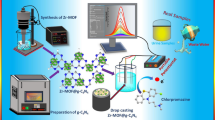
Abstract
Fentanyl is a powerful synthetic opioid used to treat severe pain. New administration routes toward its illegal consumption for recreational purposes pose a growing threat to public health, either due to misuse or abuse of this substance. As a result, the rapid qualitative and quantitative determination of fentanyl in biofluids is of great interest. A novel enzymatic biosensor based on adsorptive-stripping cyclic voltammetry is proposed as a cost-effective, reliable, and efficient device for fentanyl determination in urine samples. Disposable screen-printed carbon electrodes modified with multi-walled carbon nanotubes and cytochrome c were used to develop the testing platform. The electrochemical behavior of fentanyl exhibited a well-defined anodic wave around 0.66 V vs. pseudo reference electrode. The experimental conditions were optimized to obtain the best analytical response, and linear regression analysis of increasing concentration standards was applied to estimate the performance parameters. The results suggest a simple method with a wide linearity range, high sensitivity, low limits of detection (0.086 μg/mL) and quantification, and satisfactory precision (2.9% RSD). The feasibility and applicability of the voltammetric approach were assessed by fentanyl-spiked urine samples by standard additions calibration curves in two levels of enrichment with an accuracy of 92% and 100%.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others

References
European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA), 2001 Annual report on the state of the drugs problem in the European Union, (2001) 1–6. https://www.emcdda.europa.eu/system/files/publications/201/sel2001_3en_69551.pdf. Accessed 1 May 2022
United Nations office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), World Drug Report 2021, 2021. www.unodc.org/unodc/en/data-and-analysis/wdr2021.html. Accessed 3 May 2022
Friesen EL, Kurdyak PA, Gomes T, Kolla G, Leece P, Zhu L, Toombs E, O’Neill B, Stall NM, Jüni P, Mushquash CJ, Mah L (2021) The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on opioid-related harm in Ontario, https://doi.org/10.47326/ocsat.2021.02.42.1.0
Pardo B, Reuter P (2020) Enforcement strategies for fentanyl and other synthetic opioids. Foreign Policy and Global Economy & Development Programs. Brookings
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), (2022). https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nvss/vsrr/drug-overdose-data.htm (accessed May 3, 2022).
Manirakiza A, Irakoze L, Manirakiza S, Bizimana P (2020) Efficacy and safety of fentanyl compared with morphine among adult patients with cancer: a meta-analysis, East African. Heal. Res J. 4:8–16. https://doi.org/10.24248/eahrj.v4i1.617
Wolff RF, Aune D, Truyers C, Hernandez AV, Misso K, Riemsma R, Kleijnen J (2012) Systematic review of efficacy and safety of buprenorphine versus fentanyl or morphine in patients with chronic moderate to severe pain. Curr Med Res Opin 28:833–845. https://doi.org/10.1185/03007995.2012.678938
National Institute on Drug Abuse, Fentanyl DrugFacts, (2021) 1–7. https://nida.nih.gov/publications/drugfacts/fentanyl. Accessed 1 May 2022
United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), Global smart update: fentanyl and its analogues - 50 years on, (2017) 3–12. https://www.unodc.org/documents/scientific/Global_SMART_Update_17_web.pdf. Accessed 4 May 2022
United Nations office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), Global smart update: understanding the global opioid crisis, 21 (2019). https://www.unodc.org/documents/scientific/Global_SMART_21_web_new.pdf. Accessed 4 May 2022
United Nations office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) (2018) Recommended methods for the identification and analysis of fentanyl and its analogues in biological specimens, https://doi.org/10.18356/aca7aca5-en
Strano-Rossi S, Álvarez I, Tabernero MJ, Cabarcos P, Fernández P, Bermejo AM (2011) Determination of fentanyl, metabolite and analogs in urine by GC/MS. J Appl Toxicol 31:649–654. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.1613
Mochizuki A, Nakazawa H, Adachi N, Takekawa K, Shojo H (2018) Identification and quantification of mepirapim and acetyl fentanyl in authentic human whole blood and urine samples by GC–MS/MS and LC–MS/MS. Forensic Toxicol 36:81–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-017-0384-7
Cummings OT, Enders JR, McIntire GL, Backer R, Poklis A (2016) Fentanyl-norfentanyl concentrations during transdermal patch application: LC-MS-MS urine analysis. J Anal Toxicol 40:595–600. https://doi.org/10.1093/jat/bkw067
Palamar JJ, Salomone A, Barratt MJ (2020) Drug checking to detect fentanyl and new psychoactive substances. Curr Opin Psychiatry 33:301–305. https://doi.org/10.1097/YCO.0000000000000607
Vincenti F, Montesano C, Gobbi S, Sergi M, Curini R, Compagnone D (2021) Quantitative analysis of fentanyl, several analogues and metabolites in urine by parallel artificial liquid membrane extraction and liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry analysis. J Chromatogr Open 1:100006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcoa.2021.100006
Jornet-Martínez N, Moliner-Martínez Y, Molins-Legua C, Campíns-Falcó P (2017) Trends for the development of in situ analysis devices, Encycl. Anal Chem. 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470027318.a9593
Shaw L, Dennany L (2017) Applications of electrochemical sensors: forensic drug analysis. Curr Opin Electrochem 3:23–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coelec.2017.05.001
Anzar N, Suleman S, Parvez S, Narang J (2022) A review on Illicit drugs and biosensing advances for its rapid detection. Process Biochem 113:113–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2021.12.021
González-Hernández J, Alvarado-Gámez AL, Arroyo-Mora LE, Barquero-Quirós M (2021) Electrochemical determination of novel psychoactive substances by differential pulse voltammetry using a microcell for boron-doped diamond electrode and screen-printed electrodes based on carbon and platinum. J Electroanal Chem 882:114994. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2021.114994
González-Hernández J, Ott CE, Arcos-Martínez MJ, Colina Á, Heras A, Alvarado-Gámez AL, Urcuyo R, Arroyo-Mora LE (2022) Rapid determination of the ‘Legal Highs’ 4-MMC and 4-MEC by spectroelectrochemistry: simultaneous cyclic voltammetry and in situ surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy, Sensors . 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22010295
Cho IH, Kim DH, Park S (2020) Electrochemical biosensors: perspective on functional nanomaterials for on-site analysis. Biomater Res 24:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40824-019-0181-y
Viswanathan S, Rani C, Vijay Anand A, Ho JA (2009) Disposable electrochemical immunosensor for carcinoembryonic antigen using ferrocene liposomes and MWCNT screen-printed electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 24:1984–1989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2008.10.006
Choińska MK, Šestáková I, Hrdlička V, Skopalová J, Langmaier J, Maier V, Navrátil T (2022) Electroanalysis of fentanyl and its new analogs: a review, Biosensors. 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12010026
Naghian E, MarziKhosrowshahi E, Sohouli E, Ahmadi F, Rahimi-Nasrabadi M, Safarifard V (2020) A new electrochemical sensor for the detection of fentanyl lethal drug by a screen-printed carbon electrode modified with the open-ended channels of Zn(ii)-MOF, New. J. Chem. 44:9271–9277. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0nj01322f
MostafaNajafi E, Sohouli F. Mousavi (2020) An electrochemical sensor for fentanyl detection based on multi-walled carbon nanotubes as electrocatalyst and the electrooxidation mechanism. J Anal Chem. 75:1209–1217. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1061934820090130
Glasscott MW, Vannoy KJ, Iresh Fernando PUA, Kosgei GK, Moores LC, Dick JE (2020) Electrochemical sensors for the detection of fentanyl and its analogs: foundations and recent advances. TrAC - Trends Anal. Chem. 132:116037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2020.116037
Mishra RK, Goud KY, Li Z, Moonla C, Mohamed MA, Tehrani F, Teymourian H, Wang J (2020) Continuous opioid monitoring along with nerve agents on a wearable microneedle sensor array. J Am Chem Soc 142:5991–5995. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.0c01883
Ott CE, Cunha-Silva H, Kuberski SL, Cox JA, Arcos-Martínez MJ, Arroyo-Mora LE (2020) Electrochemical detection of fentanyl with screen-printed carbon electrodes using square-wave adsorptive stripping voltammetry for forensic applications. J Electroanal Chem 873:114425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2020.114425
Clark LC, Lyons C (1962) Electrode systems for continuous monitoring in cardiovascular surgery. Ann N Y Acad Sci 102:29–45. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1962.tb13623.x
Asturias-Arribas L, Alonso-Lomillo MA, Domínguez-Renedo O, Arcos-Martínez MJ (2011) CYP450 biosensors based on screen-printed carbon electrodes for the determination of cocaine. Anal Chim Acta 685:15–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2010.11.006
Asturias-Arribas L, Alonso-Lomillo MA, Domínguez-Renedo O, Arcos-Martínez MJ (2013) Electrochemical determination of cocaine using screen-printed cytochrome P450 2B4 based biosensors. Talanta 105:131–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2012.11.078
Ahmed SR, Chand R, Kumar S, Mittal N, Srinivasan S, Rajabzadeh AR (2020) Recent biosensing advances in the rapid detection of illicit drugs. TrAC - Trends Anal Chem 131:116006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2020.116006
Garrido C, Galluzzi L, Brunet M, Puig PE, Didelot C, Kroemer G (2006) Mechanisms of cytochrome c release from mitochondria. Cell Death Differ 13:1423–1433. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401950
Jain R, Kumar S, Chhabra R, Agarwal MC, Kumar R (2015) Analysis of the pH-dependent stability and millisecond folding kinetics of horse cytochrome c. Arch Biochem Biophys 585:52–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2015.09.011
Murgida DH, Hildebrandt P (2001) Proton-coupled electron transfer of cytochrome c. J Am Chem Soc 123:4062–4068. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja004165j
Aghamiri ZS, Mohsennia M, Rafiee-Pour HA (2018) Immobilization of cytochrome c and its application as electrochemical biosensors. Talanta 176:195–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.08.039
Eguílaz M, Venegas CJ, Gutiérrez A, Rivas GA, Bollo S (2016) Carbon nanotubes non-covalently functionalized with cytochrome c: a new bioanalytical platform for building bienzymatic biosensors. Microchem J 128:161–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2016.04.018
Shie JW, Umasankar Y, Chen SM (2008) Electroanalytical properties of cytochrome c by direct electrochemistry on multi-walled carbon nanotubes incorporated with DNA biocomposite film. Talanta 74:1659–1669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2007.10.034
Ba Hashwan SS, Fatin MF, Ruslinda AR, MdArshad MK, Hashim U, Ayub RM (2015) Functionalization of multi wall carbon nanotubes using nitric acid oxidation. Appl Mech Mater. 754–755:1156–1160. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.754-755.1156
Walt DR, Agayn VI (1994) The chemistry of enzyme and protein immobilization with glutaraldehyde, TrAC -. Trends Anal Chem 13:425–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-9936(94)85023-2
Imai M, Saio T, Kumeta H, Uchida T, Inagaki F, Ishimori K (2016) Investigation of the redox-dependent modulation of structure and dynamics in human cytochrome c. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 469:978–984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.12.079
Brenes JP, Arroyo-Mora LE, Barquero-Quirós M (2022) Enzymatic inhibitive determination of AB-Fubinaca and AB-Pinaca on screen printed carbon tetratiofulvalene electrodes modified with nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes. Sens Bio-Sensing Res 38:100515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbsr.2022.100515
Wester N, Mynttinen E, Etula J, Lilius T, Kalso E, Mikladal BF, Zhang Q, Jiang H, Sainio S, Nordlund D, Kauppinen EI, Laurila T, Koskinen J (2020) Single-walled carbon nanotube network electrodes for the detection of fentanyl citrate. ACS Appl Nano Mater 3:1203–1212. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.9b01951
Thurlkill RL, Cross DA, Scholtz JM, Pace CN (2005) pKa of fentanyl varies with temperature: implications for acid-base management during extremes of body temperature. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 19:759–762. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jvca.2004.11.039
Coletta M, Costa H, De Sanctis G, Neri F, Smulevich G, Turner DL, Santos H (1997) pH dependence of structural and functional properties of oxidized cytochrome c’’ from Methylophilus methylotrophus. J Biol Chem 272:24800–24804. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.40.24800
Segal MS, Beem E (2001) Effect of pH, ionic charge, and osmolality on cytochrome c-mediated caspase-3 activity. Am J Physiol - Cell Physiol 281:1196–1204. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.2001.281.4.c1196
Smith ET (2006) Examination of n = 2 reaction mechanisms that reproduce pH-dependent reduction potentials. Anal Chim Acta 572:259–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2006.05.025
Hegde RN, Hosamani RR, Nandibewoor ST (2009) Voltammetric oxidation and determination of cinnarizine at glassy carbon electrode modified with multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 72:259–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2009.04.013
Garrido JMPJ, Delerue-Matos C, Borges F, Macedo TRA, Oliveira-Brett AM (2004) Voltammetric oxidation of drugs of abuse III. Heroin and metabolites, Electroanalysis 16:1497–1502. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.200302975
Elgrishi N, Rountree KJ, McCarthy BD, Rountree ES, Eisenhart TT, Dempsey JL (2018) A practical beginner’s guide to cyclic voltammetry. J Chem Educ 95:197–206. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jchemed.7b00361
Smith HS (2009) Opioid metabolism. Mayo Clin Proc 84:613–624. https://doi.org/10.4065/84.7.613
Kanamori T, Togawa-Iwata Y, Segawa H, Yamamuro T, Kuwayama K, Tsujikawa K, Inoue H (2018) Use of hepatocytes isolated from a liver-humanized mouse for studies on the metabolism of drugs: application to the metabolism of fentanyl and acetylfentanyl. Forensic Toxicol 36:467–475. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-018-0425-x
Holmquist GL (2009) Opioid metabolism and effects of cytochrome P450. Pain Med 10:20–29. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1526-4637.2009.00596.x
Overholser BR, Foster DR (2011) Opioid pharmacokinetic drug-drug interactions, Am J Manag Care. 17 Suppl 1: S276—87. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/21999760. Accessed 10 May 2022
Nageswara Rao Tentu (2018) Validation of analytical methods, in: IntechOpen, Rijeka, p. Ch. 7. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.72087
Goodchild SA, Hubble LJ, Mishra RK, Li Z, Goud KY, Barfidokht A, Shah R, Bagot KS, McIntosh AJS, Wang J (2019) Ionic liquid-modified disposable electrochemical sensor strip for analysis of fentanyl. Anal Chem 91:3747–3753. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b00176
Barfidokht A, Mishra RK, Seenivasan R, Liu S, Hubble LJ, Wang J, Hall DA (2019) Wearable electrochemical glove-based sensor for rapid and on-site detection of fentanyl. Sensors Actuators, B Chem 296:126422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.04.053
Sohouli E, Keihan AH, Shahdost-fard F, Naghian E, Plonska-Brzezinska ME, Rahimi-Nasrabadi M, Ahmadi F (2020) A glassy carbon electrode modified with carbon nanoonions for electrochemical determination of fentanyl. Mater Sci Eng C 110:110684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2020.110684
Mishra RK, Krishnakumar A, Zareei A, Heredia-Rivera U, Rahimi R (2022) Electrochemical sensor for rapid detection of fentanyl using laser-induced porous carbon-electrodes. Microchim Acta. 189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05299-1
Valeriy Z, Tregubenko P (2019) Using over-the-counter and other prescription medications to potentiate opiates in the USA: literature review. Medical And Public Health Aspects Of OTC Medication Misuse. J Alcohol Drug Abus Subst Depend. 5:1–15. https://doi.org/10.24966/adsd-9594/100012
Fiorentin TR, Krotulski AJ, Martin DM, Browne T, Triplett J, Conti T, Logan BK (2019) Detection of cutting agents in drug-positive seized exhibits within the United States. J Forensic Sci 64:888–896. https://doi.org/10.1111/1556-4029.13968
Żubrycka A, Kwaśnica A, Haczkiewicz M, Sipa K, Rudnicki K, Skrzypek S, Poltorak L (2022) Illicit drugs street samples and their cutting agents. the result of the GC-MS based profiling define the guidelines for sensors development, Talanta. 237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122904
Dussy FE, Hangartner S, Hamberg C, Berchtold C, Scherer U, Schlotterbeck G, Wyler D, Briellmann TA (2016) An acute ocfentanil fatality: a case report with postmortem concentrations. J Anal Toxicol 40:761–766. https://doi.org/10.1093/jat/bkw096
Fort C, Curtis B, Nichols C, Niblo C (2016) Acetyl fentanyl toxicity: two case reports. J Anal Toxicol 40:754–757. https://doi.org/10.1093/jat/bkw068
Acknowledgements
J. González-Hernández would like to thank CELEQ and Sistema de Estudios de Posgrado de la Universidad de Costa Rica for supporting and financing the internship at Universidad de Burgos and J. García for digital images processing.
Funding
The work was funded by Vicerrectoría de Investigación de la Universidad de Costa Rica (project N° 804-C2-070) and CELEQ.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
González-Hernández, J., Moya-Alvarado, G., Alvarado-Gámez, A.L. et al. Electrochemical biosensor for quantitative determination of fentanyl based on immobilized cytochrome c on multi-walled carbon nanotubes modified screen-printed carbon electrodes. Microchim Acta 189, 483 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05578-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05578-x