Abstract
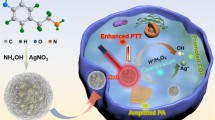
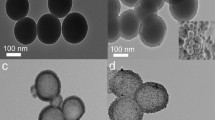
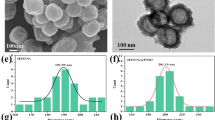
A novel near-infrared (NIR) light-triggered smart nanoplatform has been developed for cancer targeting and imaging-guided combined photothermal-chemo treatment. Notably, Ag2S has a dual function of photothermal therapy and fluorescence imaging, which greatly simplifies the structure of the system. It can emit fluorescence at 820 nm under an excitation wavelength of 560 nm. The phase-change molecule of 1-tetradecanol (TD) is introduced as a temperature-sensitive gatekeeper to provide the nanocarrier with controlled release capability of doxorubicin (DOX). The nanocarrier (HAg2S@mSiO2-TD/DOX) shows a high drug loading capacity of 26.3% and exhibits an apparent NIR-responsive DOX release property. Under NIR irradiation, the photothermal effect of HAg2S nanocores facilitated the release of DOX through the melting of TD. The cytotoxicity test shows that the nanocarriers have good biocompatibility. As the same time, the synergistic combination leads to a better cancer inhibition effect than individual therapy alone in vitro. Cell uptake tests indicate that the carriers have excellent fluorescence imaging ability and high cellular uptake for HepG2 cells. This work provides a new strategy for the fabrication of smart nanocarriers with simple structures for fluorescence-mediated combination cancer therapy.
Graphical abstract
Fabrication of a smart drug delivery system based on hollow Ag2S@mSiO2 nanoparticles for fluorescence-guided synergistic photothermal chemotherapy












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartelmess J, Milcovich G, Maffeis V, d’Amora M, Bertozzi SM, Giordani S (2020) Modulation of efficient Diiodo-BODIPY in vitro phototoxicity to cancer cells by carbon nano-onions. Front Chem 8:573211
Chen W, Qin M, Chen X, Wang Q, Zhang Z, Sun X (2018) Combining photothermal therapy and immunotherapy against melanoma by polydopamine-coated Al2O3 nanoparticles. Theranostics 8:2229–2241
Zeng JY, Zhang MK, Peng MY, Gong D, Zhang XZ (2018) Porphyrinic metal-organic frameworks coated gold nanorods as a versatile nanoplatform for combined photodynamic/photothermal/chemotherapy of tumor. Adv Funct Mater 28:1705451
Cheng L, Gong H, Zhu W, Liu J, Wang X, Liu G, Liu Z (2014) PEGylated Prussian blue nanocubes as a theranostic agent for simultaneous cancer imaging and photothermal therapy. Biomaterials 35:9844–9852
Liu T, Shi S, Liang C, Shen S, Cheng L, Wang C, Song X, Goel S, Barnhart TE, Cai W, Liu Z (2015) Iron oxide decorated MoS2 nanosheets with double PEGylation for chelator-free radiolabeling and multimodal imaging guided photothermal therapy. ACS Nano 9:950–960
Lv R, Yang P, He F, Gai S, Li C, Dai Y, Yang G, Lin J (2015) A yolk-like multifunctional platform for multimodal imaging and synergistic therapy triggered by a single near-infrared light. ACS Nano 9:1630–1647
Zhang J, Huang H, Xue L, Zhong L, Ge W, Song X, Zhao Y, Wang W, Dong X (2020) On-demand drug release nanoplatform based on fluorinated aza-BODIPY for imaging-guided chemo-phototherapy. Biomaterials 256:120211
Xia Y, Li W, Cobley CM, Chen J, Xia X, Zhang Q, Yang M, Cho EC, Brown PK (2011) Gold nanocages: from synthesis to theranostic applications. Acc Chem Res 44:914–924
Guo L, Yan DD, Yang D, Li Y, Wang X, Zalewski O, Yan B, Lu W (2014) Combinatorial photothermal and immuno cancer therapy using chitosan-coated hollow copper sulfide nanoparticles. ACS Nano 8:5670–5681
Yao C, Wang P, Li X, Hu X, Hou J, Wang L, Zhang F (2016) Near-infrared-triggered azobenzene-liposome/upconversion nanoparticle hybrid vesicles for remotely controlled drug delivery to overcome cancer multidrug resistance. Adv Mater 28:9341–9348
Alisani R, Rakhshani N, Abolhallaj M, Motevalli F, Abadi PG-S, Akrami M, Shahrousvand M, Jazi FS, Irani M (2022) Adsorption, and controlled release of doxorubicin from cellulose acetate/polyurethane/multi-walled carbon nanotubes composite nanofibers. Nanotechnology 33:155102
Wang Y, Zhao Q, Han N, Bai L, Li J, Liu J, Che E, Hu L, Zhang Q, Jiang T, Wang S (2015) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in drug delivery and biomedical applications. Nanomedicine 11:313–327
Zhang X, Zhao Y, Cao L, Sun L (2018) Fabrication of degradable lemon-like porous silica nanospheres for pH/redox-responsive drug release. Sensors Actuators B: Chem 257:105–115
Zhang X, Zhao Y, Xie S, Sun L (2017) Fabrication of functionalized porous silica nanoparticles and their controlled release behavior. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 37:38–45
Milcovich G, Antunes F, Golob S, Farra R, Grassi M, Voinovich D, Grassi G, Asaro F (2016) Thermo-responsive hydrogels from cellulose-based polyelectrolytes and catanionic vesicles for biomedical application. J Biomed Mater Res A 104:1668–1679
Hu X, Lu Y, Shi X, Yao T, Dong C, Shi S (2019) Integrating in situ formation of nanozymes with mesoporous polydopamine for combined chemo, photothermal and hypoxia-overcoming photodynamic therapy. Chem Commun 55:14785–14788
Huang S, Pa Ma, Wei Y, Cheng Z, Liu B, Deng X, Xie Z, Xing B, Lin J (2020) Controllable synthesis of hollow porous silica nanotubes/CuS nanoplatform for targeted chemo-photothermal therapy. Sci China Mater 63:864–875
Palanikumar L, Kim J, Oh JY, Choi H, Park MH, Kim C, Ryu JH (2018) Hyaluronic acid-modified polymeric gatekeepers on biodegradable mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 4:1716–1722
Cheng Y, Chen Q, Guo Z, Li M, Yang X, Wan G, Chen H, Zhang Q, Wang Y (2020) An intelligent biomimetic nanoplatform for holistic treatment of metastatic triple-negative breast cancer via photothermal ablation and immune remodeling. ACS Nano 14:15161–15181
Cheng YJ, Luo GF, Zhu JY, Xu XD, Zeng X, Cheng DB, Li YM, Wu Y, Zhang XZ, Zhuo RX, He F (2015) Enzyme-induced and tumor-targeted drug delivery system based on multifunctional mesoporous silica nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:9078–9087
Milcovich G, Contessotto P, Marsico G, Ismail S, Pandit A (2017) Synthetic/ECM-inspired hybrid platform for hollow microcarriers with ROS-triggered nanoporation hallmarks. Sci Rep 7:13138
Xiao D, Jia HZ, Ma N, Zhuo RX, Zhang XZ (2015) A redox-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticle capped with amphiphilic peptides by self-assembly for cancer targeting drug delivery. Nanoscale 7:10071–10077
Paris JL, Mannaris C, Cabañas MV, Carlisle R, Manzano M, Vallet-Regí M, Coussios CC (2018) Ultrasound-mediated cavitation-enhanced extravasation of mesoporous silica nanoparticles for controlled-release drug delivery. Chem Eng J 340:2–8
Chen W, Cheng CA, Zink JI (2019) Spatial, temporal, and dose control of drug delivery using noninvasive magnetic stimulation. ACS Nano 13:1292–1308
Choi Y, Kim J, Yu S, Hong S (2020) pH- and temperature-responsive radially porous silica nanoparticles with high-capacity drug loading for controlled drug delivery. Nanotechnology 31:335103
Zhao W, Wang H, Wang H, Han Y, Zheng Z, Liu X, Feng B, Zhang H (2021) Light-responsive dual-functional biodegradable mesoporous silica nanoparticles with drug delivery and lubrication enhancement for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Nanoscale 13:6394–6399
Lei Q, Qiu WX, Hu JJ, Cao PX, Zhu CH, Cheng H, Zhang XZ (2016) Multifunctional mesoporous silica nanoparticles with thermal-responsive gatekeeper for NIR light-triggered chemo/photothermal-therapy. Small 12:4286–4298
Han L, Hao YN, Wei X, Chen XW, Shu Y, Wang JH (2017) Hollow copper sulfide nanosphere-doxorubicin/graphene oxide core-shell nanocomposite for photothermo-chemotherapy. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 3:3230–3235
Liu Y, Bhattarai P, Dai Z, Chen X (2019) Photothermal therapy and photoacoustic imaging via nanotheranostics in fighting cancer. Chem Soc Rev 48:2053–2108
Gao M, Zhao H, Wang Z, Zhao Y, Zou X, Sun L (2021) Controllable preparation of Ag2S quantum dots with size-dependent fluorescence and cancer photothermal therapy. Adv Powder Technol 32:1972–1982
Yang T, Tang Y, Liu L, Lv X, Wang Q, Ke H, Deng Y, Yang H, Yang X, Liu G, Zhao Y, Chen H (2017) Size-dependent Ag2S nanodots for second near-infrared fluorescence/photoacoustics imaging and simultaneous photothermal therapy. ACS Nano 11:1848–1857
Li WT, Liu SK, Dong SM, Gai SL, Zhang FM, Dong YS, Yang D, He F, Zhong L, Yang PP (2021) A smart nanoplatform for synergistic starvation, hypoxia-active prodrug treatment and photothermal therapy mediated by near-infrared-II light. Chem Eng J 405:127027
Li C, Yang XQ, An J, Cheng K, Hou XL, Zhang XS, Song XL, Huang KC, Chen W, Liu B, Zhao YD, Liu TC (2019) A near-infrared light-controlled smart nanocarrier with reversible polypeptide-engineered valve for targeted fluorescence-photoacoustic bimodal imaging-guided chemo-photothermal therapy. Theranostics 9:7666–7679
You Q, Sun Q, Wang J, Tan X, Pang X, Liu L, Yu M, Tan F, Li N (2017) A single-light triggered and dual-imaging guided multifunctional platform for combined photothermal and photodynamic therapy based on TD-controlled and ICG-loaded CuS@mSiO2. Nanoscale 9:3784–3796
Li Q, Sun L, Hou M, Chen Q, Yang R, Zhang L, Xu Z, Kang Y, Xue P (2019) Phase-change material packaged within hollow copper sulfide nanoparticles carrying doxorubicin and chlorin e6 for fluorescence-guided trimodal therapy of cancer. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:417–429
Lee J, Jeong C, Kim WJ (2014) Facile fabrication and application of near-IR light-responsive drug release system based on gold nanorods and phase change material. J Mater Chem B 2:8338–8345
Clogston JD, Patri AK (2011) Zeta potential measurement. Methods Mol Biol 697:63–70
Chen F, Zhang J, Wang L, Wang Y, Chen M (2015) Tumor pH(e)-triggered charge-reversal and redox-responsive nanoparticles for docetaxel delivery in hepatocellular carcinoma treatment. Nanoscale 7:15763–15779
Moore CJ, Monton H, O’Kennedy R, Williams DE, Nogues C, Crean Nee Lynam C, Gubala V (2015) Controlling colloidal stability of silica nanoparticles during bioconjugation reactions with proteins and improving their longer-term stability, handling and storage. J Mater Chem B 3:2043–2055
Tallarida RJ (2011) Quantitative methods for assessing drug synergism. Genes Cancer 2:1003–1008
Yang J, Su H, Sun W, Cai J, Liu S, Chai Y, Zhang C (2018) Dual chemodrug-loaded single-walled carbon nanohorns for multimodal imaging-guided chemo-photothermal therapy of tumors and lung metastases. Theranostics 8:1966–1984
Ma T, Zhang Q, Xuan Q, Zhuang J, Zhang W, Li H, Chen C, Wang P (2021) pH/near-infrared light dual activated Ce6-doped silicon nanoparticles with tumor chemo-photodynamic synergistic therapy for improving efficiency of monotherapy. Chem Eng J 424:130536
Funding
This work received funding support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. U1604126) and the Key Scientific Research Project of Colleges and Universities in Henan Province (Grant No. 21A150014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, M., Han, Z., Wang, Z. et al. Fabrication of a smart drug delivery system based on hollow Ag2S@mSiO2 nanoparticles for fluorescence-guided synergistic photothermal chemotherapy. Microchim Acta 189, 376 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05468-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05468-2