Abstract
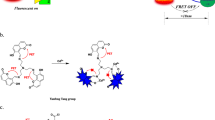
The catalytic hairpin-rigidified Y-shaped DNA through layer-by-layer assembly has been fixed on the surface of copper sulfide nanoparticles for the detection of survivin mRNA. The distance between the CHA probes fixed on the Y-shaped DNA is significantly shortened. The results show that the fluorescence of this nanomachine reached the maximum value in 50 min (excitation wavelength at 488 nm and emission wavelength 526 nm), and its reaction rate is more than 5-fold faster than that of the free-CHA control system. In addition, the nanomachine showed high sensitivity (LOD of 3.5 pM) and high specificity for the survivin mRNA detection. Given its fast response time and excellent detection performance, we envision that the catalytic hairpin-rigidified Y-shaped DNA-functionalized nanomachine will offer potential applications in disease diagnostics and clinical applications.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Qing Z, Xu J, Hu J, Zheng J, He L, Zou Z, Yang S, Tan W, Yang R (2019) In situ amplification-based imaging of RNA in living cells. Angew Chem Int Ed 131:11698–11709. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201812449
Jung C, Allen PB, Ellington AD (2016) A stochastic DNA-functionalized nanomachine that traverses a microparticle surface. Nat Nanotechnol 11:157–163. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2015.246
Li D, Wu Y, Gan C, Yuan R, Xiang Y (2018) Bio-cleavable nanoprobes for target-triggered catalytic hairpin assembly amplification detection of microRNAs in live cancer cells. Nanoscale 10:17623–17628. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NR05229H
Wu Z, Fan H, Satyavolu NSR, Wang W, Lake R, Jiang J, Lu Y (2017) Imaging endogenous metal ions in living cells using a DNAzyme-catalytic hairpin assembly probe. Angew Chem Int Ed 129:8847–8851. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201703540
Liu J, Zhang Y, Xie H, Zhao L, Zheng L, Ye H (2019) Applications of catalytic hairpin assembly reaction in biosensing. Small 15:1902989. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201902989
Wang S, Zhang F, Chen C, Cai C (2019) Ultrasensitive graphene quantum dots-based catalytic hairpin assembly amplification resonance light scattering assay for p53 mutant DNA detection. Sens Actuators B Chem 291:42–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.04.015
Su F, Yang C, Yan X (2017) Intracellular messenger RNA triggered catalytic hairpin assembly for fluorescence imaging guided photothermal therapy. Anal Chem 89:7277–7281. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b01348
Liu C, Chen C, Li S, Dong H, Dai W, Xu T, Liu Y, Yang F, Zhang X (2018) Target-triggered catalytic hairpin assembly-induced core-satellite nanostructures for high-sensitive “off-to-on” SRES detection of intracellular microRNA. Anal Chem 90:10591–10599. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b02819
Chen J, Wu Y, Fu C, Cao H, Tan X, Shi W, Wu Z (2019) Ratiometric SERS biosensor for sensitive and reproducible detection of microRNA based on mismatched catalytic hairpin assembly. Biosens Bioelectron 143:111619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111619
Cao X, Sun Y, Mao Y, Ran M, Liu Y, Lu D, Bi C (2021) Rapid and sensitive detection of dual lung cancer-associated miRNA biomarkers by a novel SERS-LFA strip coupling with catalytic hairpin assembly signal amplification. J Mater Chem C 9:3661–3671. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0TC05737A
Zhang Y, Yan Y, Chen W, Cheng W, Li S, Ding X, Li D, Wang H, Ju H, Ding S (2015) A simple electrochemical biosensor for highly sensitive and specific detection of microRNA based on mismatched catalytic hairpin assembly. Biosens Bioelectron 68:343–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.01.026
Qing M, Xie S, Cai W, Tang D, Tang Y, Zhang J, Yuan R (2018) Click chemistry reaction-triggered 3D DNA walking machine for sensitive electrochemical detection of copper ion. Anal Chem 90:11439–11445. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b02555
Park C, Park H, Lee HJ, Lee HS, Park KH, Choi CH, Na S (2019) Double amplified colorimetric detection of DNA using gold nanoparticles, enzymes and a catalytic hairpin assembly. Microchim Acta 186:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3154-2
Cheng W, Zhang Y, Yu H, Diao W, Mo F, Wen B, Cheng W, Yan Y (2018) An enzyme-free colorimetric biosensing strategy for ultrasensitive and specific detection of microRNA based on mismatched stacking circuits. Sens Actuators B Chem 255:3298–3304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.09.157
Mudiyanselage APKKK, Yu Q, Leon-Duque MA, Zhao B, Wu R, You M (2018) Genetically encoded catalytic hairpin assembly for sensitive RNA imaging in live cells. J Am Chem Soc 140:8739–8745. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.8b03956
Liu Y, Shen T, Li J, Gong H, Chen C, Chen X, Cai C (2017) Ratiometric fluorescence sensor for the microRNA determination by catalyzed hairpin assembly. ACS Sens 2:1430–1434. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.7b00313
Zhang X, Yin Y, Du S, Kong L, Chai Y, Li Z, Yuan R (2021) Dual 3D DNA nanomachine-mediated catalytic hairpin assembly for ultrasensitive detection of microRNA. Anal Chem 93:13952–13959. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.1c03215
Cui W, Hu G, Lv E, Li C, Wang Z, Li Q, Qian Z, Wang J, Xu S, Wang R (2022) A label-free and enzyme-free fluorescent aptasensor for amplified detection of kanamycin in milk sample based on target-triggered catalytic hairpin assembly. Food Control 133:108654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.108654
Luan Q, Gan N, Cao Y, Li T (2017) Mimicking an enzyme-based colorimetric aptasensor for antibiotic residue detection in milk combining magnetic loop-DNA probes and CHA-assisted target recycling amplification. J Agric Food Chem 65:5731–5740. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b02139
Wu Y, Fu C, Xiang J, Cao Y, Deng Y, Xu R, Zhang H, Shi W (2020) “Signal-on” SERS sensing platform for highly sensitive and selective Pb2+ detection based on catalytic hairpin assembly. Anal Chim Acta 1127:106–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.06.038
Li X, Xie J, Jiang B, Yuan R, Xiang Y (2017) Metallo-toehold-activated catalytic hairpin assembly formation of three-way DNAzyme junctions for amplified fluorescent detection of Hg2+. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:5733–5738. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b13717
Tang Y, Lin Y, Yang X, Wang Z, Le XC, Li F (2015) Universal strategy to engineer catalytic DNA hairpin assemblies for protein analysis. Anal Chem 87:8063–8066. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b02504
Yang L, Wu Q, Chen Y, Liu X, Wang F, Zhou X (2018) Amplified microRNA detection and intracellular imaging based on an autonomous and catalytic assembly of DNAzyme. ACS Sens 4:110–117. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.8b01000
Wan Y, Li G, Zou L, Wang H, Wang Q, Tan K, Liu X, Wang F (2021) A deoxyribozyme-initiated self-catalytic DNA machine for amplified live-cell imaging of microRNA. Anal Chem 93:11052–11059. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.1c02596
Yang P, Chen H, Zhu Q, Chen Z, Yang Z, Yuan R, Li Y, Liang W (2022) A target-initiated autocatalytic 3D DNA nanomachine for high-efficiency amplified detection of microRNA. Talanta 240:123219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123219
Bao T, Fu R, Jiang Y, Wen W, Zhang X, Wang S (2021) Metal-mediated polydopamine nanoparticles-DNA nanomachine coupling electrochemical conversion of metal-organic frameworks for ultrasensitive microRNA sensing. Anal Chem 93:13475–13484. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.1c02125
Zou R, Wang S, Chen C, Chen X, Gong H, Cai C (2021) An enzyme-free DNA circuit-assisted MoS2 nanosheet enhanced fluorescence assay for label-free DNA detection. Talanta 222:121505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121505
Zhang Z, Xiang X, Hu Y, Deng Y, Li L, Zhao W, Wu T (2021) A sensitive biomolecules detection device with catalytic hairpin assembly and cationic conjugated polymer-assisted dual signal amplification strategy. Talanta 223:121716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121716
Feng Q, Zhang Y, Zhang W, Hao Y, Wang Y, Zhang H, Hou L, Zhang Z (2017) Programmed near-infrared light-responsive drug delivery system for combined magnetic tumor-targeting magnetic resonance imaging and chemo-phototherapy. Acta Biomater 49:402–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2016.11.035
Huo M, Li S, Zhang P, Feng Y, Liu Y, Wu N, Ju H, Ding L (2019) Nanoamplicon comparator for live-cell microRNA imaging. Anal Chem 91:3374–3381. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b04661
Xiang MH, Li N, Liu JW, Yu RQ, Jiang JH (2020) A tumour mRNA-triggered nanoassembly for enhanced fluorescence imaging-guided photodynamic therapy. Nanoscale 12:8727–8731. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NR00941E
Zhao S, Zheng P, Wu Z, Jiang J (2022) DNA-templated bioorthogonal reactions via catalytic hairpin assembly for precise RNA imaging in live cells. Anal Chem 94:2693–2698. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.1c05509
Wang J, Huang J, Quan K, Li J, Wu Y, Wei Q, Yang X, Wang K (2018) Hairpin-fuelled catalytic nanobeacons for amplified microRNA imaging in live cells. Chem Commun 54:10336–10339. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8CC06298F
Zheng J, Li N, Li C, Wang X, Liu Y, Mao G, Ji X, He Z (2018) A nonenzymatic DNA nanomachine for biomolecular detection by target recycling of hairpin DNA cascade amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 107:40–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.01.054
Qing Z, Hu J, Xu J, Zou Z, Lei Y, Qing T, Yang R (2020) An intramolecular catalytic hairpin assembly on a DNA tetrahedron for mRNA imaging in living cells: improving reaction kinetics and signal stability. Chem Sci 11:1985–1990. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9SC04916A
Duan Z, Li Z, Dai J, He H, Xiao D (2017) Nucleotide base analog pyrrolo-deoxycytidine as fluorescent probe signal for enzyme-free and signal amplified nucleic acids detection. Talanta. 164:34–38. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b02555
Wei Q, Huang J, Li J, Wang J, Yang X, Liu J, Wang K (2018) A DNA nanowire based localized catalytic hairpin assembly reaction for microRNA imaging in live cells. Chem. Sci. 9:7802–7808. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SC02943A
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21775132), the National Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (No. 2022JJ30557), and Hunan 2011 Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemical Engineering & Technology with Environmental Benignity and Effective Resource Utilization, the project of innovation team of the Ministry of Education (IRT_17R90).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, S., Zou, R., Chen, F. et al. Engineering of catalytic hairpin-rigidified Y-shaped DNA-functionalized nanomachine to rapidly detect mRNA. Microchim Acta 190, 210 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05708-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05708-z