Abstract
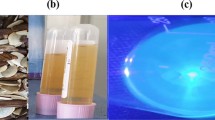
Nitrogen-doped carbon dots (NCDs) have been constructed in which coal washing wastewater is used as carbon precursor, tryptophan is added for nitrogen doping and surface functional together with polyethylene glycol. The nitrogen doping and surface functional with electron rich groups resulted in excellent fluorescent properties regarding stability, reversibility, printability with high quantum yield which not only enable the NCDs as fluorescent ink for advanced message encryption, but also realize specific on-off-on fluorescent sensing of Hg2+ and GSH as solution, hydrogel and filter paper sensors. The NCDs had a linear range of 0.01-100 μM and a detection limit of 6.27 nM (RSD 0.33%) for Hg2+ and the NCDs@Hg2+ had a linear range of 0.01–60 μM and a detection limit of 3.53 nM (RSD 1.53%) for GSH in sensing studies with aqueous solutions. In addition, with the low cytotoxicity and good biocompatibility NCDs have been successfully used for imaging Hg2+ and GSH in living MG-63 cells. The presented NCDs recycle waste coal washing water into worthwhile material which can be implemented as promising anti-counterfeiting and message encryption candidates as well as effective Hg2+ and GSH sensing, tracking and removing tools in complicated environmental and biological systems.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li YJ, Xia WC, Peng YL, Xie GY (2020) A novel coal tar-based collector for effective flotation cleaning of low rank coal. J Clean Prod 273:123172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123172
Wang HN, Yang WQ, Li DL, Zhang CQ, Yan XK, Wang LJ, Zhang HJ (2020) Enhancement of coal flotation using impact flow conditioning pulp. J Clean Prod 262:122124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122124
Zhang ZX, Yan GH, Zhu GQ, Zhao PF, Ma ZJ, Zhang B (2020) Microwave pretreatment improves the high-gradient magnetic-separation desulfurization of pulverized coal before combustion. Fuel 274:117826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.117826
Ütnü YE, Okutan H, Aydın AA (2020) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) content of malkara lignite and its ex-situ underground coal gasification (UCG) char residues. Fuel 275:117949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.117949
Vaseem H, Singh VK, Singh MP (2017) Heavy metal pollution due to coal washery effluent and its decontamination using a macrofungus, pleurotus ostreatus. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 145:42–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.07.001
Aliyu A, Kariim I, Abdulkareem SA (2017) Effects of aspect ratio of multi-walled carbon nanotubes on coal washery waste water treatment. J Environ Manage 202:84–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.07.011
Ponnudurai V, Rajarathinam R, Muthuvelu KS, Velmurugan S, Nalajala RK, Arumugam L (2022) Investigation on the utilization of coal washery rejects by different microbial sources for biogenic methane production. Chemosphere 287:132165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132165
Zulfajri M, Abdelhamid HN, Sudewi S, Dayalan S, Rasool A, Habib A, Huang GG (2020) Plant part-derived carbon dots for biosensing. Biosensors 10(6):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10060068
Gao PL, Xie ZG, Zheng M (2022) The synthesis, modification, photoluminescence and sensing applications of carbon cots. Chin Chem Lett 33:1659–1672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2021.09.085
Wu YFS, Fang XY, Shi JQ, Yao WJ, Wu W (2021) Blue-to-green manipulation of carbon dots from fluorescence to ultralong room-temperature phosphorescence for high-level anti-counterfeiting. Chin Chem Lett 32:3907–3910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2021.04.040
Yang Z, Xu TT, Zhang X, Li H, Jia XD, Zhao SS, Yang ZW, Liu XR (2022) Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots as fluorescent nanosensor for selective determination and cellular imaging of ClO-. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 271:120941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2022.120941
Abdelhamid HN, Talib A, Wu HF (2017) One pot synthesis of gold-carbon dots nanocomposite and its application for cytosensing of metals for cancer cells. Talanta 166:357–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.11.030
Zou GY, Chen S, Liu NZ, Yu YL (2022) A ratiometric fluorescent probe based on carbon dots assembly for intracellular lysosomal polarity imaging with wide range response. Chin Chem Lett 33:778–782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2021.08.076
Zhang L, Wang ZH, Wang HP, Dong WJ, Liu Y, Hu Q, Shuang SM, Dong C, Gong XJ (2021) Nitrogen-doped carbon dots for wash-free imaging of nucleolus orientation. Microchim Acta 188:183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04837-7
Zhou WY, Cao GZ, Yuan MX, Zhong SL, Wang YD, Liu XR, Cao D, Peng WW, Liu J, Wang GG, Dang ZM, Li B (2023) Core-shell engineering of conductive fillers toward enhanced dielectric properties: a universal polarization mechanism in polymer conductor composites. Adv Mater 35(2):2207829. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202207829
Chu SY, Wang HQ, Du YX, Yang F, Yang L, Jiang CL (2020) Portable smartphone platform integrated with a nanoprobe-based fluorescent paper strip: visual monitoring of glutathione in human serum for health prognosis. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 8:8175–8183. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c00690
Guo JZ, Lu YS, Xie AQ, Li G, Liang ZB, Wang CF, Yang XN, Chen S (2022) Yellow-emissive carbon dots with high solid-state photoluminescence. Adv Funct Mater 32:2110393. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202110393
Guo JZ, Li H, Ling LT, Li G, Cheng R, Lu X, Xie AQ, Li Q, Wang CF, Chen S (2020) Green synthesis of carbon dots toward anti-counterfeiting. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8:1566–1572. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b06267
Si MY, Zhang J, He YY, Yang ZQ, Yan X, Liu MR, Zhuo SN, Wang S, Min XB, Gao CJ, Chai LY, Shi Y (2018) Synchronous and rapid preparation of lignin nanoparticles and carbon quantum dots from natural lignocellulose. Green Chem 20:3414–3419. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8GC00744F
Li XL, Zheng JZ, Liu WJ, Qiao QL, Chen J, Zhou W, Xu ZC (2020) Long-term super-resolution imaging of mitochondrial dynamics. Chin Chem Lett 31:2937–2940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2020.05.043
Cai TT, Liu B, Pang EN, Ren WJ, Li SJ, Hu SL (2021) A review on the preparation and applications of coal-based fluorescent carbon dots. Carbon 176:650. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2021.02.027
Yao T, Zhou WY, Cao GZ, Peng WW, Liu J, Dong XB, Chen XL, Zhang YQ, Chen YR, Yuan MX (2023) Engineering of core@ double-shell structured Zn@ZnO@PS particles in poly (vinylidene fluoride) composites towards significantly enhanced dielectric performances. J Appl Polym Sci 140:e53772. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.53772
Li MY, Yu C, Hu C, Yang WB, Zhao CT, Wang S, Zhang MD, Zhao JZ, Wang XN, Qiu JS (2017) Solvothermal conversion of coal into nitrogen-doped carbon dots with singlet oxygen generation and high quantum yield. Chem Eng J 320:570–575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.03.090
Yu XW, Liu XY, Jiang YW, Li YH, Gao G, Zhu YX, Lin FM, Wu GF (2022) Rose bengal-derived ultrabright sulfur-doped carbon dots for fast discrimination between live and dead cells. Anal Chem 94:4243–4251. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.1c04658
Wu SH, Zhou RH, Chen HJ, Zhang JY, Wu P (2020) Highly efficient oxygen photosensitization of carbon dots: the role of nitrogen doping. Nanoscale 12:5543–5553. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9NR10986B
Wu YP, Liu X, Wu QH, Yi J, Zhang GL (2017) Differentiation and determination of metal ions using fluorescent sensor array based on carbon nanodots. Sens Actuators B Chem 246:680–685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.02.132
Gu TT, Zou W, Gong FC, Xia JY, Chen C, Chen XJ (2018) A specific nanoprobe for cysteine based on nitrogen-rich fluorescent quantum dots combined with Cu2+. Biosens Bioelectron 100:79–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.08.031
Fu LN, Wang J, Chen N, Ma QQ, Lu DQ, Yuan Q (2020) Enhancement of long-lived luminescence in nanophosphors by surface defect passivation. Chem Commum 56:6660–6663. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CC02658A
Abdelhamid HN, Lin YC, Wu HF (2017) Thymine chitosan nanomagnets for specific preconcentration of mercury (II) prior to analysis using SELDI-MS. Microchim Acta 184:1517–1527. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2125-3
Hussain M, Maile N, Tahir K, Ghani AA, Kim B, Jang J, Lee DX (2022) Flexible thiourea-based covalent organic frameworks for ultrahigh mercury removal from aqueous solutions. Chem Eng J 446:137410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.137410.
Pang LF, Wu H, Fu MJ, Guo XF, Wang H (2019) Red emissive boron and nitrogen co-doped “on-off-on” carbon dots for detecting and imaging of mercury(II) and biothiols. Microchim Acta 186:708. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3852-4
Yin CX, Xiong KM, Huo FJ, Salamanca JC, Strongin RM (2017) Fluorescent probes with multiple binding sites for the discrimination of Cys, Hcy, and GSH. Angew Chem Int Ed 56:13188–13198. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201704084
Fu W, Yan XC, Guo ZQ, Zhang JJ, Zhang HY, Tian H, Zhu WH (2019) Rational design of near-infrared AIE-active probes: in situ mapping of amyloid-β plaques with ultra-sensitivity and high-fidelity. J Am Chem Soc 141:3171–3177. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.8b12820
Liang XC, Chen SQ, Gao JM, Zhang HY, Wang Y, Wang JH, Feng L (2018) A versatile fluorimetric chemosensor for mercury (II) assay based on carbon nanodots. Sens Actuators B Chem 265:293–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.01.182
Yang H, Su XK, Cai L, Sun ZC, Lin YC, Yu J, Hao LK, Liu C (2022) Glutathione assisting the waste tobacco leaf to synthesize versatile biomass-based carbon dots for simultaneous detection and efficient removal of mercury ions. J Environ Chem Eng 10:108718. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.108718
Acknowledgements
Authors acknowledge Professor Jianli Li and Dr. Mengyao She of Northwest University for their help. This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 22179107, U1903133), Shaanxi Provincial Natural Science Fund Project (No. 2018JQ2061), the Outstanding Youth Science Fund of Xi’an University of Science and Technology (No. 2018YQ3-14).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 597 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Yan, H., Li, H. et al. Carbon dots as specific fluorescent sensors for Hg2+ and glutathione imaging. Microchim Acta 190, 224 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05805-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05805-z