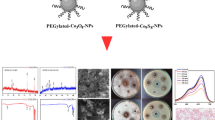
Abstract
Sulfhydryl functionalized silicon quantum dots (S-SiQDs) with a fluorescence quantum yield of 38.5% were synthesized using 3-mercaptopropyltrimethoxysilane (MPTMS) and m-phenylenediamine by a simple one-pot method. It is worth noting that by oxidizing the surface sulfhydryl groups and statically quenching, the fluorescence of S-SiQDs at 492 nm (excitation at 383 nm) can be selectively quenched by hypochlorite (ClO-) in a linear range of 0.05 to 1.8 μM with a low detection limit of 13 nM. The reaction was completed in 10 s with no interference from other ROS, metal ions, anions and reducing species. The silicon source containing sulfhydryl groups was used to synthesize silicon quantum dots for the first time, and the surface of the S-SiQDs was provided with sulfhydryl groups and reacted rapidly and sensitively with ClO-. The S-SiQDs have good photostability and biocompatibility, and can be further used for ClO- imaging in MCF-7 cells and zebrafish, showing great promise in biological imaging. The proposed assay demonstrates that 3-mercaptopropyltrimethoxysilane is a good choice to obtain a functionalized fluorescent nanoprobe for redox species.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu H, Pang LF, Wei N, Guo XF, Wang H (2021) Nucleus-targeted N-doped carbon dots via DNA-binding for imaging of hypochlorous in cells and zebrafish. Sens Actuators B Chem 333:129626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.129626
Breen C, Pal R, Elsegood MRJ, Teat SJ, Iza F, Wende K, Buckley BR, Butler SJ (2020) Time-resolved luminescence detection of peroxynitrite using a reactivity-based lanthanide probe. Chem Sci 11(12):3164–3170. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9sc06053g
Wu D, Chen L, Xu Q, Chen X, Yoon J (2019) Design principles, sensing mechanisms, and applications of highly specific fluorescent probes for HOCl/OCl(-). Acc Chem Res 52(8):2158–2168. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00307
Huo B, Du M, Shen A, Li M, Lai Y, Bai X, Gong A, Fang L, Yang Y (2019) A “light-up” fluorescent probe based on TEMPO-oxidation for the detection of ClO- and application in real samples. Sens Actuators B Chem 284:23–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.12.115
Tantry IQ, Waris S, Habib S, Khan RH, Mahmood R, Ali A (2018) Hypochlorous acid induced structural and conformational modifications in human DNA: a multi-spectroscopic study. Int J Biol Macromol 106:551–558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.08.051
Lan J, Guo J, Jiang X, Chen Y, Hu Z, Que Y, Li H, Gu J, Ho RJY, Zeng R, Ding Y, Zhang T (2020) A new dicyanoisophorone-based ratiometric and colorimetric near-infrared fluorescent probe for specifically detecting hypochlorite and its bioimaging on a model of acute inflammation. Anal Chim Acta 1094:70–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.09.076
Zhang H, Li Z, Wang M, Luo T, Yi L, Wang J (2019) Novel hepatocyte-targeting fluorescent probes for detection of hypochlorous acid: synergistic effect of phosphate and galactose. Sens Actuators, B Chem 279:102–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.09.123
Jia M, Mi W, Guo S, Yang QZ, Jin Y, Shao N (2020) Peptide-capped functionalized Ag/Au bimetal nanoclusters with enhanced red fluorescence for lysosome-targeted imaging of hypochlorite in living cells. Talanta 216:120926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.120926
Li Y, He Y, Ge Y, Song G, Zhou J (2021) Smartphone-assisted visual ratio-fluorescence detection of hypochlorite based on copper nanoclusters. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 255:119740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2021.119740
Sun YQ, Cheng Y, Yin XB (2021) Dual-ligand lanthanide metal-organic framework for sensitive ratiometric fluorescence detection of hypochlorous acid. Anal Chem 93(7):3559–3566. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c05040
Ye Y, Zhao L, Hu S, Liang A, Li Y, Zhuang Q, Tao G, Gu J (2019) Specific detection of hypochlorite based on the size-selective effect of luminophore integrated MOF-801 synthesized by a one-pot strategy. Dalton Trans 48(8):2617–2625. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8dt04692a
Wang Y, Zhang P, Lu Q, Wang Y, Fu W, Tan Q, Luo W (2018) Water-soluble MoS2 quantum dots are a viable fluorescent probe for hypochlorite. Mikrochim Acta 185(4):233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2768-8
Xu Y, Hao J, Niu X, Qi S, Chen H, Wang K, Chen X, Yi T (2016) Seed-mediated growth approach for rapid synthesis of high-performance red-emitting CdTe quantum dots in aqueous phase and their application in detection of highly reactive oxygen species. Chem Eng J 299:201–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.04.008
Yang H, Zhao Q, Wang X, Wu Y, Su Y, Wei W (2021) Facile and highly selective sensing of hypochlorous acid in aqueous solution and living cells by using as-prepared WSe2 quantum dots. Sens Actuators B Chem 337:129782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.129782
Zhang C, Liu M, Li T, Liu S, Chen Q, Zhang J, Zhang K (2020) One-pot hydrothermal synthesis of dual-emission fluorescent carbon dots for hypochlorous acid detection. Dyes Pigm 180:108507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2020.108507
Jiao Y, Meng Y, Lu W, Gao Y, Liu Y, Gong X, Liu Y, Shuang S, Dong C (2020) Design of long-wavelength emission carbon dots for hypochlorous detection and cellular imaging. Talanta 219:121170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121170
Zhang P, Wang Y, Chen L, Yin Y (2017) Bimetallic nanoclusters with strong red fluorescence for sensitive detection of hypochlorite in tap water. Microchim Acta 184(10):3781–3787. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2398-6
Li LS, Jiao XY, Zhang Y, Cheng C, Huang K, Xu L (2018) Green synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots from Hongcaitai for selective detection of hypochlorite and mercuric ions and cell imaging. Sens Actuators B Chem 263:426–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.02.141
Huang BH, Shen SS, Wei N, Guo XF, Wang H (2020) Fluorescence biosensor based on silicon quantum dots and 5,5’-dithiobis-(2-nitrobenzoic acid) for thiols in living cells. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 229:117972. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2019.117972
Park JH, Gu L, von Maltzahn G, Ruoslahti E, Bhatia SN, Sailor MJ (2009) Biodegradable luminescent porous silicon nanoparticles for in vivo applications. Nat Mater 8(4):331–336. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat2398
Hemmateenejad B, Shamsipur M, Samari F, Rajabi HR (2015) Study of the interaction between human serum albumin and Mn-doped ZnS quantum dots. J Iran Chem Soc 12(10):1729–1738. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-015-0647-3
Rajabi HR, Shamsipur M, Khosravi AA, Khani O, Yousefi MH (2013) Selective spectrofluorimetric determination of sulfide ion using manganese doped ZnS quantum dots as luminescent probe. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 107:256–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2013.01.045
Shamsipur M, Rajabi HR (2014) Pure zinc sulfide quantum dot as highly selective luminescent probe for determination of hazardous cyanide ion. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 36:139–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2013.12.001
Roushani M, Shamsipur M, Rajabi HR (2014) Highly selective detection of dopamine in the presence of ascorbic acid and uric acid using thioglycolic acid capped CdTe quantum dots modified electrode. J Electroanal Chem 712:19–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2013.08.027
Roushani M, Mavaei M, Rajabi HR (2015) Graphene quantum dots as novel and green nano-materials for the visible-light-driven photocatalytic degradation of cationic dye. J Mol Catal A: Chem 409:102–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2015.08.011
Rajabi HR, Farsi M (2015) Quantum dot based photocatalytic decolorization as an efficient and green strategy for the removal of anionic dye. Mater Sci Semicond Process 31:478–486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2014.11.044
Karimi F, Rajabi HR, Kavoshi L (2019) Rapid sonochemical water-based synthesis of functionalized zinc sulfide quantum dots: study of capping agent effect on photocatalytic activity. Ultrason Sonochem 57:139–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2019.05.019
Karimi H, Rajabi HR, Kavoshi L (2020) Application of decorated magnetic nanophotocatalysts for efficient photodegradation of organic dye: a comparison study on photocatalytic activity of magnetic zinc sulfide and graphene quantum dots. J Photochem Photobiol, A 397:112534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2020.112534
Rajabi HR, Shahrezaei F, Farsi M (2016) Zinc sulfide quantum dots as powerful and efficient nanophotocatalysts for the removal of industrial pollutant. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 27(9):9297–9305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4969-4
Alvand ZM, Rajabi HR, Mirzaei A, Masoumiasl A, Sadatfaraji H (2019) Rapid and green synthesis of cadmium telluride quantum dots with low toxicity based on a plant-mediated approach after microwave and ultrasonic assisted extraction: synthesis, characterization, biological potentials and comparison study. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 98:535–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.01.010
Zhao QQ, Zhang R, Ye DX, Zhang S, Chen H, Kong JL (2017) Ratiometric fluorescent silicon quantum dots-Ce6 complex probe for the live cell imaging of highly reactive oxygen species. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(3):2052–2058. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b12047
Zhang Y, Hou D, Yu X (2020) Facile preparation of FITC-modified silicon nanodots for ratiometric pH sensing and imaging. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 234:118276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2020.118276
Shen SS, Huang BH, Guo XF, Wang H (2019) A dual-responsive fluorescent sensor for Hg(2+) and thiols based on N-doped silicon quantum dots and its application in cell imaging. J Mater Chem B 7(44):7033–7041. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9tb01502g
Liu LR, Zhu GB, Zeng W, Lv BH, Yi YH (2019) Highly sensitive and selective “off-on” fluorescent sensing platform for ClO- in water based on silicon quantum dots coupled with nanosilver. Anal Bioanal Chem 411(8):1561–1568. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-01597-5
Taheri M, Mansour N (2019) Functionalized silicon nanoparticles as fluorescent probe for detection of hypochlorite in water. J Photochem Photobiol -Chem 382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2019.111906
Li Q, He Y, Chang J, Wang L, Chen HZ, Tan YW, Wang HY, Shao ZZ (2013) Surface-modified silicon nanoparticles with ultrabright photoluminescence and single-exponential decay for nanoscale fluorescence lifetime imaging of temperature. J Am Chem Soc 135(40):14924–14927. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja407508v
Dasog M, De los Reyes GB, Titova LV, Hegmann FA, Veinot J, (2014) Size vs surface tuning the photoluminescence of freestanding silicon nanocrystals across the visible spectrum via surface groups. ACS Nano 8(9):9636–9648. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn504109a
Zhong YL, Song B, Shen XB, Guo DX, He Y (2019) Fluorescein sodium ligand-modified silicon nanoparticles produce ultrahigh fluorescence with robust pH- and photo-stability. Chem Commun 55(3):365–368. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8cc07340f
Li W, Liu D, Dong D, You T (2021) Microwave-assisted synthesis of fluorescent silicon quantum dots for ratiometric sensing of Hg (II) based on the regulation of energy transfer. Talanta 226:122093. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122093
Li Q, Peng KT, Lu YZ, Li AX, Che FF, Liu YY, Xi XJ, Chu Q, Lan T, Wei Y (2018) Synthesis of fluorescent ionic liquid-functionalized silicon nanoparticles with tunable amphiphilicity and selective determination of Hg2+. J Mater Chem B 6(48):8214–8220. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8tb02109k
Zhong YL, Peng F, Bao F, Wang SY, Ji XY, Yang L, Su YY, Lee ST, He Y (2013) Large-scale aqueous synthesis of fluorescent and biocompatible silicon nanoparticles and their use as highly photostable biological probes. J Am Chem Soc 135(22):8350–8356. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja4026227
Wei N, Wei MX, Huang BH, Guo XF, Wang H (2021) One-pot facile synthesis of green-emitting fluorescent silicon quantum dots for the highly selective and sensitive detection of nitrite in food samples. Dyes and Pigments 184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2020.108848
Sun YC, Pang LF, Guo XF, H Wang (2022) Synthesis of metal ion-tolerant Mn-doped fluorescence silicon quantum dots with green emission and its application for selective imaging of center dot OH in living cells. Microchimica Acta 189(2). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-05082-8
Na M, Zhang SP, Liu JJ, Ma SD, Han YX, Wang Y, He YX, Chen HL, Chen XG (2020) Determination of pathogenic bacteria-Bacillus anthrax spores in environmental samples by ratiometric fluorescence and test paper based on dual-emission fluorescent silicon nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 386:121956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121956
Zhan YJ, Zeng YB, Li L, Luo F, Qiu B, Lin ZY, Guo LH (2019) Ratiometric fluorescent hydrogel test kit for on-spot visual detection of nitrite. ACS Sensors 4(5):1252–1260. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.9b00125
Gopu CL, Krishna Shanti A, Sreenivasan K (2015) Fluorimetric detection of hypochlorite using albumin stabilized gold nanoclusters. Sens Actuators B Chem 209:798–802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.12.004
Malankar GS, Sakunthala A, Navalkar A, Maji SK, Raju S, Manjare ST (2021) Organoselenium-based BOPHY as a sensor for detection of hypochlorous acid in mammalian cells. Anal Chim Acta 1150:338205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2021.338205
Liu M, Bai Y, He Y, Zhou J, Ge Y, Zhou J, Song G (2021) Facile microwave-assisted synthesis of Ti3C2 MXene quantum dots for ratiometric fluorescence detection of hypochlorite. Mikrochim Acta 188(1):15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04668-y
Konar S, Samanta D, Mandal S, Das S, Mahto MK, Shaw M, Mandald M, Pathak A (2018) Selective and sensitive detection of cinnamaldehyde by nitrogen and sulphur co-doped carbon dots: a detailed systematic study. RSC Adv 8(74):42361–42373. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra09285k
Ko SK, Chen X, Yoon J, Shin I (2011) Zebrafish as a good vertebrate model for molecular imaging using fluorescent probes. Chem Soc Rev 40(5):2120–2130. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0cs00118j
Pang LF, Sun YC, Guo XF, Wang H (2021) Cell membrane-targeted near-infrared carbon dots for imaging of hydrogen sulfide released through the cell membrane. Sensors Actuators B-Chem 345:130403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.130403
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 32070398 and 21777126, Beijing, China).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The manuscript was written through contributions of all authors. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, N., Sun, YC., Guo, XF. et al. Synthesis of sulfhydryl functionalized silicon quantum dots with high quantum yield for imaging of hypochlorite in cells and zebrafish. Microchim Acta 189, 329 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05435-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05435-x