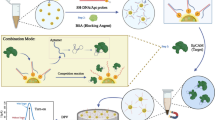
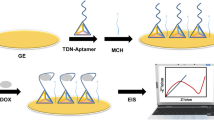
Abstract
A novel aptasensor has been designed for quantitative monitoring of epinephrine (EP) based on cerium metal–organic framework (CeMOF) loaded gold nanoparticles (AuNPs). The aptamer, specific to EP, is immobilized on a flexible screen-printed electrode modified with AuNPs@CeMOF, enabling highly selective binding to the target biomolecule. Under optimized operational conditions, the peak currents using voltammetric detection measured at voltage of 83 mV (vs. Ag/AgCl) for epinephrine exhibit a linear increase within concentration in the range 1 pM–10 nM. Following this detection strategy, a boasted limit of detection of 0.3 pM was achieved, surpassing the sensitivity of most reported methods. The developed biosensor showcased exceptional performance in detection of EP in spiked serum sample, with remarkable recovery range of 95.8–113% and precision reflected by low relative standard deviation (RSD) ranging from 2.23 to 6.19%. These results indicate the potential utility of this biosensor as a valuable clinical diagnostic tool. Furthermore, in vitro experiments were carried out using the presented biosensor to monitor the release of epinephrine from PC12 cells upon extracellular stimulation with K+ ions.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data will be made available on request.
Change history
24 September 2023
Missing Supplementary Information has been added.
References
Degering M, Linz R, Puhlmann LMC et al (2023) Revisiting the stress recovery hypothesis: differential associations of cortisol stress reactivity and recovery after acute psychosocial stress with markers of long-term stress and health. Brain Behavior & Immunity Health 28:100598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbih.2023.100598
Liao C-P, Chiang Y-C, Tam WH et al (2022) Neurophysiological basis of stress-induced aversive memory in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Curr Biol 32:5309-5322.e6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2022.11.012
Prasad BB, Prasad A, Tiwari MP, Madhuri R (2013) Multiwalled carbon nanotubes bearing ‘terminal monomeric unit’ for the fabrication of epinephrine imprinted polymer-based electrochemical sensor. Biosens Bioelectron 45:114–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2013.01.042
Umek N (2022) The effects of biologically important divalent and trivalent metal cations on the cyclization step of dopamine autoxidation reaction: a quantum chemical study. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 15:104153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2022.104153
Bacchella C, Dell’Acqua S, Nicolis S et al (2022) The reactivity of copper complexes with neuronal peptides promoted by catecholamines and its impact on neurodegeneration. Coordination Chem Rev 471:214756. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2022.214756
Pandey SN, Rangra NK, Singh S et al (2021) Evolving role of natural products from traditional medicinal herbs in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. ACS Chem Neurosci 12:2718–2728. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.1c00206
Xie W, Yin Y, Gu R et al (2022) Label-free and highly selective MOFs-based dopamine detection in urine of Parkinson’s patients. Chem Engineering J 443:136371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.136371
Savransky A, Chiappelli J, Du X et al (2021) Association of working memory and elevated overnight urinary norepinephrine in patients with schizophrenia. J Psychiatr Res 137:89–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2021.02.005
Gubbi S, Nazari MA, Taieb D et al (2020) Catecholamine physiology and its implications in patients with COVID-19. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 8:978–986. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30342-9
Derakhshan M, Ansarian HR, Ghomshei M (2020) Possible effect of epinephrine in minimizing COVID-19 severity: a review. J Int Med Res 48:0300060520958594. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300060520958594
Ray P, Steckl AJ (2019) Label-free optical detection of multiple biomarkers in sweat, plasma, urine, and saliva. ACS Sens 4:1346–1357. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.9b00301
Helmschrodt C, Becker S, Perl S et al (2020) Development of a fast liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for simultaneous quantification of neurotransmitters in murine microdialysate. Anal Bioanal Chem 412:7777–7787. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-02906-z
Vollmer RR, Balcita JJ, Sved AF, Edwards DJ (1997) Adrenal epinephrine and norepinephrine release to hypoglycemia measured by microdialysis in conscious rats. Am J Physiol 273:R1758-1763. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.1997.273.5.R1758
Esteve C, Tolner EA, Shyti R et al (2016) Mass spectrometry imaging of amino neurotransmitters: a comparison of derivatization methods and application in mouse brain tissue. Metabolomics 12:30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-015-0926-0
Zhao Y, Zhao S, Huang J, Ye F (2011) Quantum dot-enhanced chemiluminescence detection for simultaneous determination of dopamine and epinephrine by capillary electrophoresis. Talanta 85:2650–2654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2011.08.032
Kongkiatpaiboon S, Duangdee N, Chewchinda S et al (2019) Development and validation of stability indicating HPLC method for determination of adrenaline tartrate. Journal of King Saud University - Science 31:48–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2017.05.016
Saraf N, Bosak A, Willenberg A et al (2017) Colorimetric detection of epinephrine using an optimized paper-based aptasensor. RSC Adv 7:49133–49143. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA10272K
Zaytsev VD, Furletov AA, Apyari VV et al (2020) Label-free silver triangular nanoplates for spectrophotometric determination of catecholamines and their metabolites. Mikrochim Acta 187:610. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04576-1
An J, Shi Y, Fang J et al (2021) Multichannel ratiometric fluorescence sensor arrays for rapid visual monitoring of epinephrine, norepinephrine, and levodopa. Chem Engineering J 425:130595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.130595
Fredj Z, Sawan M (2023) Advanced nanomaterials-based electrochemical biosensors for catecholamines detection: challenges and trends. Biosensors 13:211. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13020211
Bahri M, Baraket A, Zine N et al (2020) Capacitance electrochemical biosensor based on silicon nitride transducer for TNF-α cytokine detection in artificial human saliva: heart failure (HF). Talanta 209:120501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120501
Qian L, Durairaj S, Prins S, Chen A (2021) Nanomaterial-based electrochemical sensors and biosensors for the detection of pharmaceutical compounds. Biosens Bioelectron 175:112836. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112836
Lv M, Zhou W, Tavakoli H et al (2021) Aptamer-functionalized metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) for biosensing. Biosens Bioelectron 176:112947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112947
Palakollu VN, Chen D, Tang J-N et al (2022) Recent advancements in metal-organic frameworks composites based electrochemical (bio)sensors. Mikrochim Acta 189:161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05238-0
Du Y, Wang B, Kang K et al (2022) Signal synergistic amplification strategy based on functionalized CeMOFs for highly sensitive electrochemical detection of phenolic isomers. Microchem J 177:107285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2022.107285
Fu X, He J, Zhang C et al (2019) Trimetallic signal amplification aptasensor for TSP-1 detection based on Ce-MOF@Au and AuPtRu nanocomposites. Biosens Bioelectron 132:302–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.02.054
Yoo H, Jo H, Oh SS (2020) Detection and beyond: challenges and advances in aptamer-based biosensors. Mater Adv 1:2663–2687. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0MA00639D
Zhao C, Cheung KM, Huang I-W et al (2021) Implantable aptamer-field-effect transistor neuroprobes for in vivo neurotransmitter monitoring. Sci Adv 7:eabj7422. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abj7422
Geng X, Zhang M, Long H et al (2021) A reusable neurotransmitter aptasensor for the sensitive detection of serotonin. Anal Chim Acta 1145:124–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.11.010
Gordon CKL, Wu D, Pusuluri A et al (2019) Click-particle display for base-modified aptamer discovery. ACS Chem Biol 14:2652–2662. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.9b00587
Fredj Z, Azzouzi S, Turner APF et al (2017) Neutravidin biosensor for direct capture of dual-functional biotin-molecular beacon-AuNP probe for sensitive voltammetric detection of microRNA. Sens Actuators, B Chem 248:77–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.03.160
Chen J, Chen Y, Li S et al (2022) In-situ growth of cerium-based metal organic framework on multi-walled carbon nanotubes for electrochemical detection of gallic acid. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochem Engineering Aspects 650:129318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.129318
Dong P, Zhu L, Huang J et al (2019) Electrocatalysis of cerium metal-organic frameworks for ratiometric electrochemical detection of telomerase activity. Biosens Bioelectron 138:111313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.05.018
Suriyaprakash J, Gupta N, Wu L, Shan L (2022) Engineering of all solution/substrate processable biosensors for the detection of epinephrine as low as pM with rapid readout. Chem Engineering J 436:135254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.135254
Zhan S, Xu C, Chen J et al (2023) A novel epinephrine biosensor based on gold nanoparticles coordinated polydopamine-functionalized acupuncture needle microelectrode. Electrochim Acta 437:141468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2022.141468
Ramu AG, Umar A, Ibrahim AA et al (2021) Synthesis of porous 2D layered nickel oxide-reduced graphene oxide (NiO-rGO) hybrid composite for the efficient electrochemical detection of epinephrine in biological fluid. Environ Res 200:111366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111366
Yang X, Zhao P, Xie Z et al (2021) Selective determination of epinephrine using electrochemical sensor based on ordered mesoporous carbon / nickel oxide nanocomposite. Talanta 233:122545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122545
Fallah F, Shishehbore MR, Sheibani A (2023) Fabrication of a novel sensor based on Cu quantum dot and SH-SiO2 nanoparticles supported on copper-based metal organic framework (Cu QD-SH-SiO2@Cu-MOF) and its application for the simultaneous determination of norepinephrine, piroxicam and epinephrine. Talanta 252:123776. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123776
Banu R, Kumara Swamy BE, Jayaprakash GK, Sharma SC (2022) Simultaneous resolution of serotonin and epinephrine at poly (Victoria blue B) amplified carbon paste electrode: a voltammetric study with density functional theory evidences. Inorganic Chem Comm 144:109627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2022.109627
Kumar S, Awasthi A, Sharma MD et al (2022) Functionalized multiwall carbon nanotube-molybdenum disulphide nanocomposite based electrochemical ultrasensitive detection of neurotransmitter epinephrine. Materials Chem Physics 290:126656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2022.126656
BanuKumara SwamyEbenso RBEE (2022) Voltammetric analysis of serotonin and epinephrine in the presence of guanine and adenine at Bismarck brown R amplified pencil graphite electrode. Inorganic Chem Comm 144:109868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2022.109868
Baluta S, Meloni F, Halicka K et al (2022) Differential pulse voltammetry and chronoamperometry as analytical tools for epinephrine detection using a tyrosinase-based electrochemical biosensor. RSC Adv 12:25342–25353. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2RA04045J
Alizadeh N, Ghasemi S, Salimi A et al (2020) CuO nanorods as a laccase mimicking enzyme for highly sensitive colorimetric and electrochemical dual biosensor: application in living cell epinephrine analysis. Colloids Surf, B 195:111228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2020.111228
Funding
The authors would like to acknowledge funding support from Westlake University, grant number 10318A992001; Leading Innovative and Entrepreneur Team Introduction Program of Zhejiang, grant number 2020R01005; and Research Center for Industries of the Future, Westlake University, grant number 210230006022219/001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• A novel sensing platform design based on cerium metal–organic framework (CeMOF) coupled with AuNPs and specific aptamer for electrochemical sensing of epinephrine (EP).
• High specificity for EP when compared to common interfering species.
• Enhanced response for the epinephrine within an interesting limit of detection down to 0.3 pM.
• Accurate quantification of epinephrine levels in human serum samples and within living cells.
• Good recovery levels ranged between 95.8 and 113% in diluted healthy human serum.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1
(DOCX 826 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fredj, Z., Wang, P., Ullah, F. et al. A nanoplatform-based aptasensor to electrochemically detect epinephrine produced by living cells. Microchim Acta 190, 343 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05902-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05902-z