapid, sensitive, and stable in detecting spores, providing strong technical support for the application of SERS technology in food safety.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Paidhungat M, Ragkousi K, Setlow P (2001) Genetic requirements for induction of germination of spores of Bacillus subtilis by Ca(2+)-dipicolinate. J Bacteriol 183:4886–4893. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.183.16.4886-4893.2001
Setlow P (2006) Spores of Bacillus subtilis: their resistance to and killing by radiation, heat and chemicals. J Appl Microbiol 101:514–525. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2005.02736.x
Zhu Y, Liu W, Liu S, Li M, Zhao L, Xu L, Wang N, Zhao G, Yu Q (2022) Preparation of AgNPs self-assembled solid-phase substrate via seed-mediated growth for rapid identification of different bacterial spores based on SERS. Food Res Int 160:111426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111426
Wong YL, Kang WCM, Reyes M, Teo JWP, Kah JCY (2020) Rapid detection of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriacae based on surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy with gold nanostars. ACS Infect Dis 6:947–953. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsinfecdis.9b00318
Zhang C, Huang L, Pu H, Sun D-W (2021) Magnetic surface-enhanced Raman scattering (MagSERS) biosensors for microbial food safety: fundamentals and applications. Trends in Food Sci Technol 113:366–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2021.05.007
Teng Y, Wang Z, Ren Z, Qin Y, Pan Z, Shao K, She Y, Huang W (2020) Interface-induced Ag monolayer film for surface-enhanced raman scattering detection of water-insoluble enrofloxacin. Plasmonics 16:349–358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-020-01258-9
Liu X, Ye Z, Xiang Q, Xu Z, Yue W, Li C, Xu Y, Wang L, Cao X, Zhang J (2023) Boosting electromagnetic enhancement for detection of non-adsorbing analytes on semiconductor SERS substrates. Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chempr.2023.01.017
Wang K, Sun D-W, Pu H, Wei Q (2020) Two-dimensional Au@Ag nanodot array for sensing dual-fungicides in fruit juices with surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy technique. Food Chem 310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125923
Liu Y, Zhou H, Hu Z, Yu G, Yang D, Zhao J (2017) Label and label-free based surface-enhanced Raman scattering for pathogen bacteria detection: a review. Biosens Bioelectron 94:131–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.02.032
Sharma B, Frontiera RR, Henry A-I, Ringe E, Van Duyne RP (2012) SERS: materials, applications, and the future. Materials Today 15:16–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1369-7021(12)70017-2
Alsammarraie FK, Lin M (2017) Using standing gold nanorod arrays as surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) substrates for detection of carbaryl residues in fruit juice and milk. J Agric Food Chem 65:666–674. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.6b04774
Keeler AJ, Salazar-Banda GR, Russell AE (2019) Mechanistic insights into electrocatalytic reactions provided by SERS. Curr Opin Electrochem 17:90–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coelec.2019.04.009
Konrad MP, Doherty AP, Bell SE (2013) Stable and uniform SERS signals from self-assembled two-dimensional interfacial arrays of optically coupled Ag nanoparticles. Anal Chem 85:6783–6789. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac4008607
Ma Y, Liu H, Mao M, Meng J, Yang L, Liu J (2016) Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy on liquid interfacial nanoparticle arrays for multiplex detecting drugs in urine. Anal Chem 88:8145–8151. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b01884
Park Y-K, Yoo S-H, Park S (2007) Assembly of highly ordered nanoparticle monolayers at a water/hexane interface. Langmuir 23:10505–10510. https://doi.org/10.1021/la701445a
Sun J, Gong L, Gong Z, Wang D, Yin X, Fan M (2019) Facile fabrication of a large-area and cost-effective PDMS-SERS substrate by sandpaper template-assisted lithography. Anal Methods 11:4917–4922. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ay01494b
Zhang D, Pu H, Huang L, Sun D-W (2021) Advances in flexible surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) substrates for nondestructive food detection: fundamentals and recent applications. Trends in Food Sci Technol 109:690–701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2021.01.058
Zhang Y, Tan YW, Stormer HL, Kim P (2005) Experimental observation of the quantum Hall effect and Berry’s phase in graphene. Nature 438:201–204. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04235
Mohaghegh F, Mazaheri Tehrani A, Materny A (2016) Investigation of the chemical enhancement contribution to SERS using a Kretschmann arrangement. J Raman Spectr 47:1029–1035. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrs.4920
Xie L, Ling X, Fang Y, Zhang J, Liu Z (2009) Graphene as a substrate to suppress fluorescence in resonance Raman spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc 131:9890–9891. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja9037593
Vishakha K, Hardik L, Dheeraj K, Sachin (2022) Enhancement of SERS effect in Graphene-Silver hybrids. Appl Surface Sci 574: 151724. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.151724
Chang C-J, Liu C-A, Pu Y-H, Yang T-Y, Chiu H-T, Chen C-H, Huang G-G (2020) Gold nanoparticles grown by galvanic replacement on graphene-coated aluminum panels as large-area substrates for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. ACS Appl Nano Mater 3:5783–5793. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.0c00846
Preeti G, Bharti RKS, Raman R (2020) Graphene oxide–silver nanocomposite SERS substrate for sensitive detection of nitro explosives. J Mater Sci Mater Electr 31:1094–1104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02621-1
Xu W, Mao N, Zhang J (2013) Graphene: a platform for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Small 9:1206–1224. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201203097
Li D, Duan X, Sun H, Kang J, Zhang H, Tade MO, Wang S (2017) Facile synthesis of nitrogen-doped graphene via low-temperature pyrolysis: the effects of precursors and annealing ambience on metal-free catalytic oxidation. Carbon 115:649–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2017.01.058
Deng CH, Gong JL, Zeng GM, Niu CG, Niu QY, Zhang W, Liu HY (2014) Inactivation performance and mechanism of Escherichia coli in aqueous system exposed to iron oxide loaded graphene nanocomposites. J Hazard Mater 276:66–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.05.011
Mungroo NA, Oliveira G, Neethirajan S (2015) SERS based point-of-care detection of food-borne pathogens. Microchimica Acta 183:697–707. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1698-y
Lemma T, Saliniemi A, Hynninen V, Hytönen VP, Toppari JJ (2016) SERS detection of cell surface and intracellular components of microorganisms using nano-aggregated Ag substrate. Vibr Spectr 83:36–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vibspec.2016.01.006
Kong L, Zhang P, Wang G, Yu J, Setlow P, Li YQ (2011) Characterization of bacterial spore germination using phase-contrast and fluorescence microscopy, Raman spectroscopy and optical tweezers. Nat Protoc 6:625–639. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2011.307
Luo Z, Yang W, Peng A, Ma Y, Fu H, Yao J (2009) Net-like assembly of Au nanoparticles as a highly active substrate for surface-enhanced raman and infrared spectroscopy. J Phys Chem A 113:2467–2472. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp810387w
Cara E, Mandrile L, Ferrarese Lupi F, Giovannozzi AM, Dialameh M, Portesi C, Sparnacci K, De Leo N, Rossi AM, Boarino L (2018) Influence of the long-range ordering of gold-coated Si nanowires on SERS. Sci Rep 8:11305. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-29641-x
Venkatesan C, Karthigaikumar P, Varatharajan R (2018) A novel LMS algorithm for ECG signal preprocessing and KNN classifier based abnormality detection. Multimedia Tools and Appl 77:10365–10374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-5762-6
Zhu Y, Zhang J, Li M, Ren H, Zhu C, Yan L, Zhao G, Zhang Q (2020) Near-infrared spectroscopy coupled with chemometrics algorithms for the quantitative determination of the germinability of Clostridium perfringens in four different matrices. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 232:117997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2019.117997
Chen Q, Jiang P, Zhao J (2010) Measurement of total flavone content in snow lotus (Saussurea involucrate) using near infrared spectroscopy combined with interval PLS and genetic algorithm. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 76:50–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2010.02.045
Li JL, Sun DW, Pu H, Jayas DS (2017) Determination of trace thiophanate-methyl and its metabolite carbendazim with teratogenic risk in red bell pepper (Capsicumannuum L.) by surface-enhanced Raman imaging technique. Food Chem 218:543–552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.09.051
Funding
This research was supported by the Major science and technology projects in Henan province (221100110500), the Science Foundation for Outstanding Youth of Henan Province (212300410008), the Science and Technology Innovation Team of Henan Universities (22IRTSTHN021), the key scientific and technological projects of Henan Province (232102110136), the National Modern Agriculture (beef yak) Industrial Technology System Construction Special (CARS-37), and the Key R&D Project of Henan Provincial Department of Education (22A550009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YZ: investigation, data curation, writing—original draft. JT: writing—original draft. ML: supervision, resources, conceptualization, writing—review and editing. LZ: supervision, funding acquisition. JS: data curation. WL: investigation. SL: helped collect test data. DL: supervision. GZ: investigation. LX: writing—review and editing. SY: assisted the experiment and collected test data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 18 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Y., Tian, J., Li, M. et al. Construction of Graphene@Ag-MLF composite structure SERS platform and its differentiating performance for different foodborne bacterial spores. Microchim Acta 190, 472 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-06031-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-06031-3